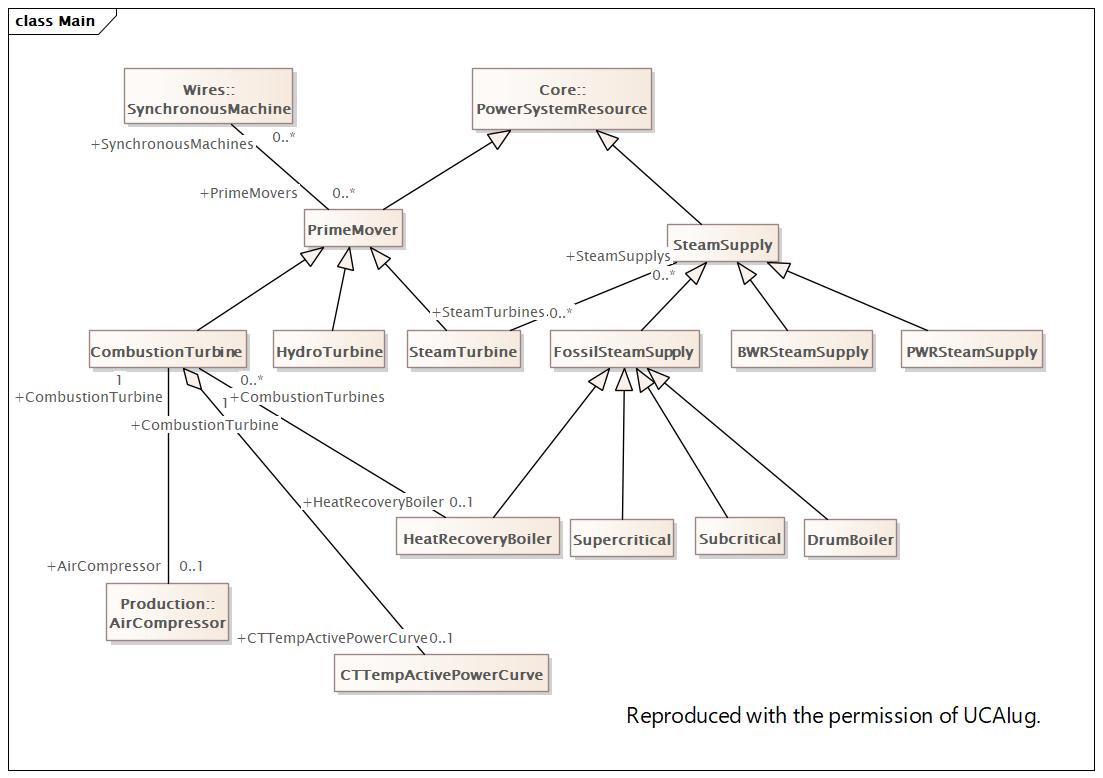
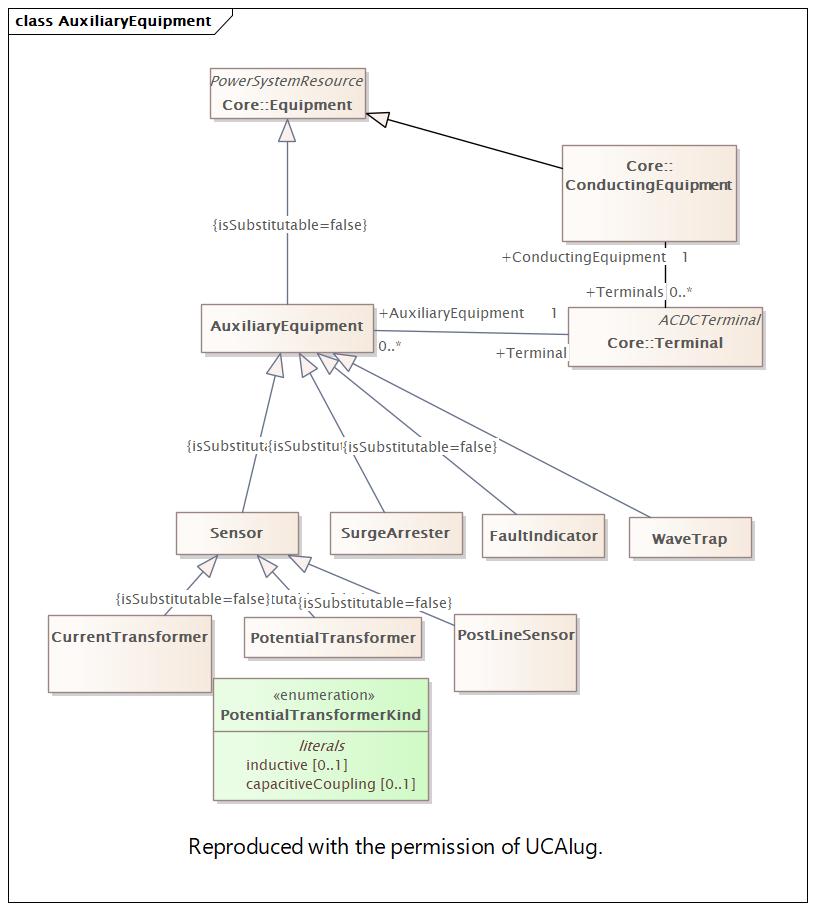
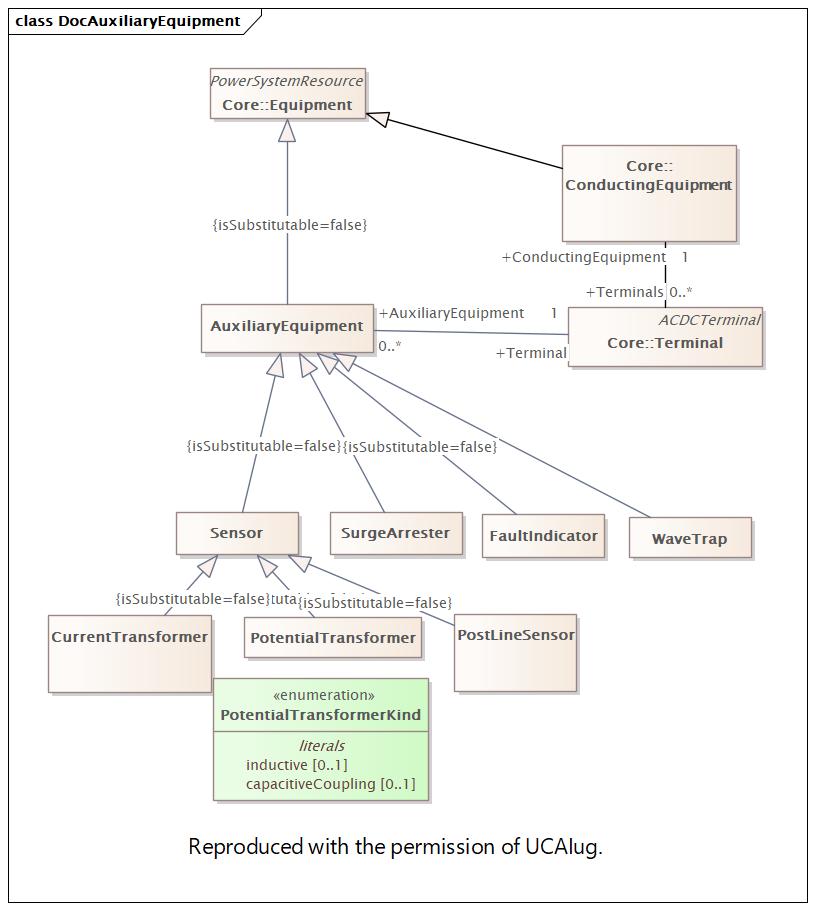
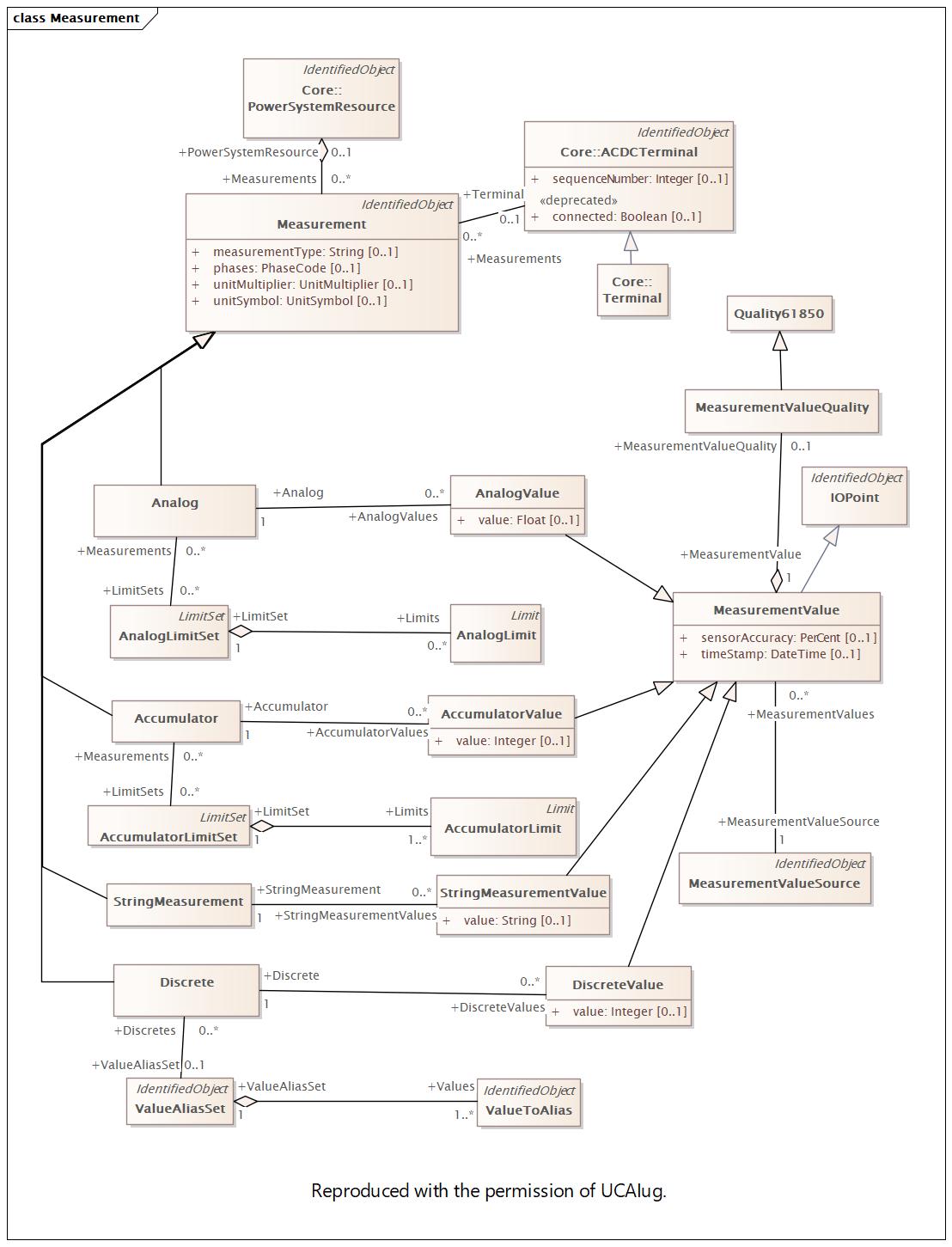
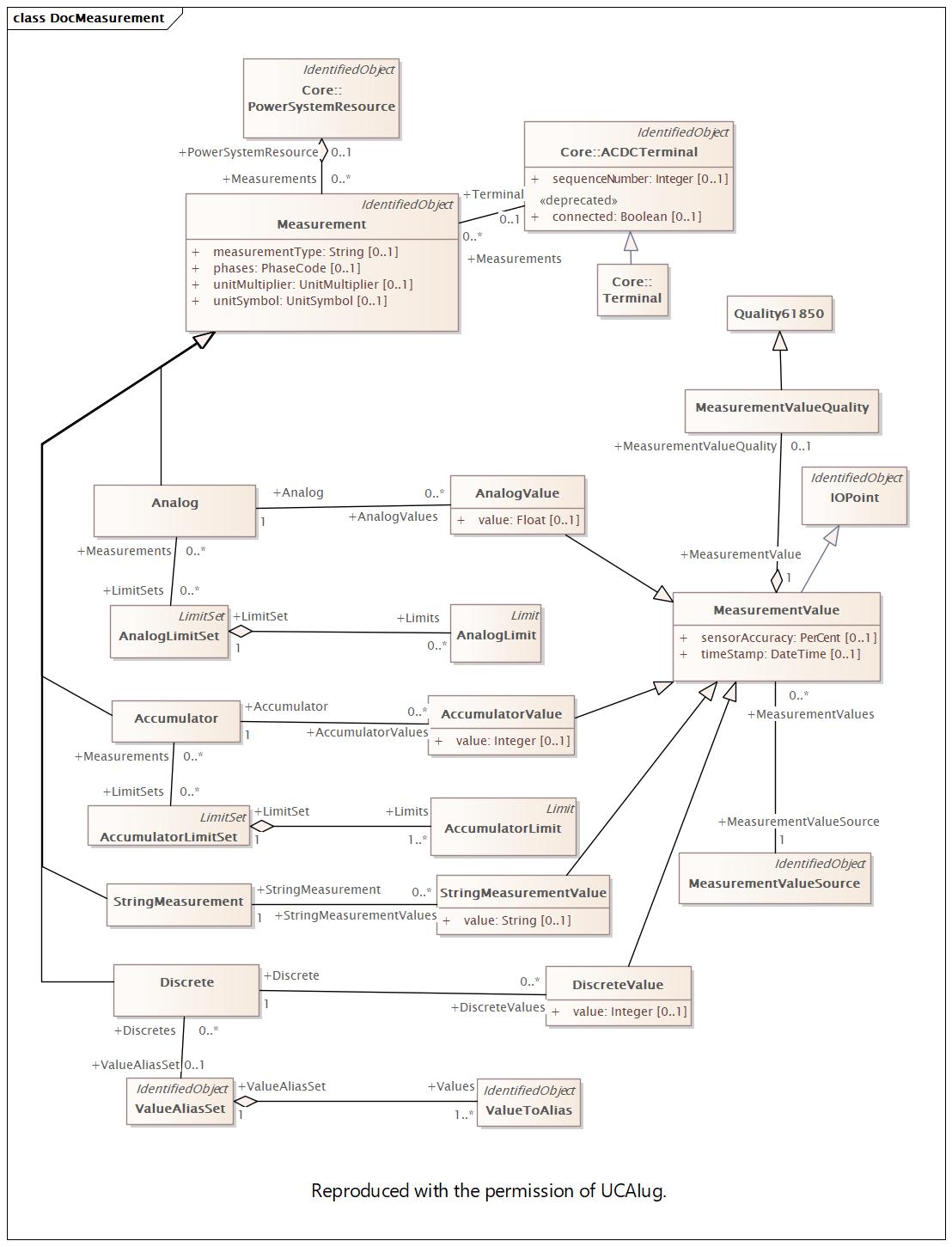
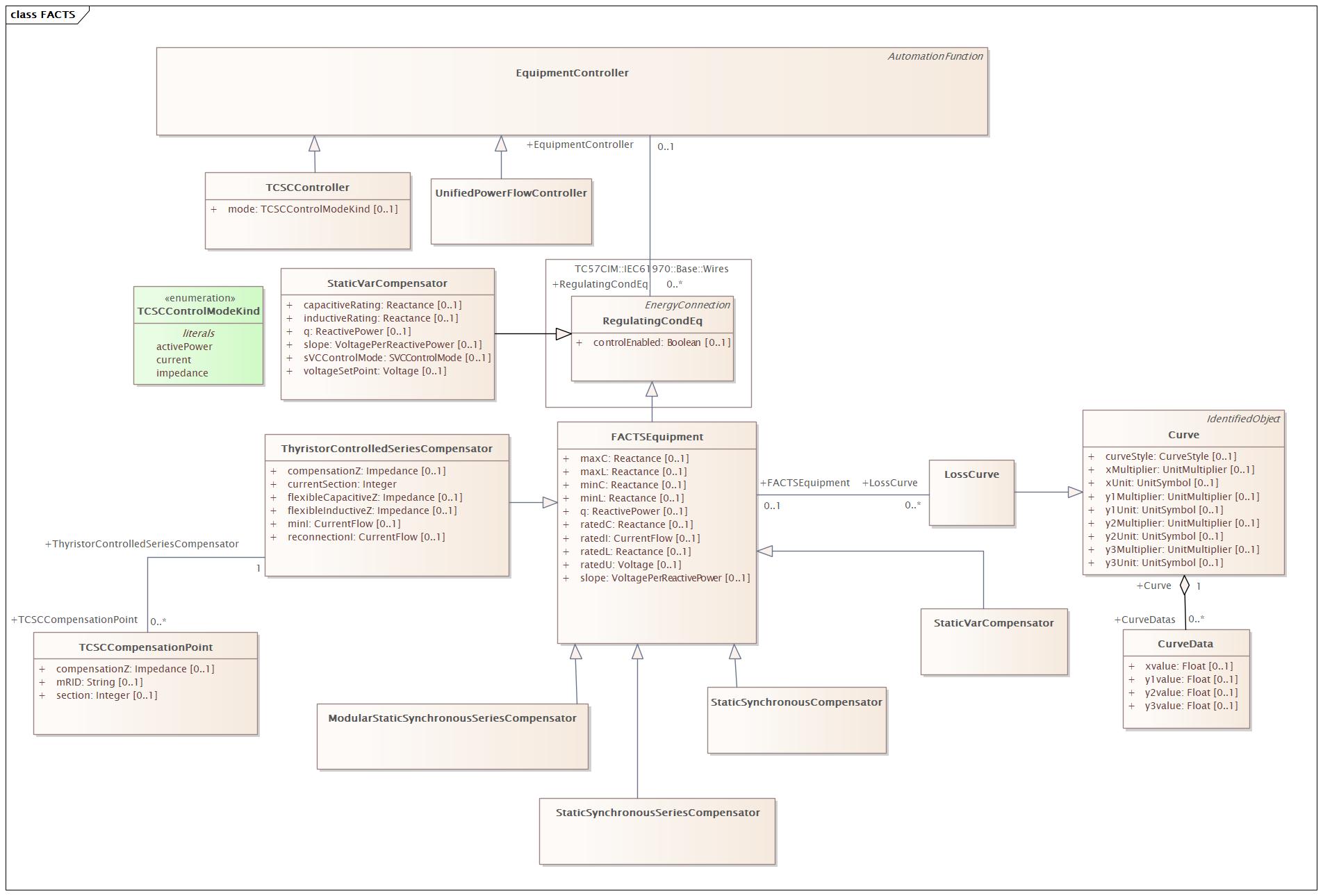
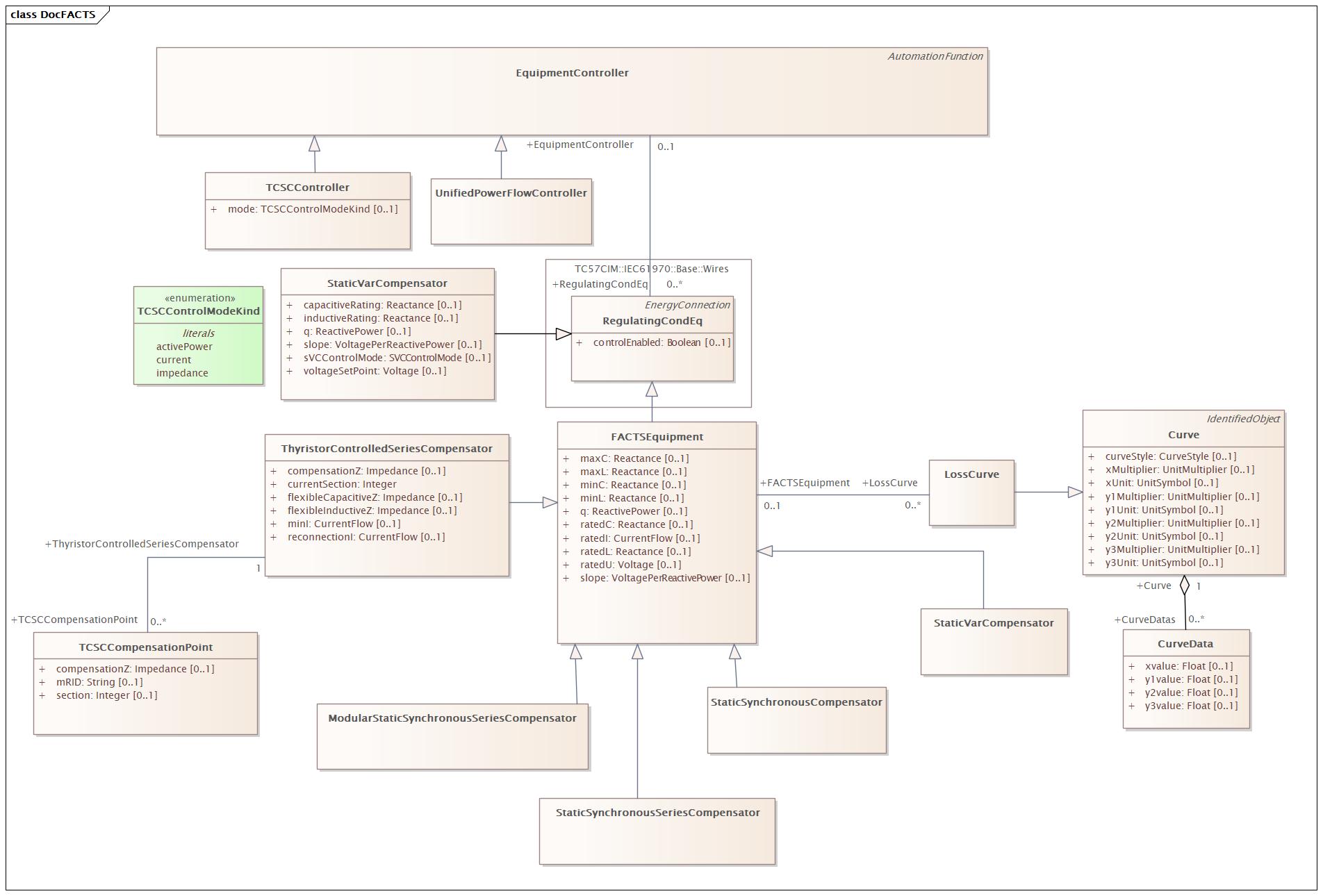
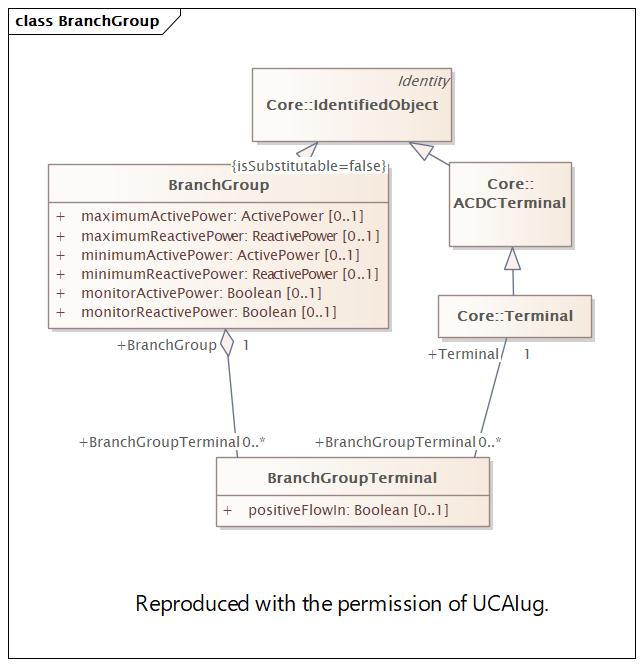
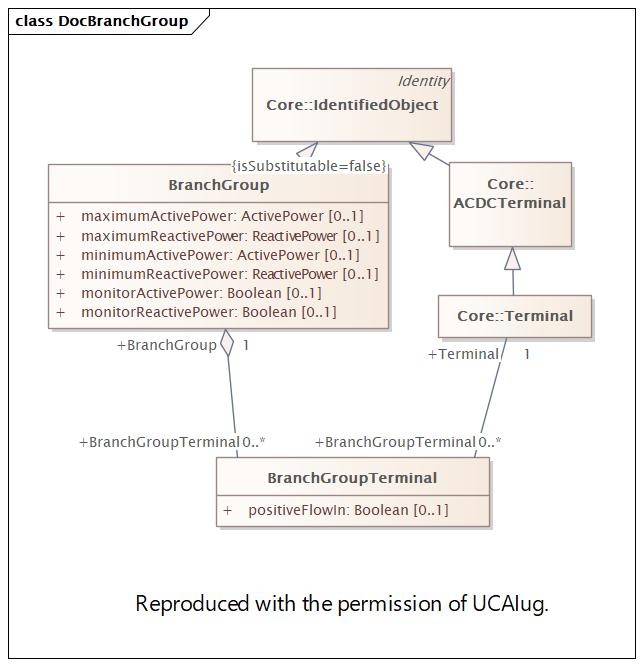
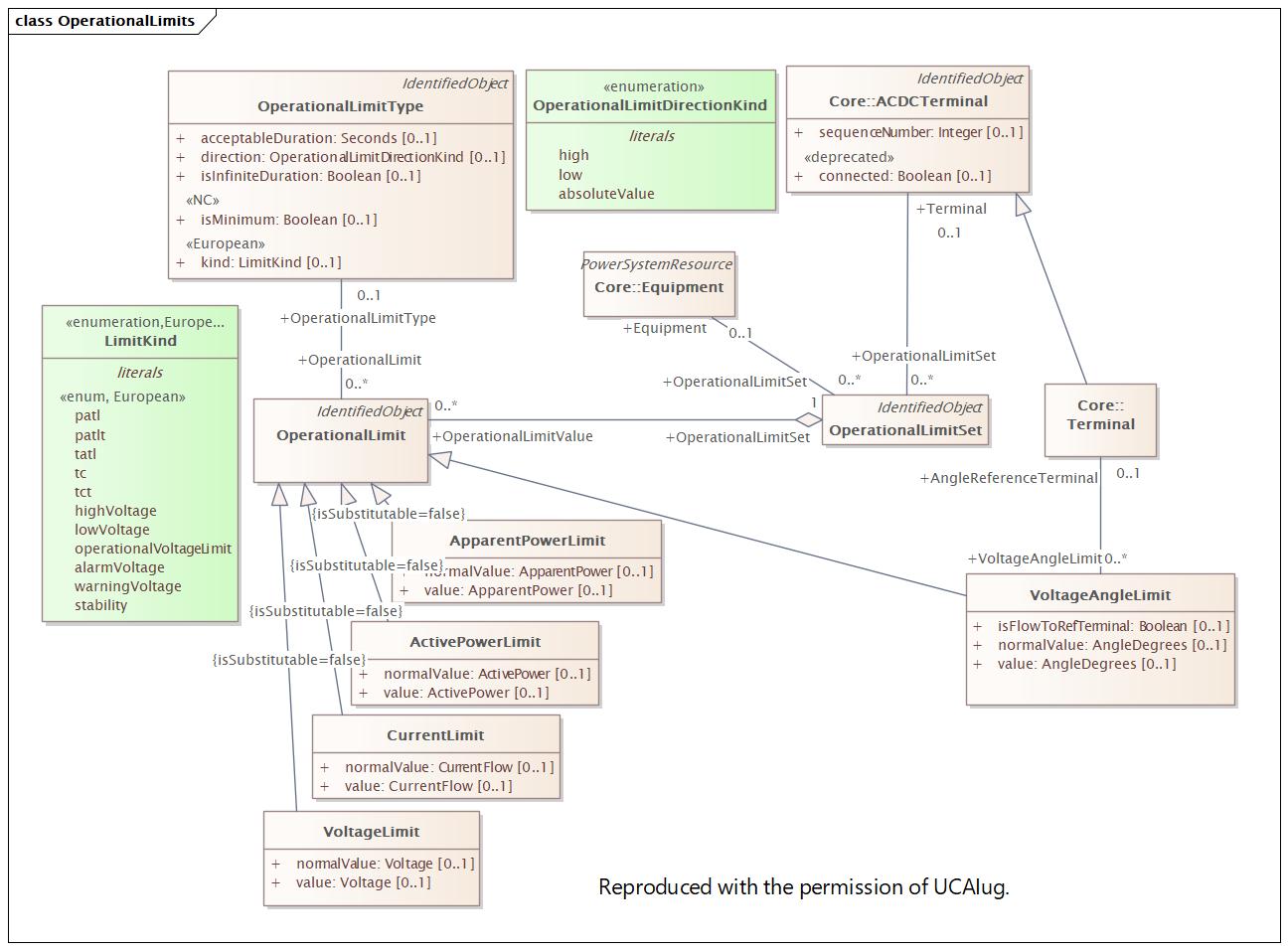
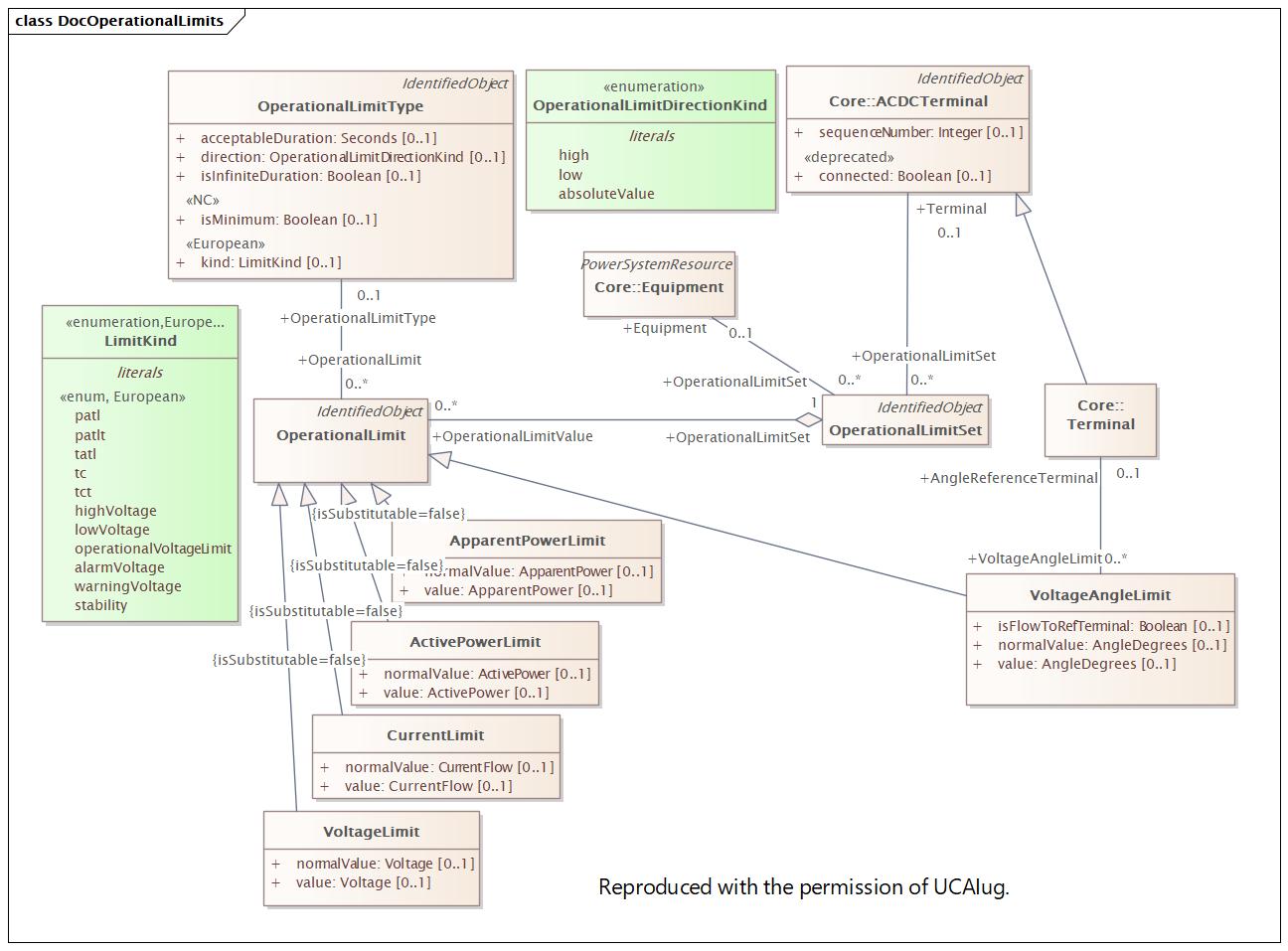
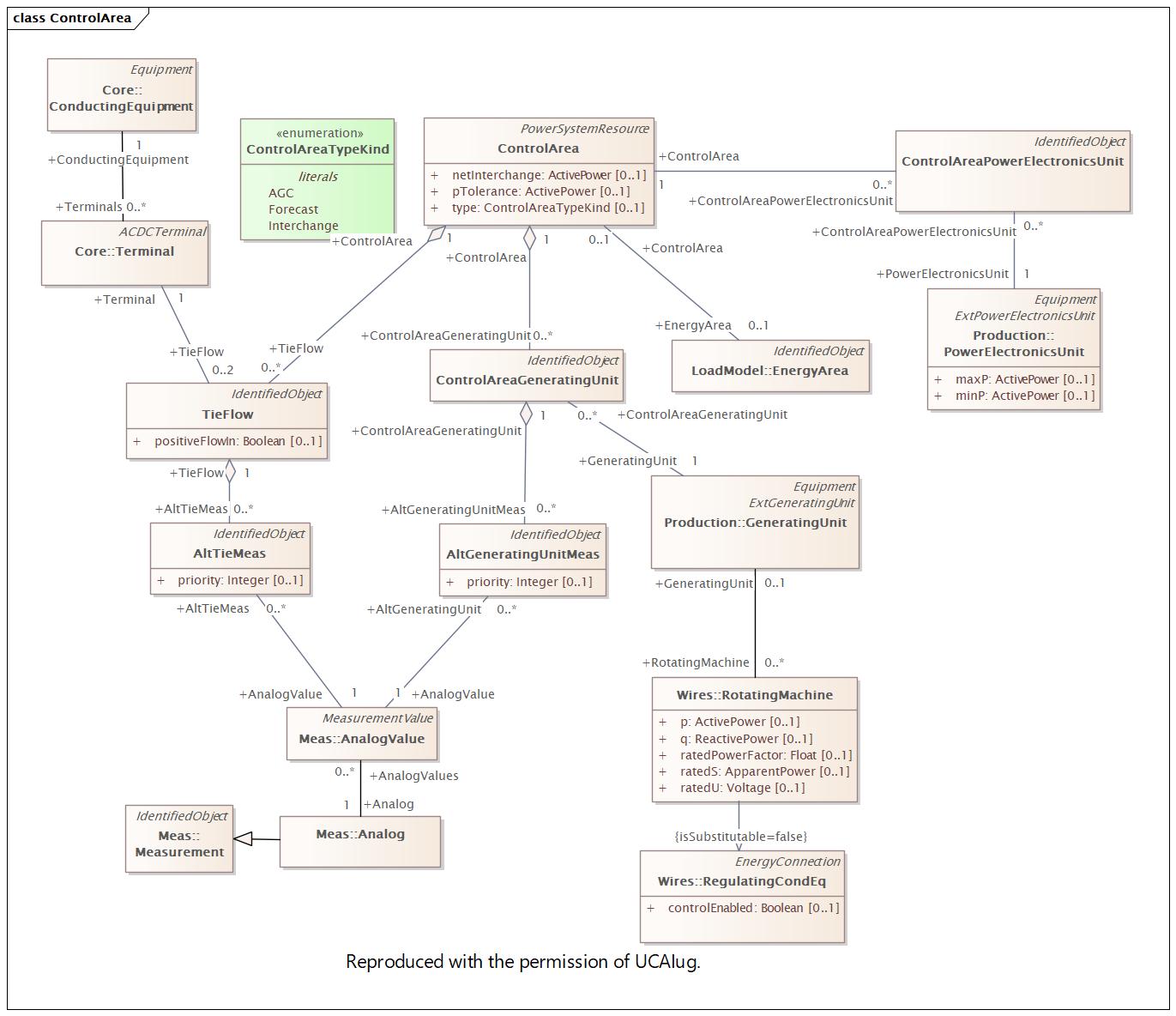
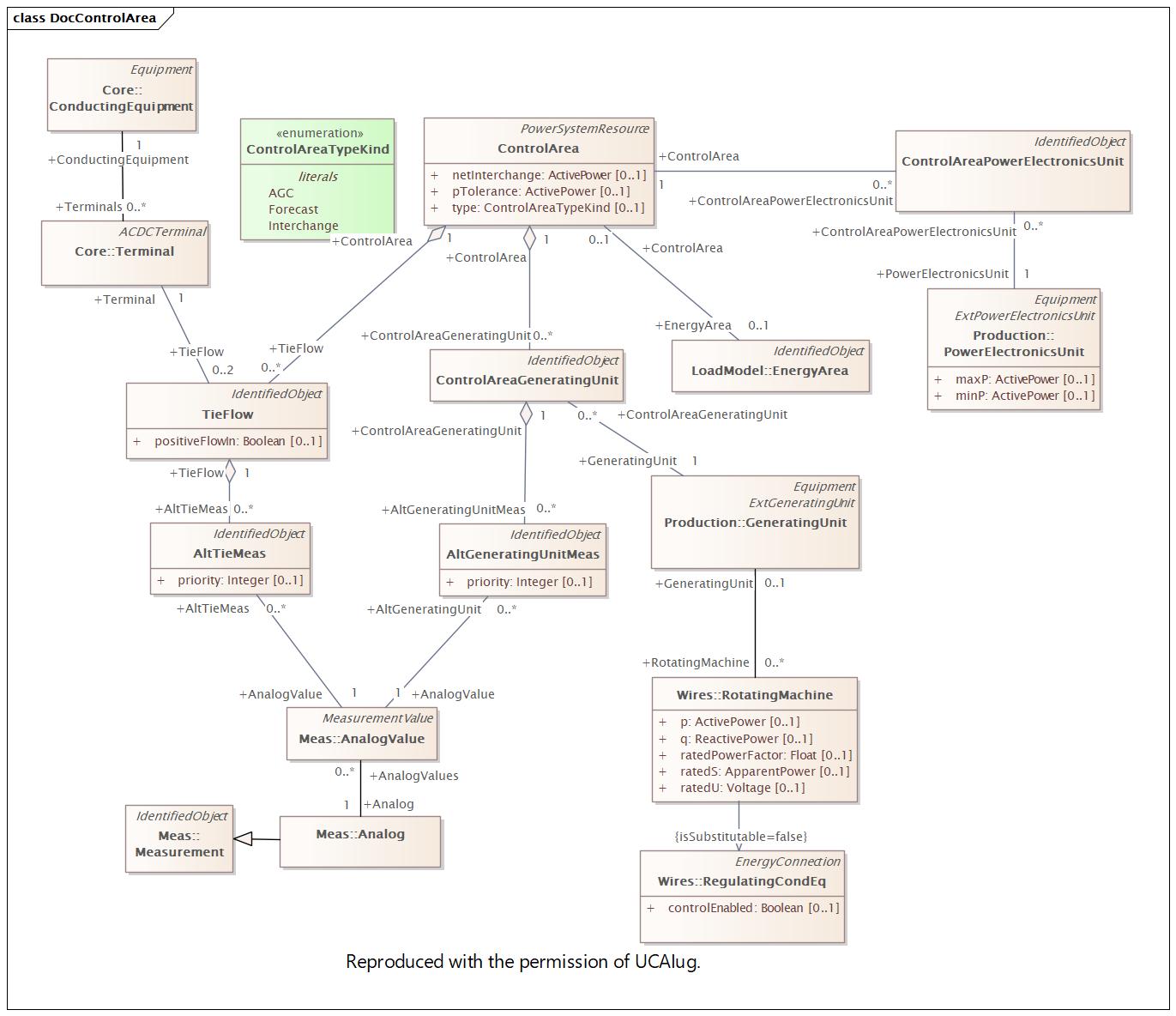
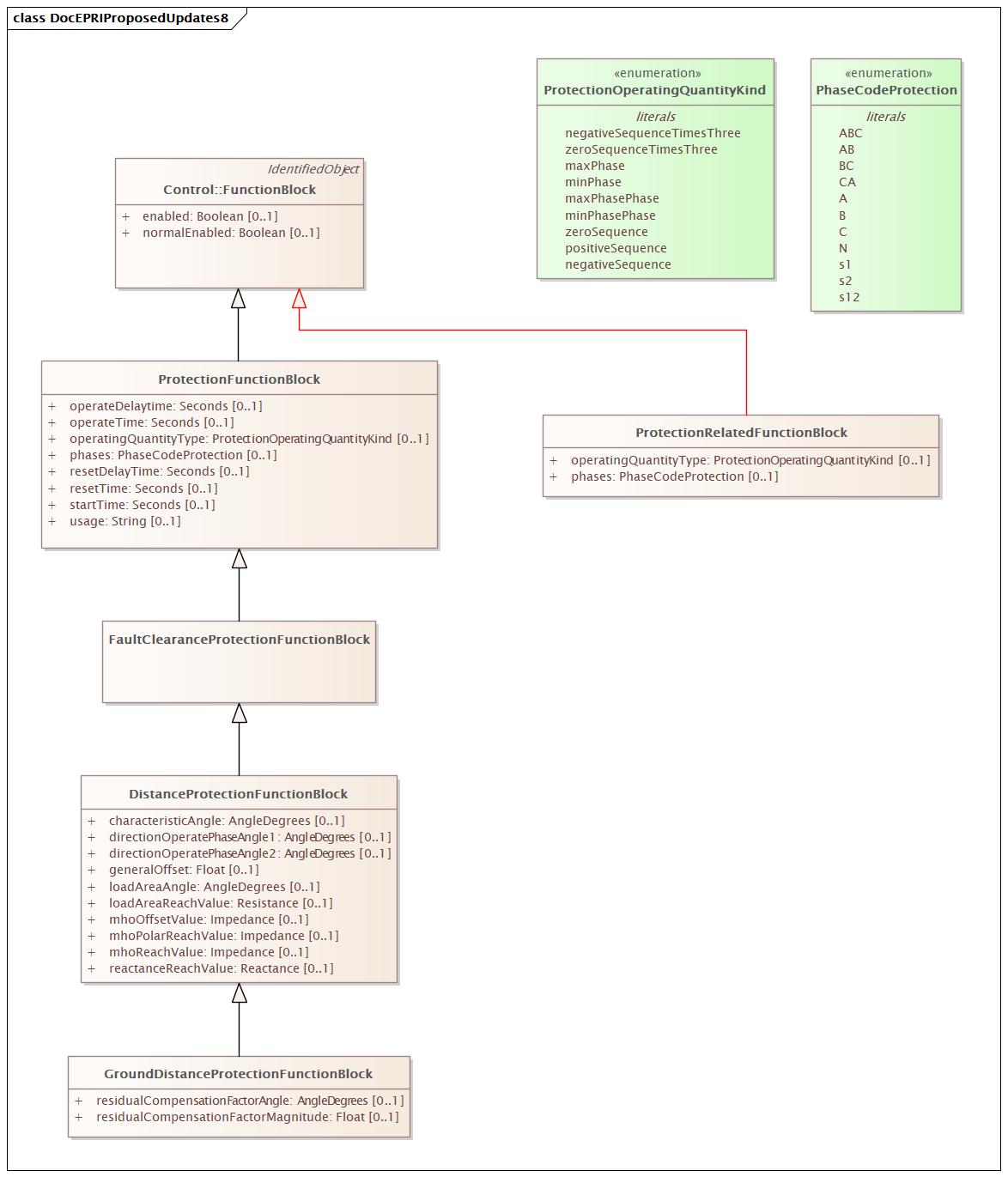
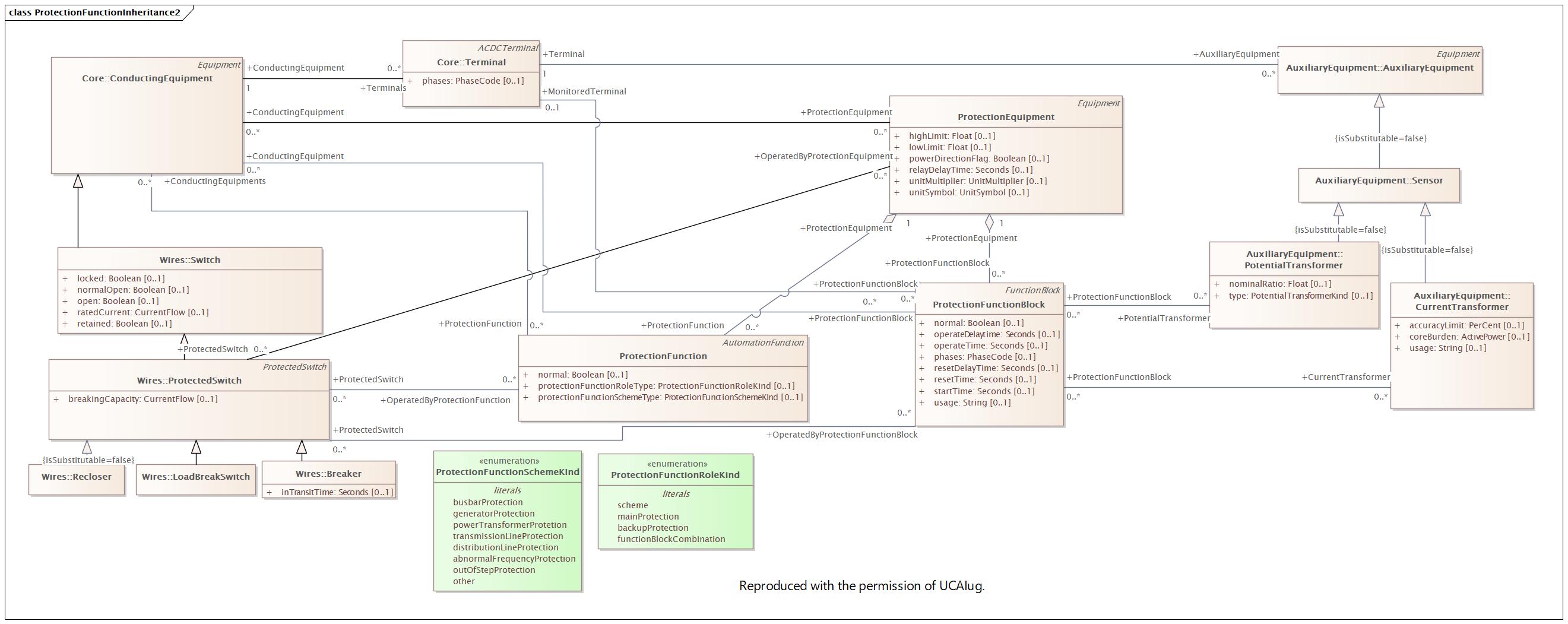
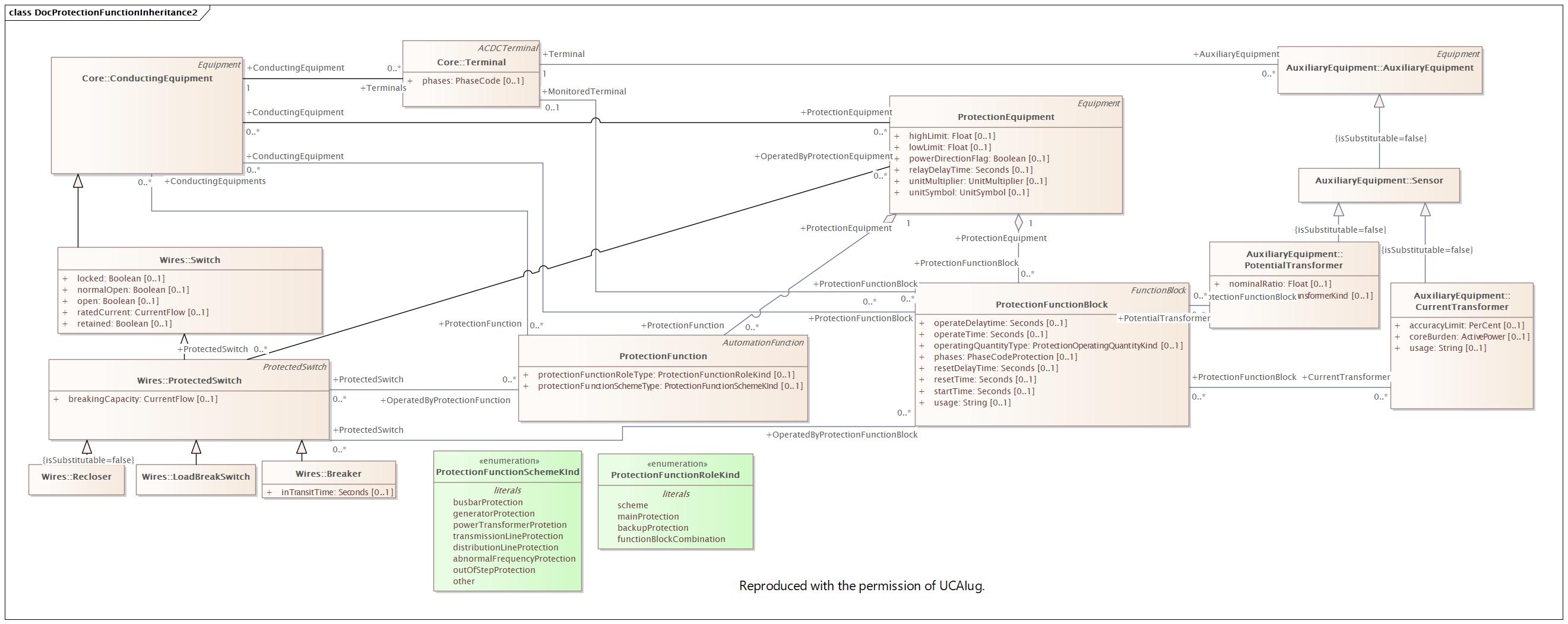
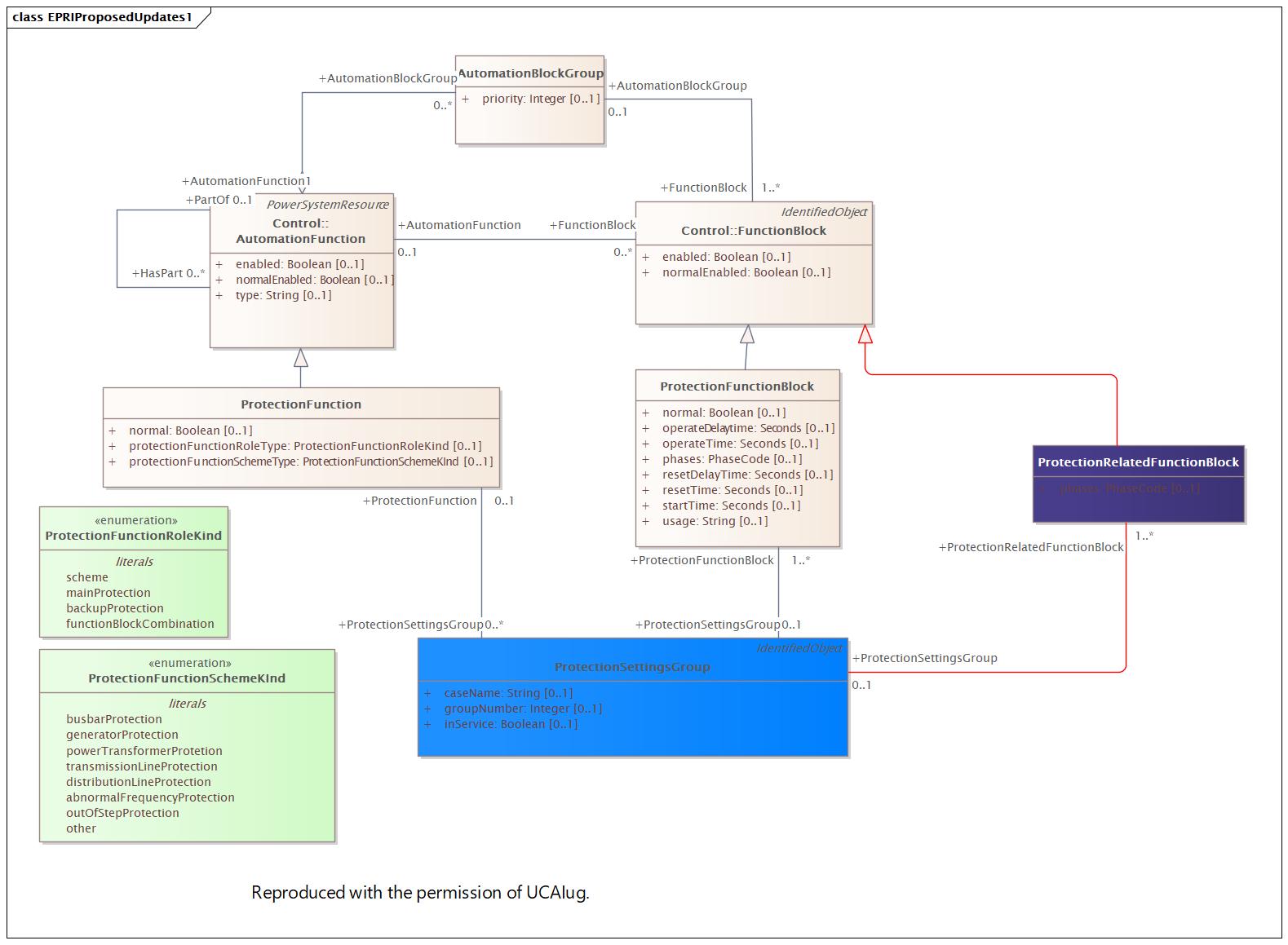
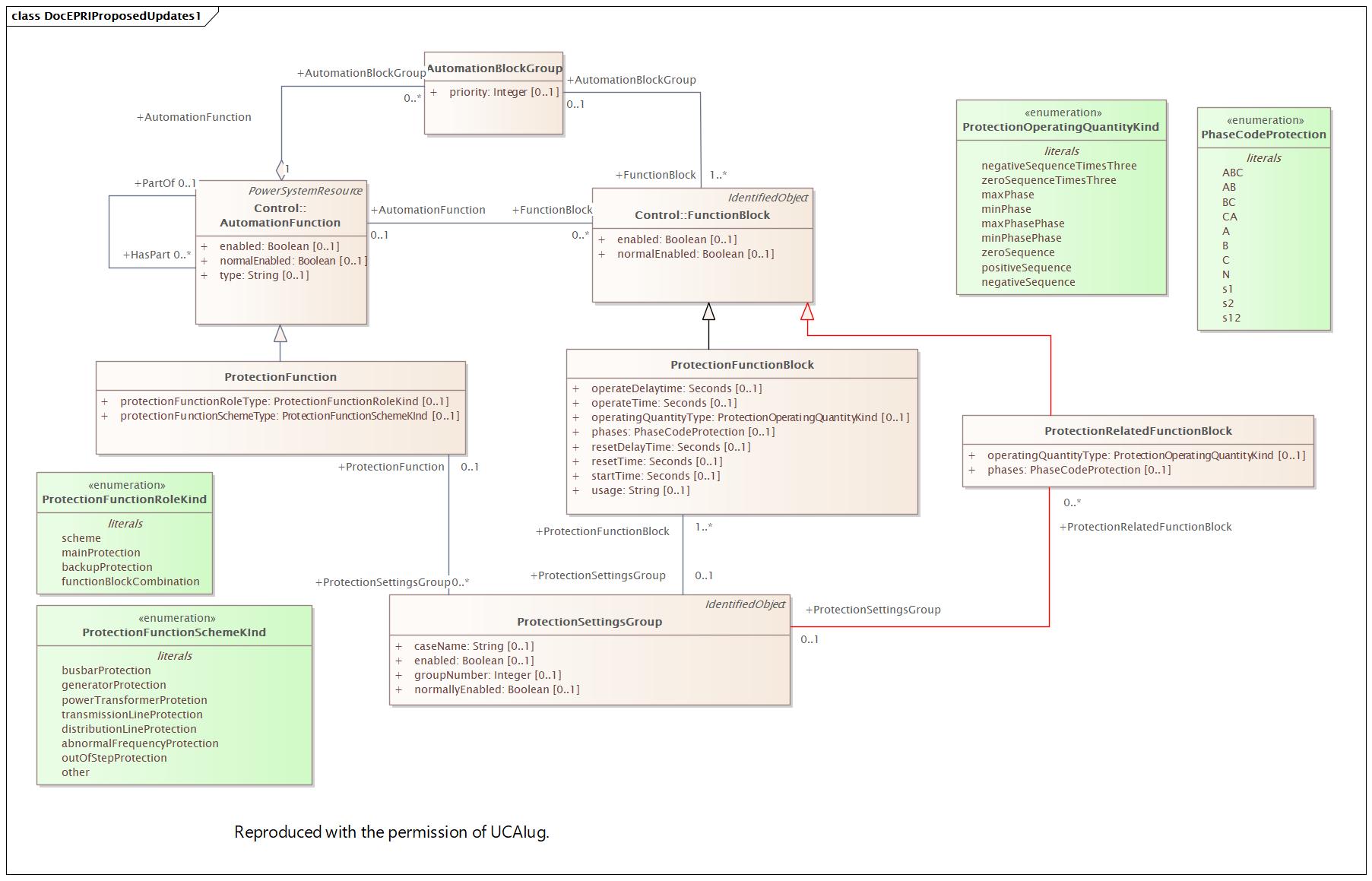
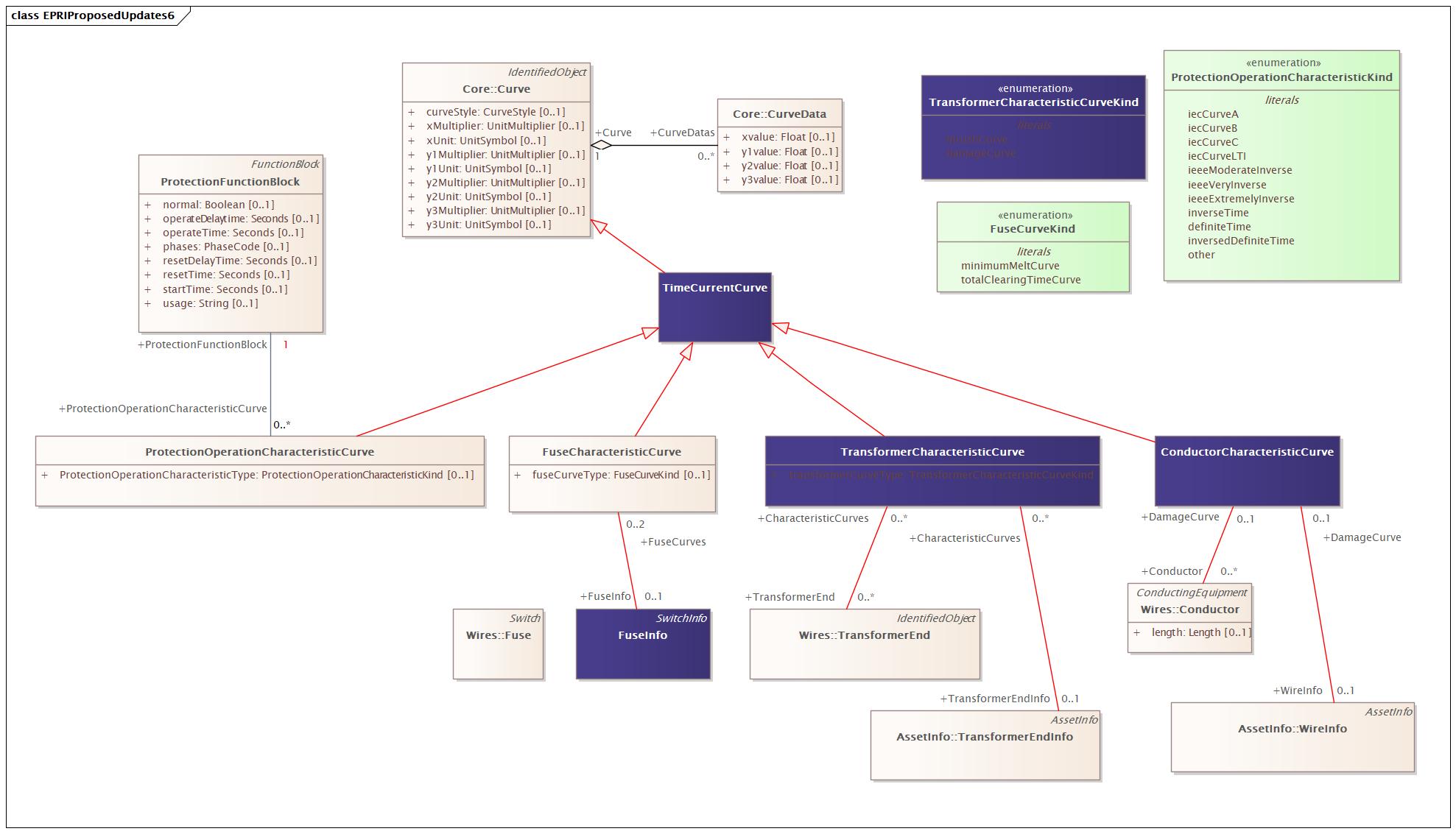
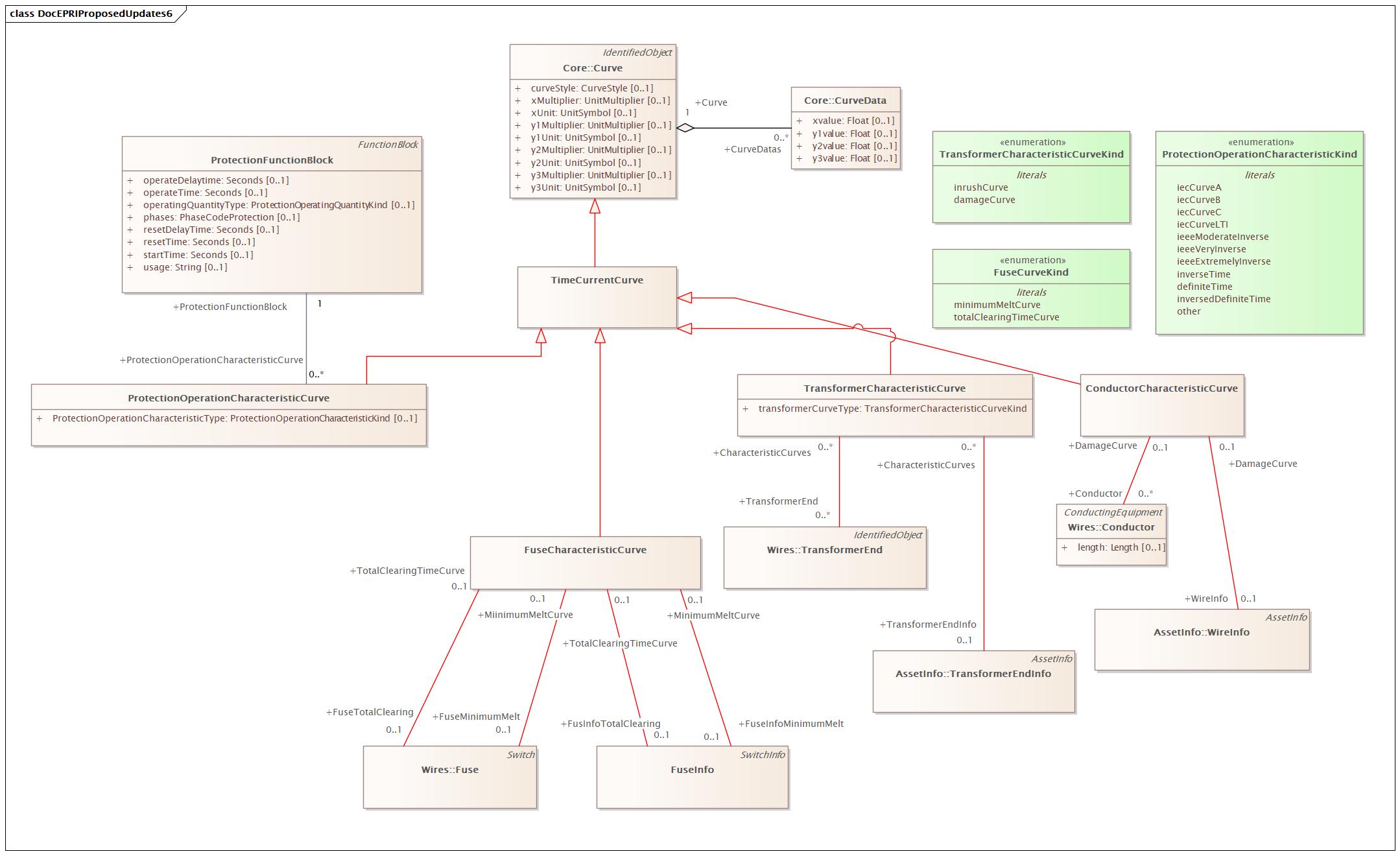
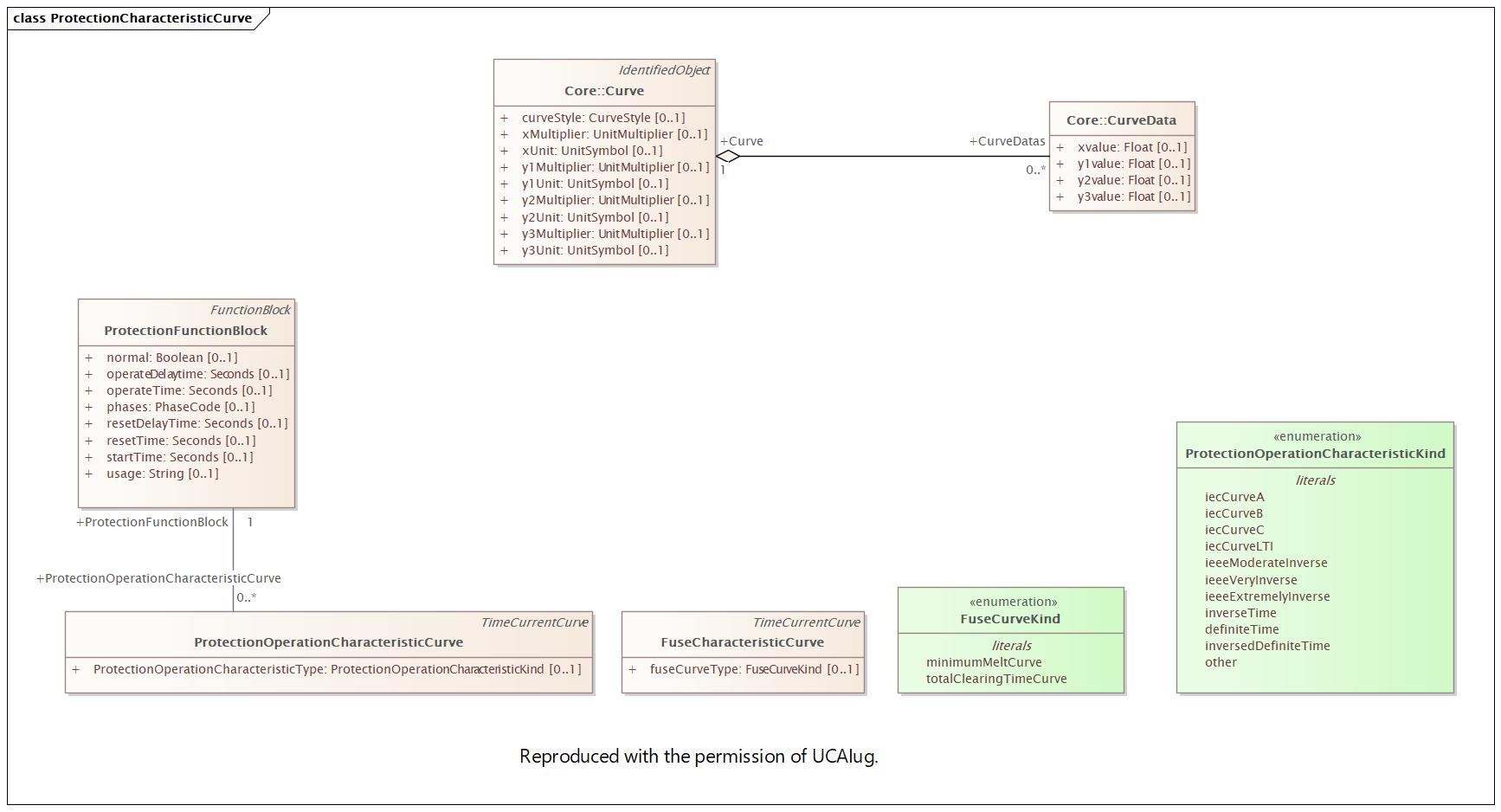
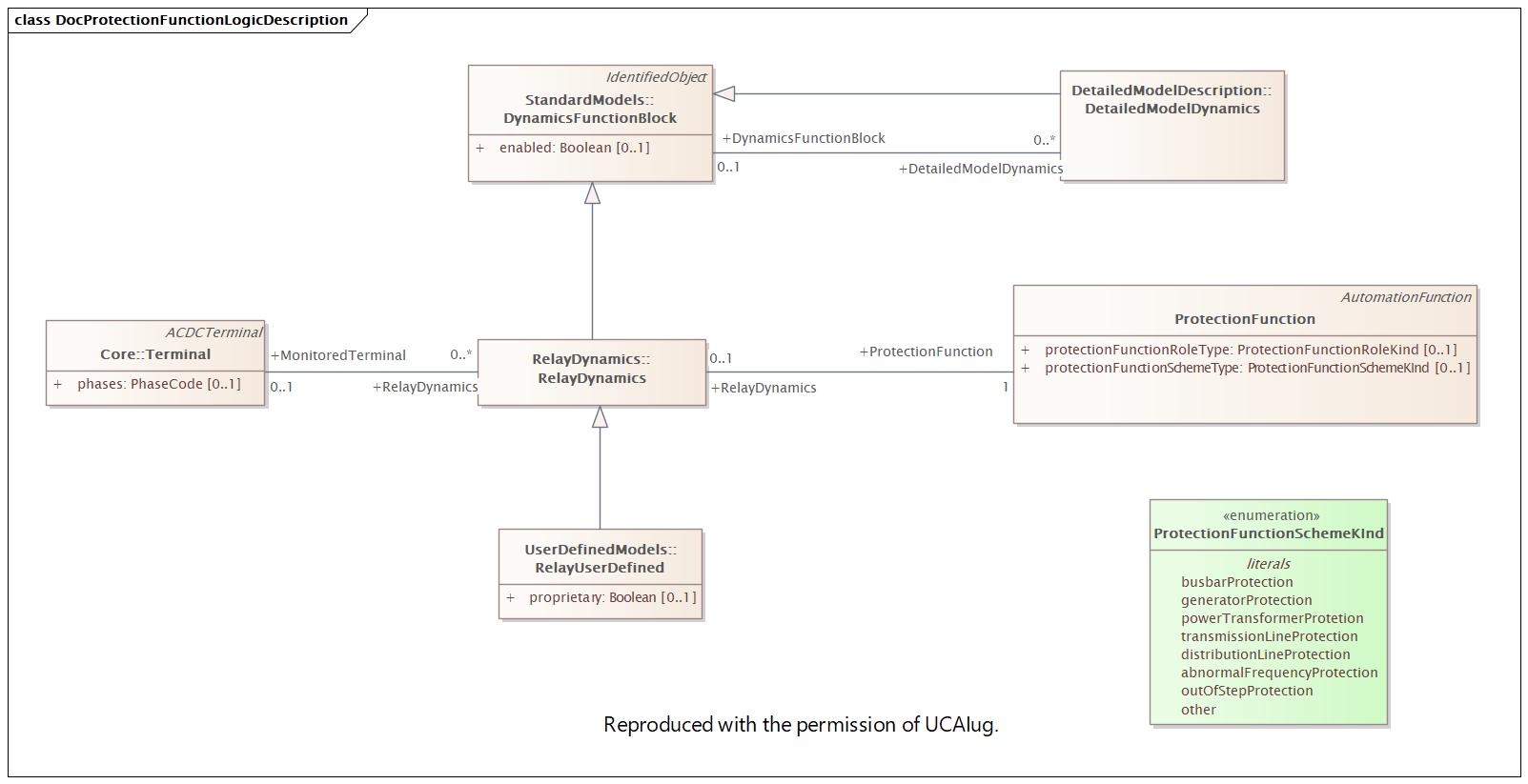
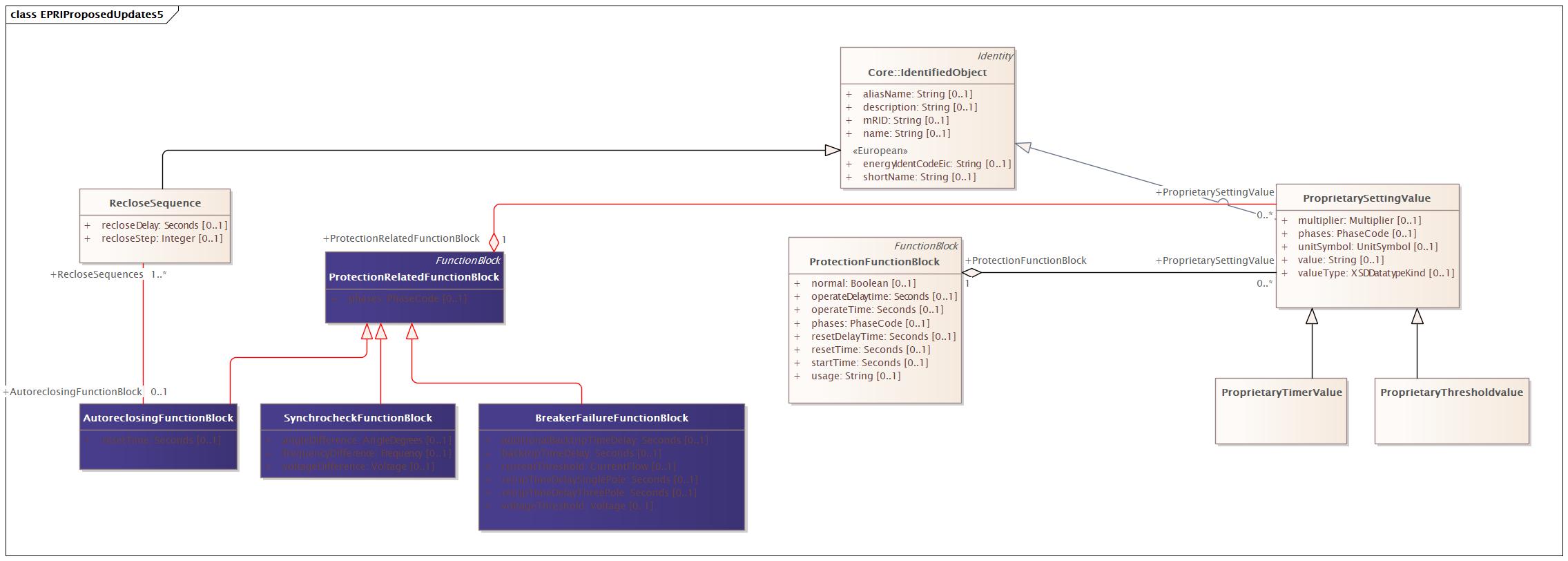
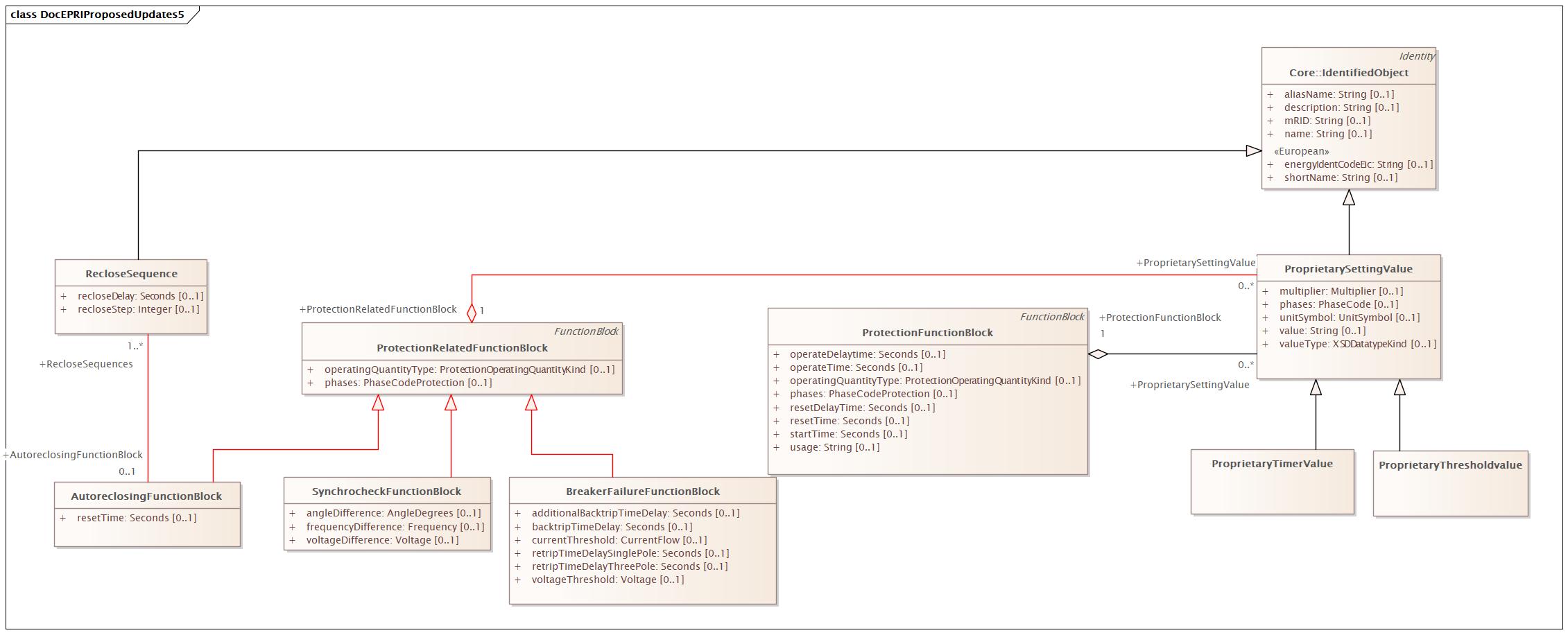
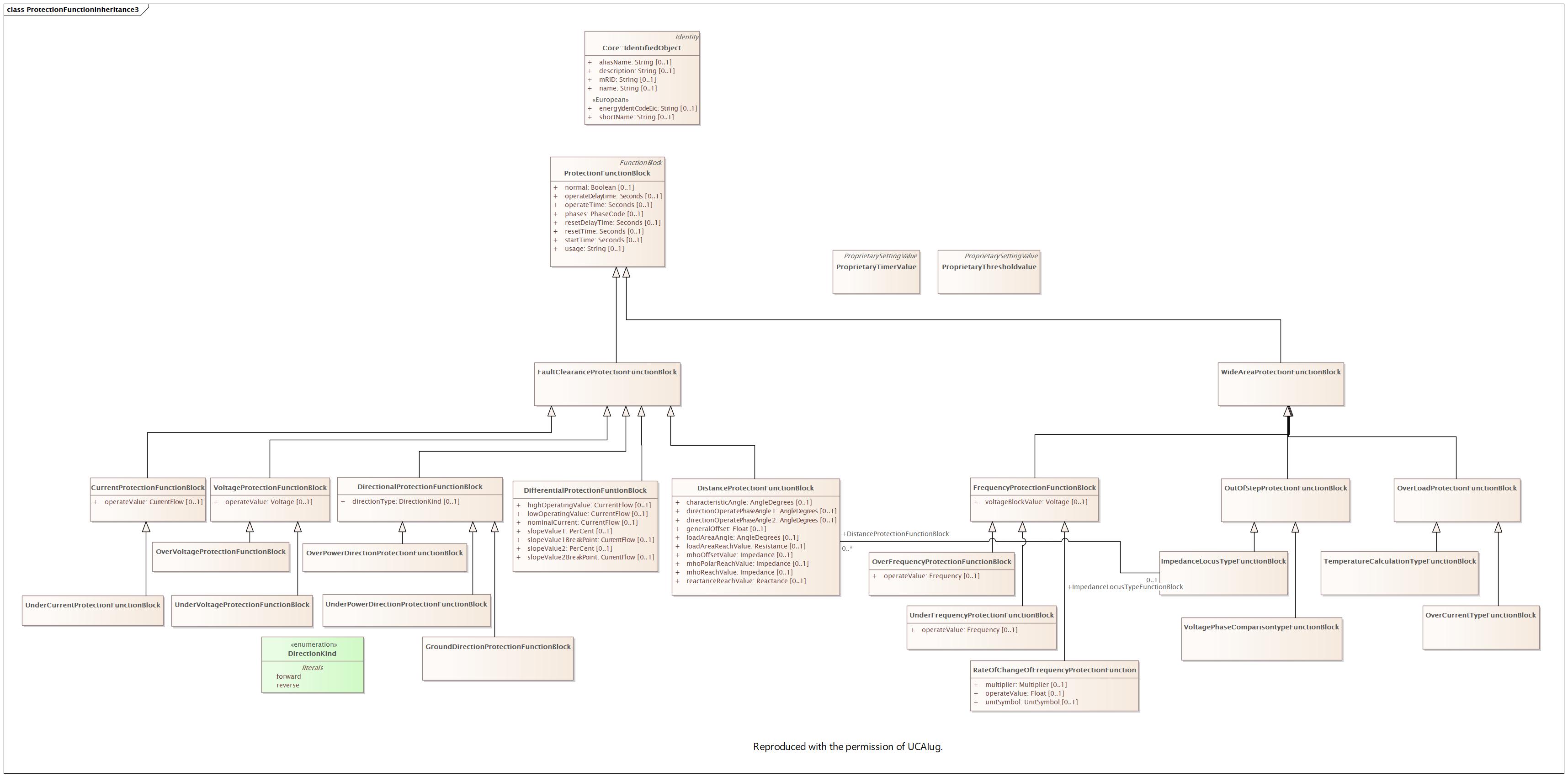
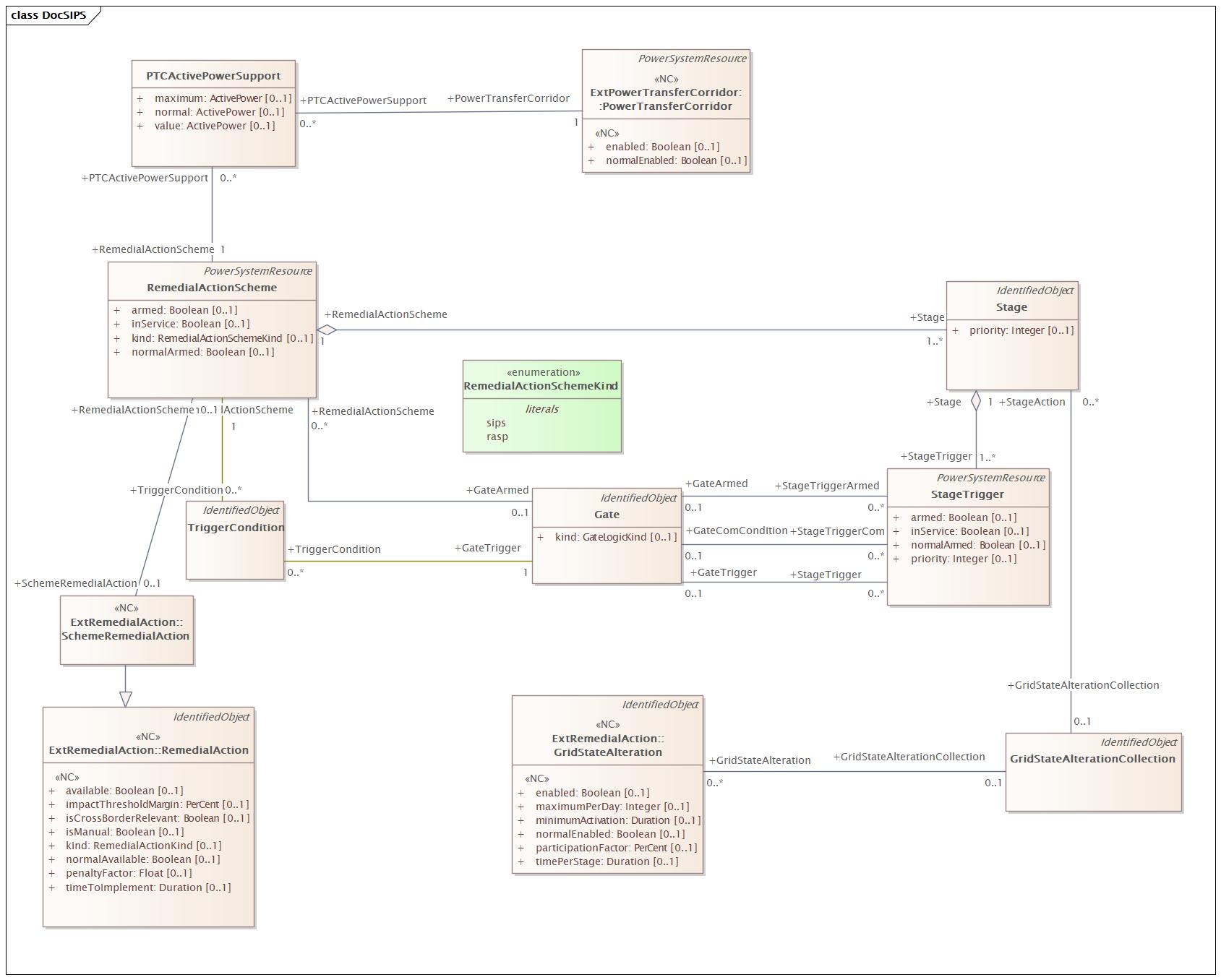
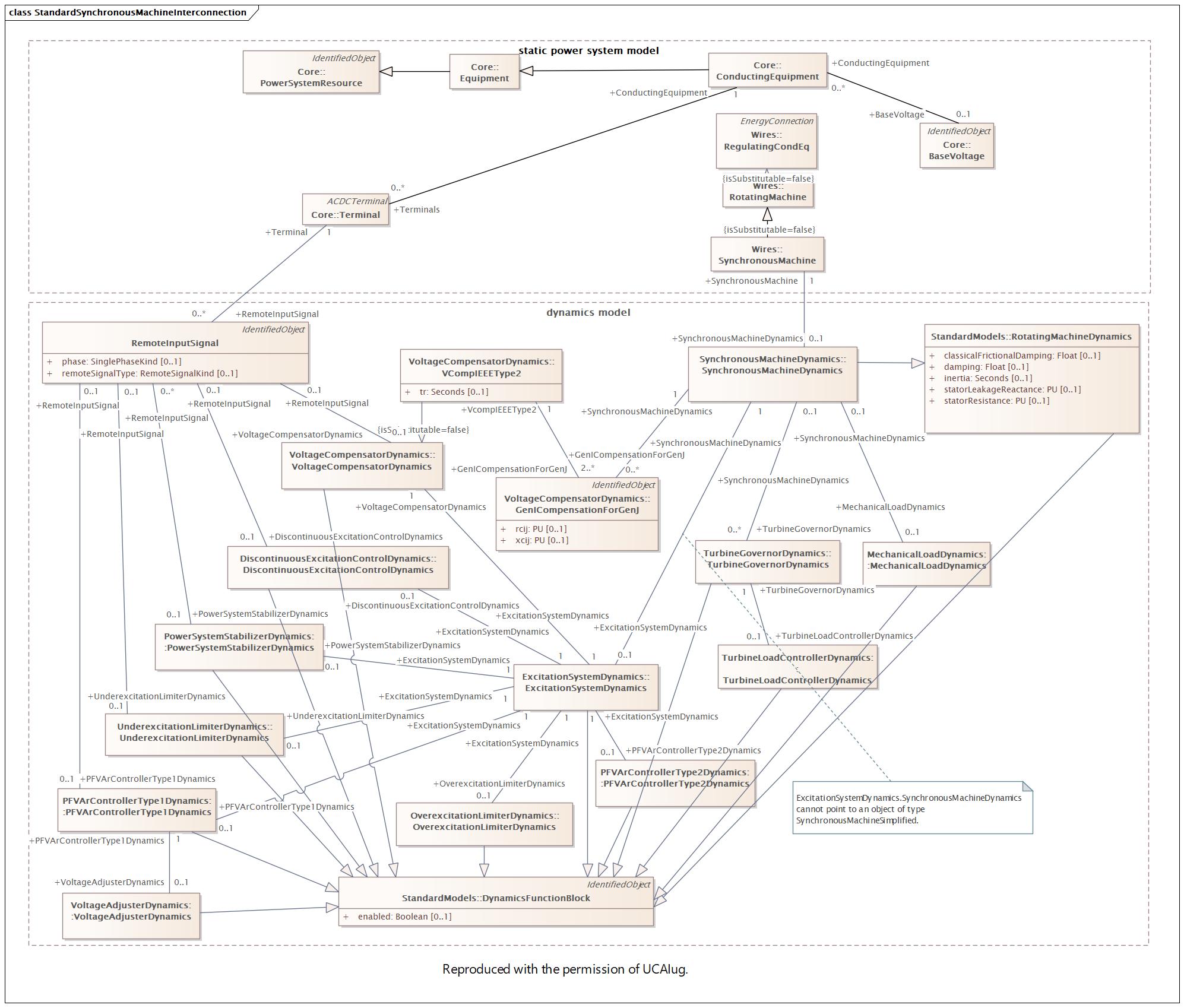
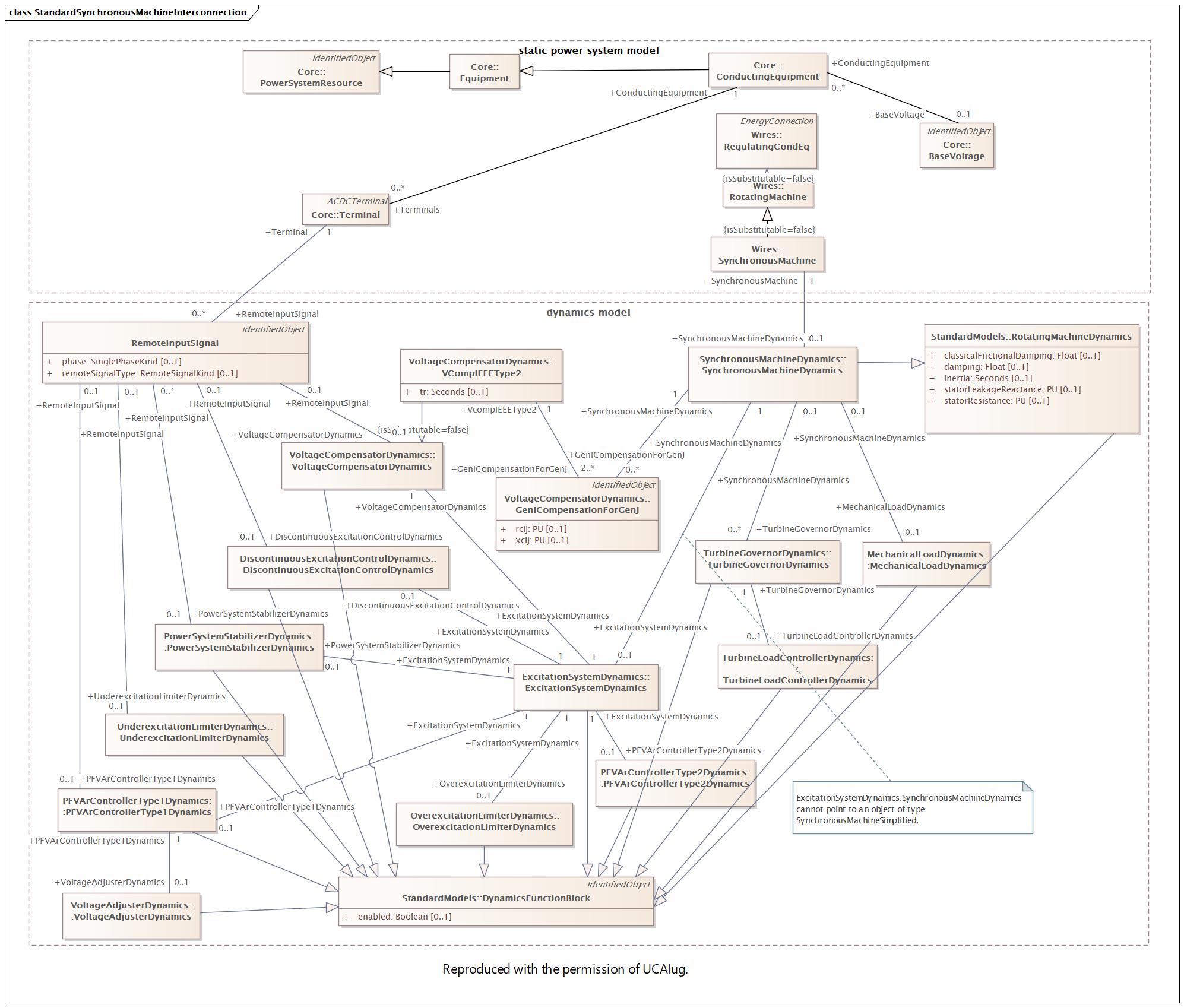
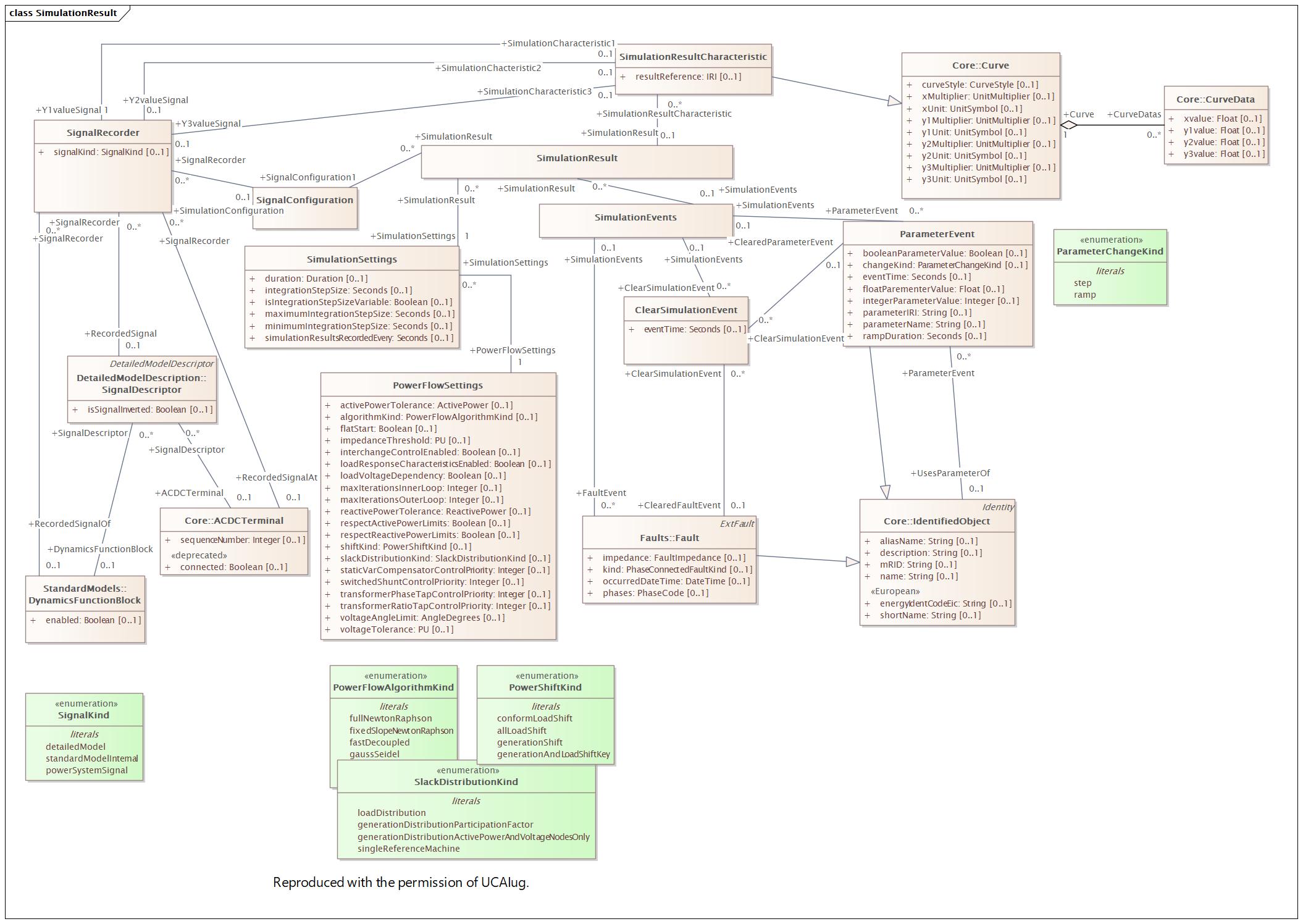
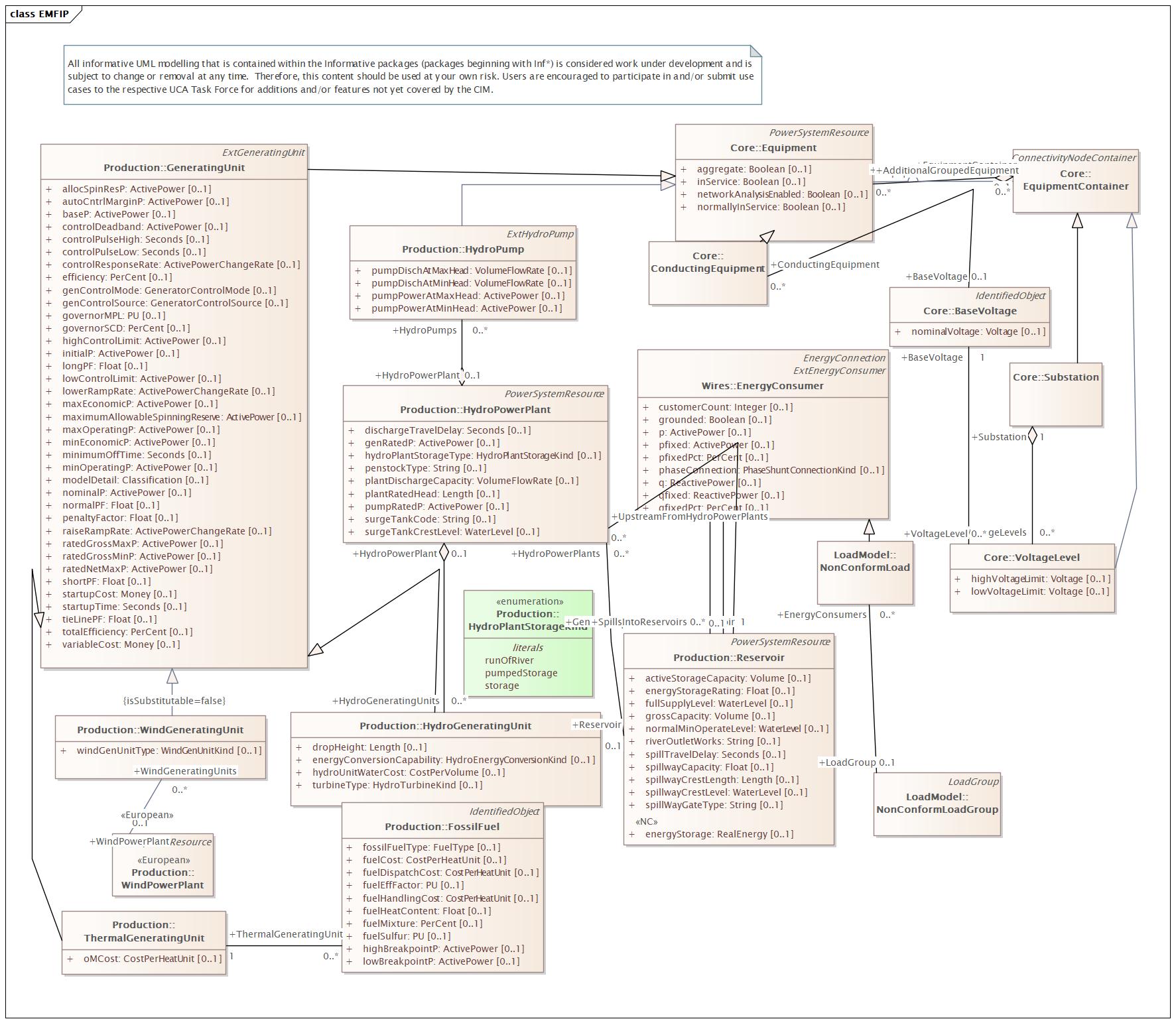
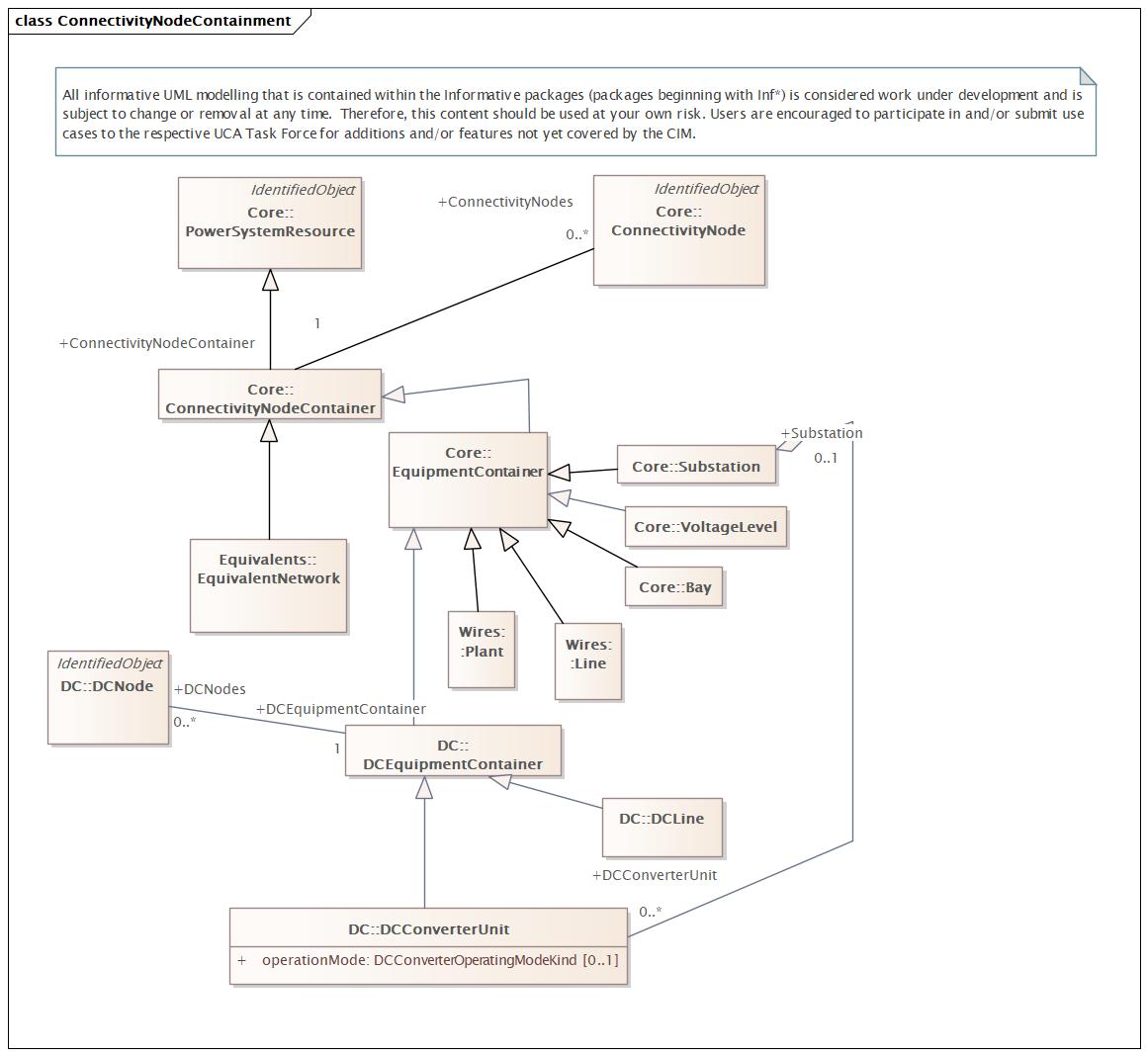
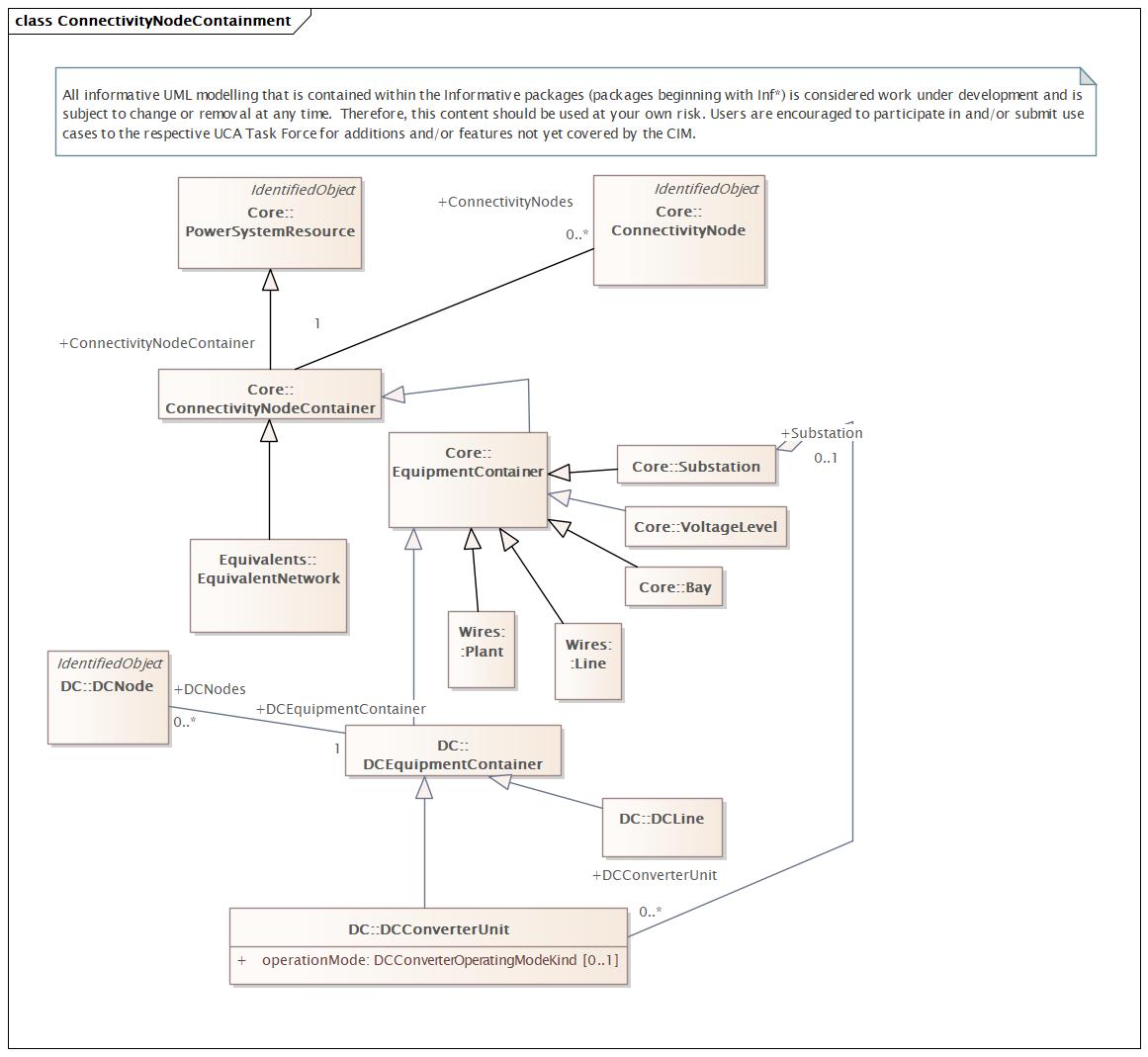
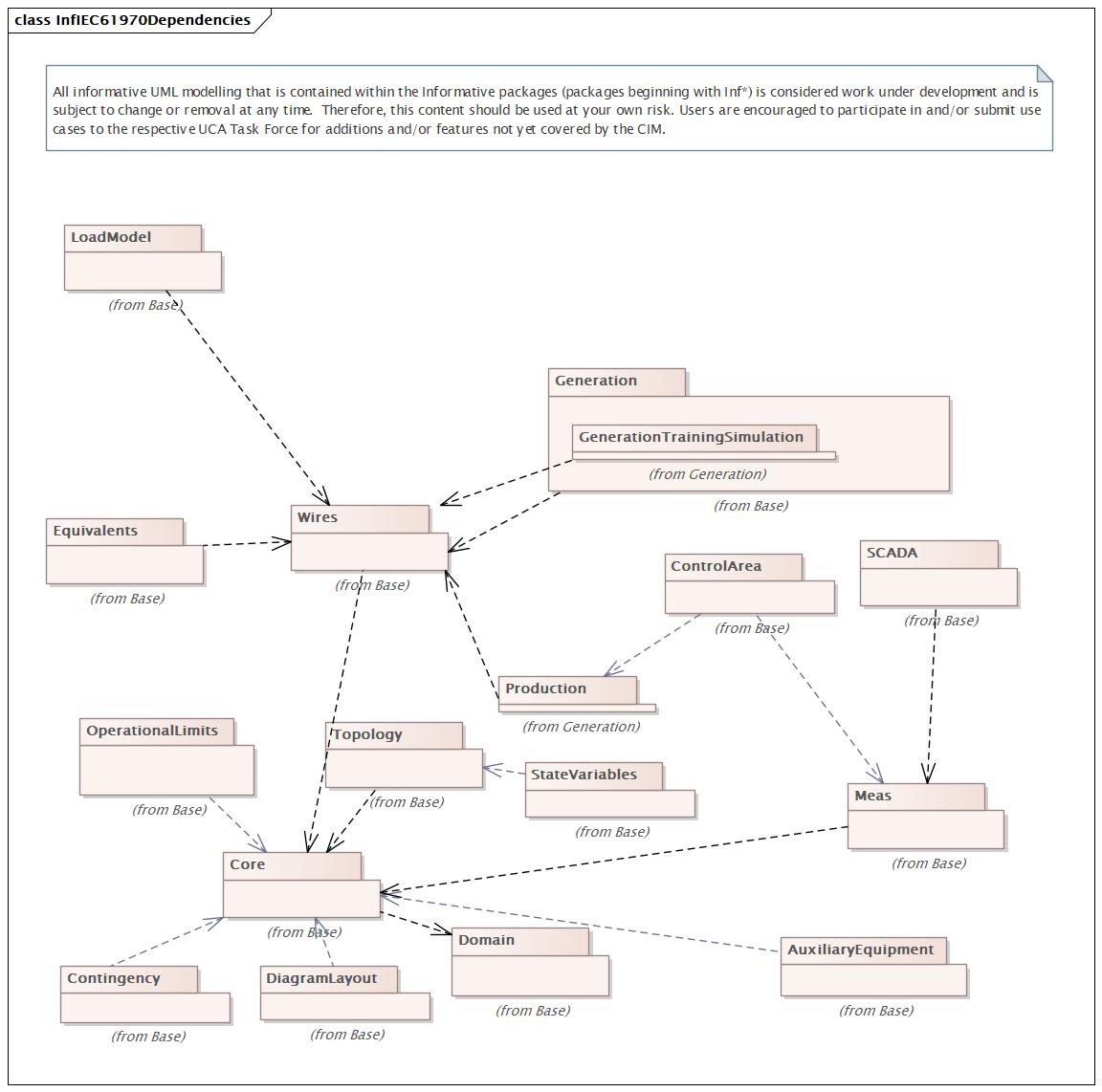
Changed Classes:
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
normalEnabled |
Attribute 'normalEnabled' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
True, if the function block is enabled (active). Otherwise false. |
normalEnabled |
Attribute 'normalEnabled' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
True, if the function block is normally enabled (active). Otherwise false. |
||||||||||||||
Links:
Generalization:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Alias |
| |
|
Direction |
|
Source -> Destination |
|
Name |
| |
|
Notes |
| |
|
Stereotype |
| |
|
Type |
|
Generalization |
|
Baseline Model |
|
Destination Model |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Source Role End Changes |
|
Target Role End Changes |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Generalization:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Alias |
| |
|
Direction |
|
Source -> Destination |
|
Name |
| |
|
Notes |
| |
|
Stereotype |
| |
|
Type |
|
Generalization |
|
Baseline Model |
|
Destination Model |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Source Role End Changes |
|
Target Role End Changes |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Generalization:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Alias |
| |
|
Direction |
|
Source -> Destination |
|
Name |
| |
|
Notes |
| |
|
Stereotype |
| |
|
Type |
|
Generalization |
|
Baseline Model |
|
Destination Model |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Source Role End Changes |
|
Target Role End Changes |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Generalization:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Alias |
| |
|
Direction |
|
Source -> Destination |
|
Name |
| |
|
Notes |
| |
|
Stereotype |
| |
|
Type |
|
Generalization |
|
Baseline Model |
|
Destination Model |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Source Role End Changes |
|
Target Role End Changes |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Generalization:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Alias |
| |
|
Direction |
|
Source -> Destination |
|
Name |
| |
|
Notes |
| |
|
Stereotype |
| |
|
Type |
|
Generalization |
|
Baseline Model |
|
Destination Model |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Source Role End Changes |
|
Target Role End Changes |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Generalization:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Alias |
| |
|
Direction |
|
Source -> Destination |
|
Name |
| |
|
Notes |
| |
|
Stereotype |
| |
|
Type |
|
Generalization |
|
Baseline Model |
|
Destination Model |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Source Role End Changes |
|
Target Role End Changes |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
normalEnabled |
Attribute 'normalEnabled' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
True, if the automation function is enabled (active). Otherwise false. |
normalEnabled |
Attribute 'normalEnabled' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
True, if the automation function is normally enabled (active). Otherwise false. |
||||||||||||||
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Name |
FrequencyControlFuntion |
FrequencyControlFunction |
Links:
Generalization:
|
Baseline Model |
|
Destination Model |
||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Source Role End Changes |
|
Target Role End Changes |
||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
normalMaxAllowedTargetValue |
Attribute 'normalMaxAllowedTargetValue' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Normal maximum allowed target value given by the percent of target value.The allowed value range is [0,100]. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
normalMinAllowedTargetValue |
Attribute 'normalMinAllowedTargetValue' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Normal minimum allowed target value given by the percent of target value.The allowed value range is [0,100]. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Links:
Generalization:
|
Baseline Model |
|
Destination Model |
||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Source Role End Changes |
|
Target Role End Changes |
||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-13 22:21:14 |
2024-12-06 19:43:20 |
|
Name |
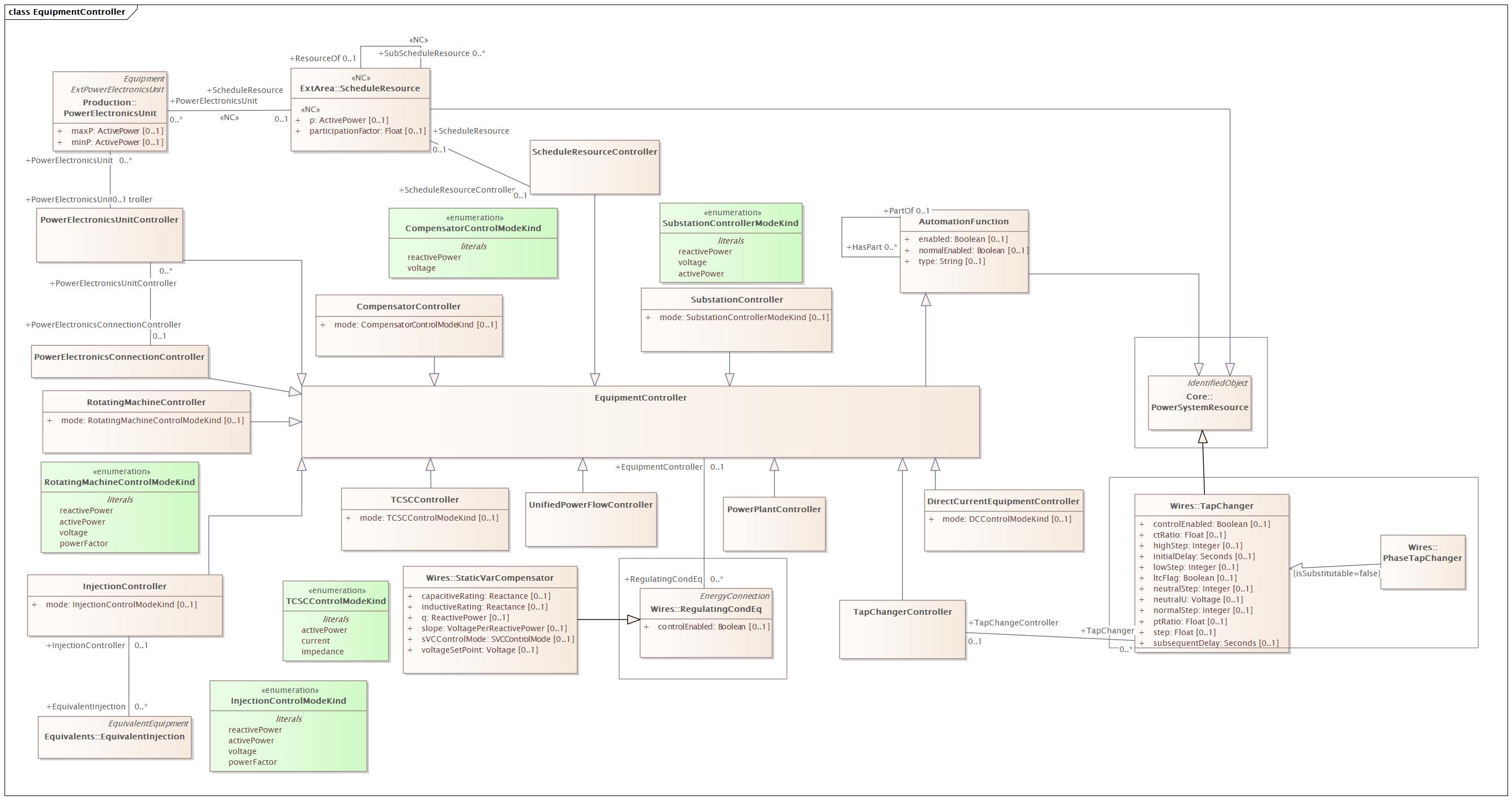
EquipmentController |
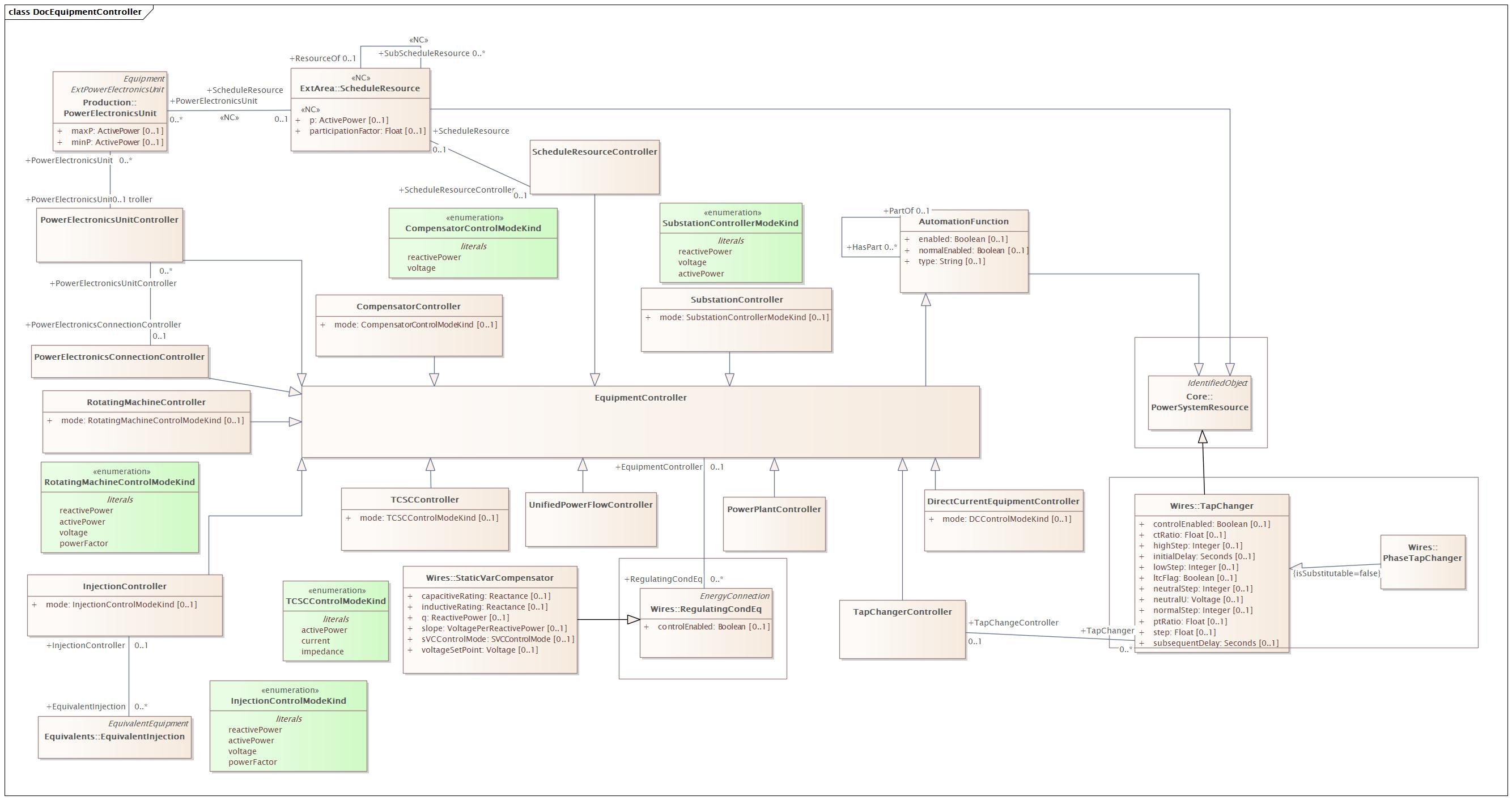
DocEquipmentController |
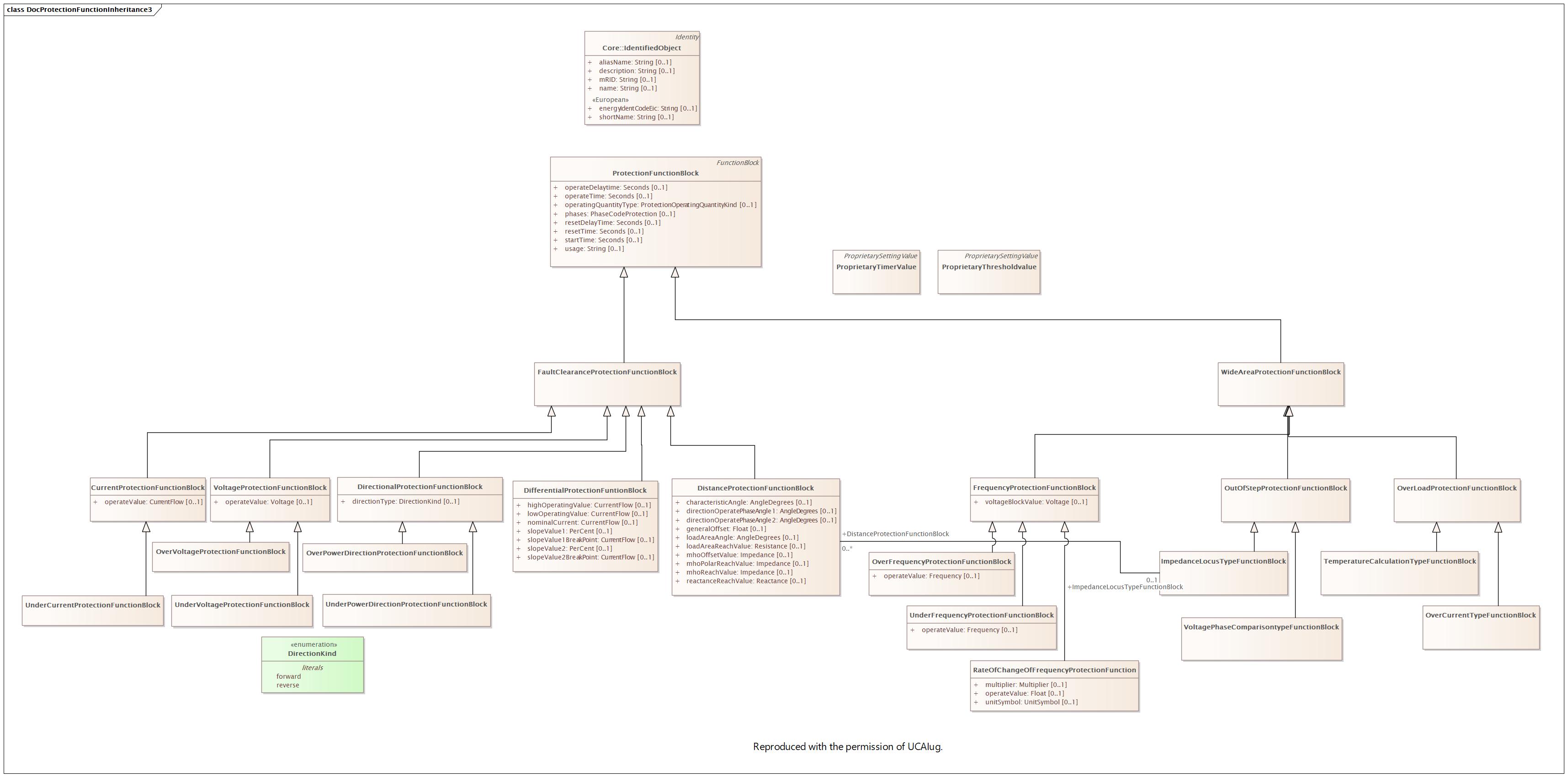
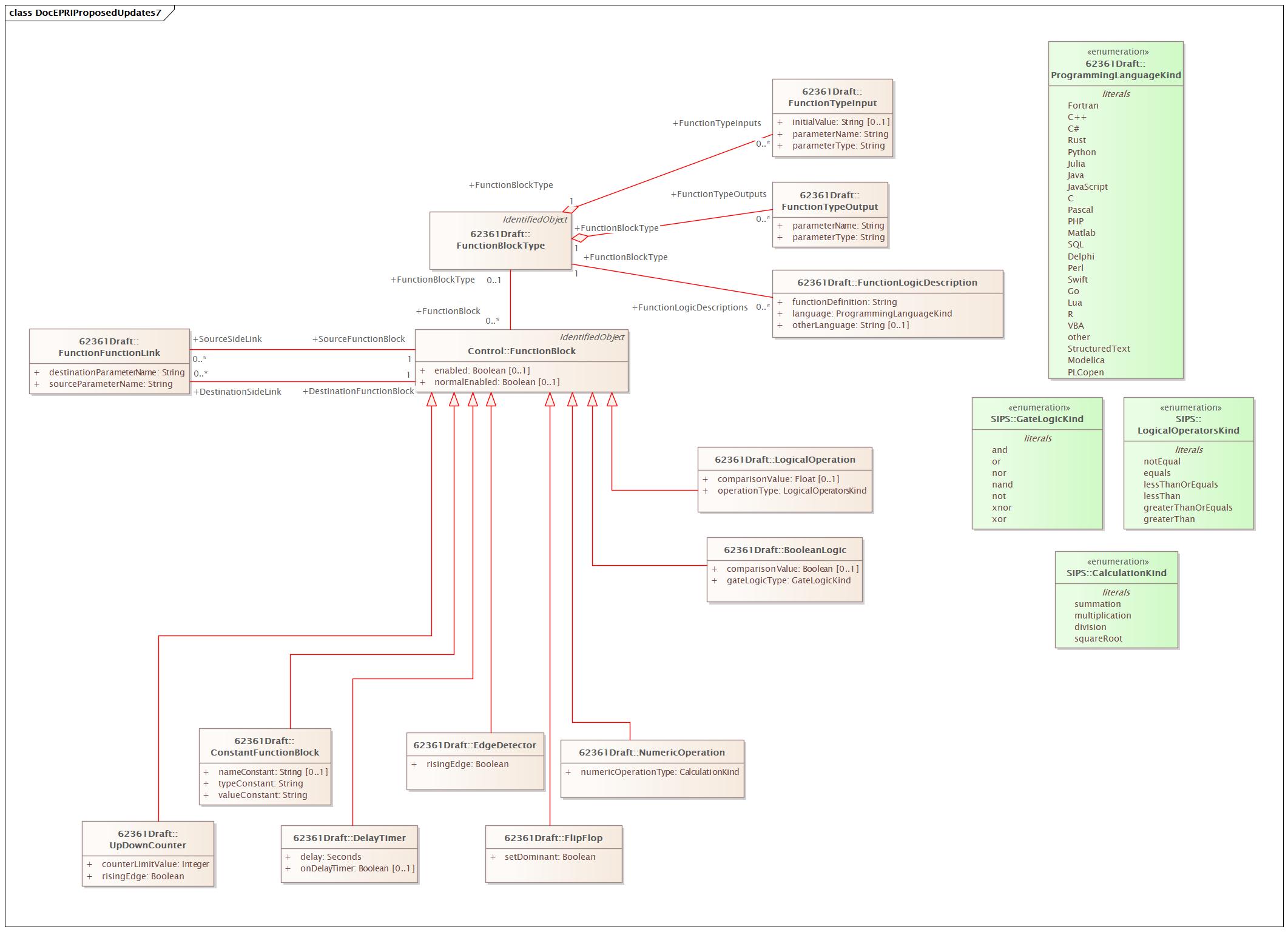
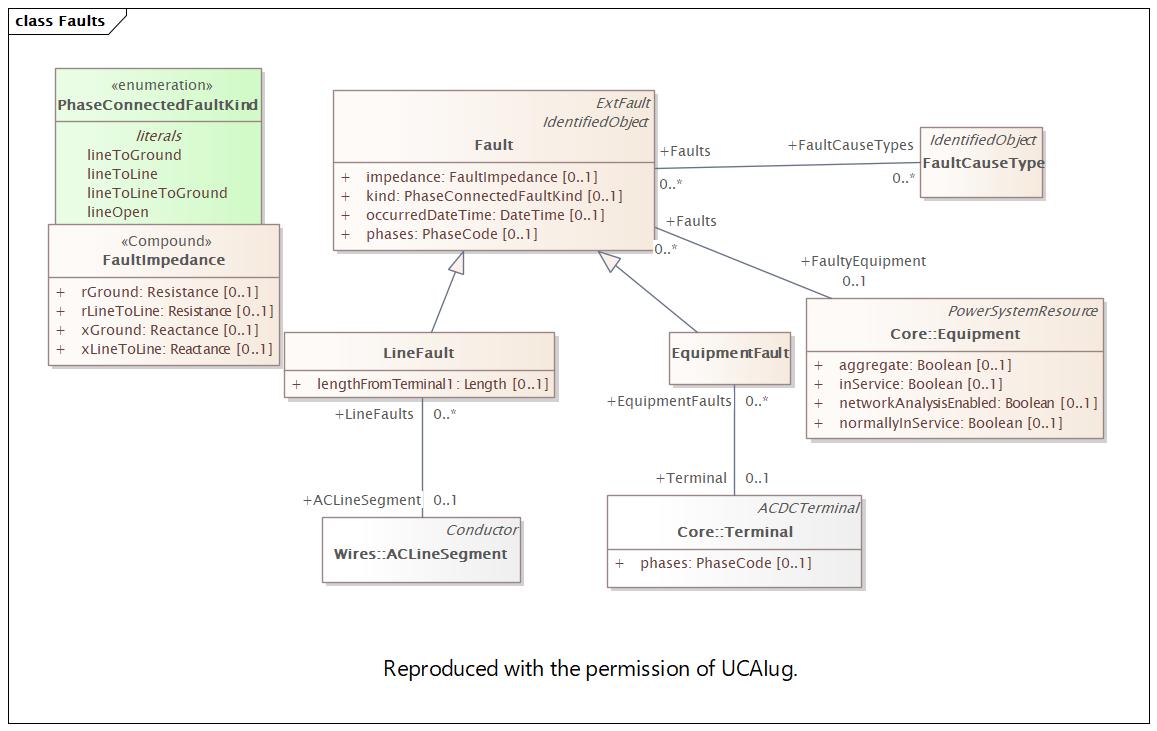
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-13 22:21:39 |
2024-12-06 19:43:25 |
|
Name |
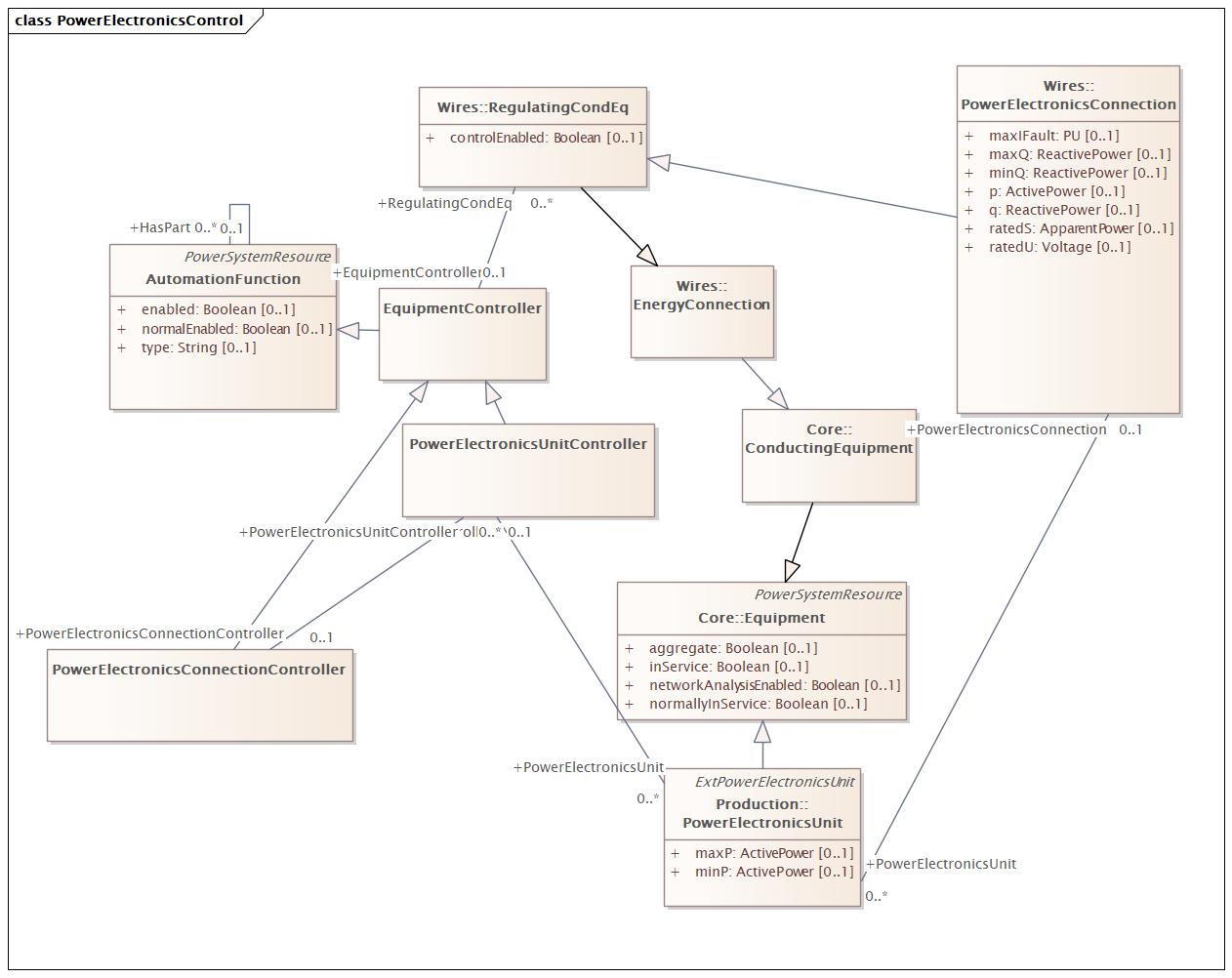
PowerElectronicsControl |
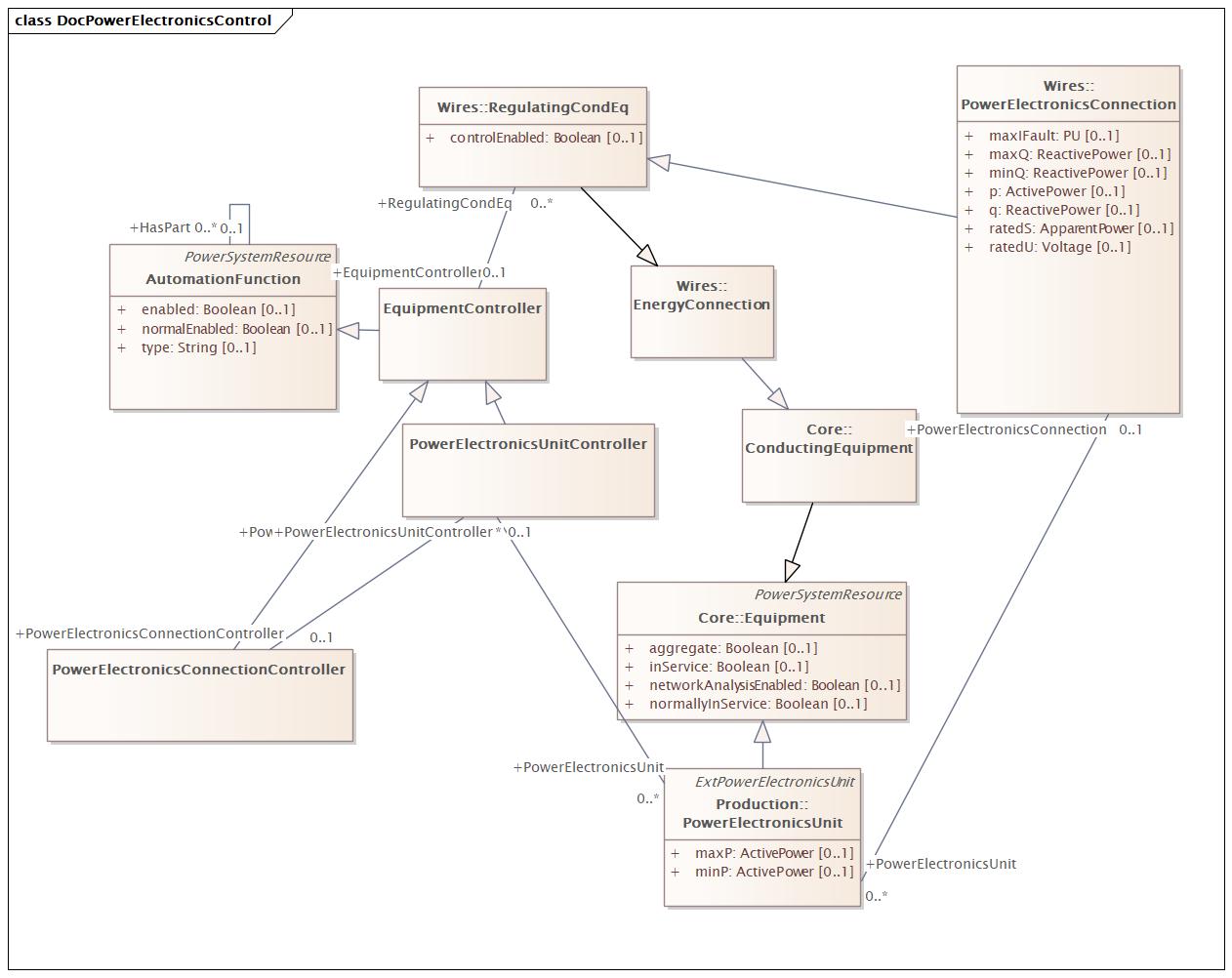
DocPowerElectronicsControl |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-13 22:21:56 |
2024-12-06 19:43:38 |
|
Name |
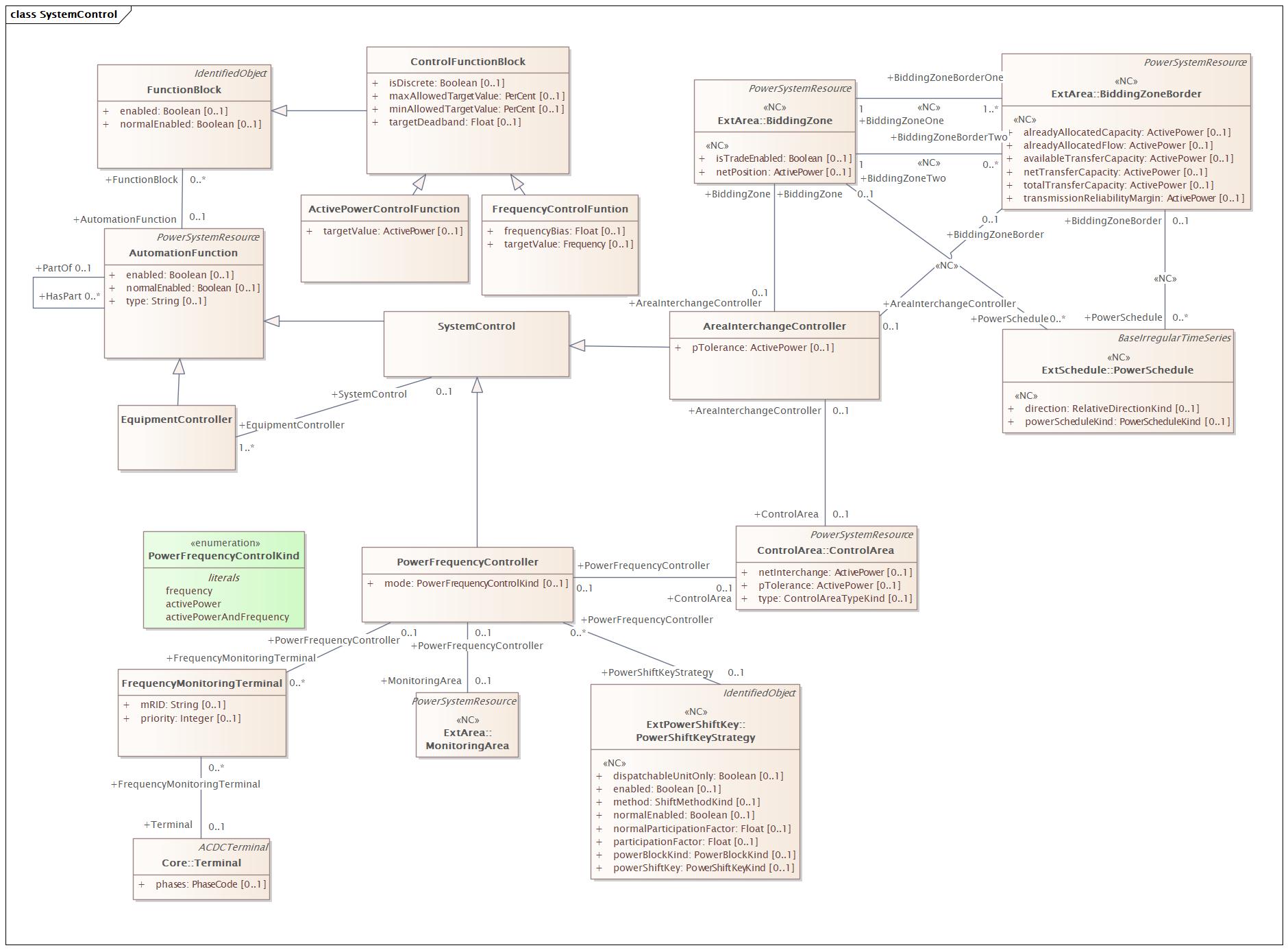
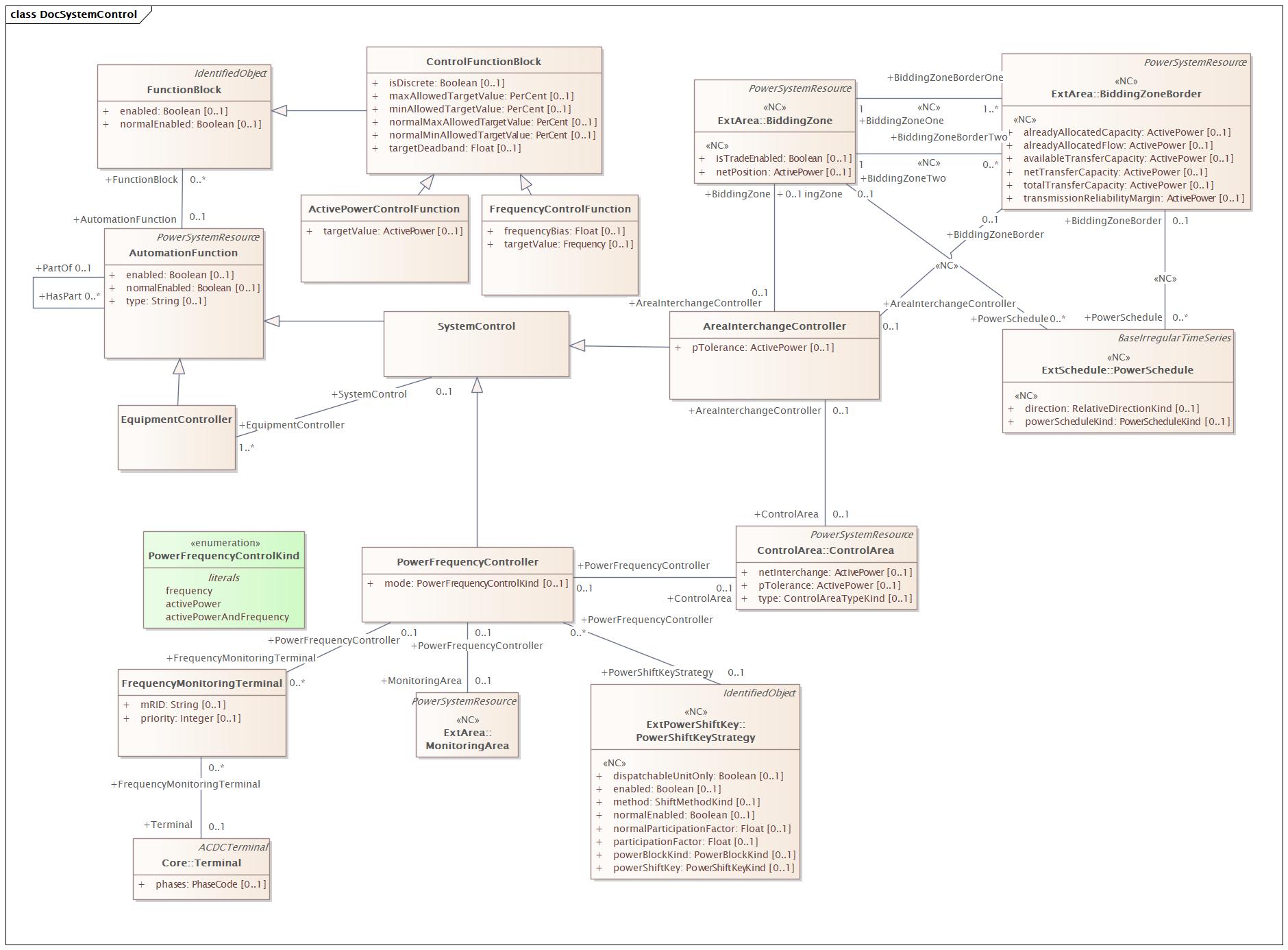
SystemControl |
DocSystemControl |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-13 22:20:34 |
2024-12-06 19:43:09 |
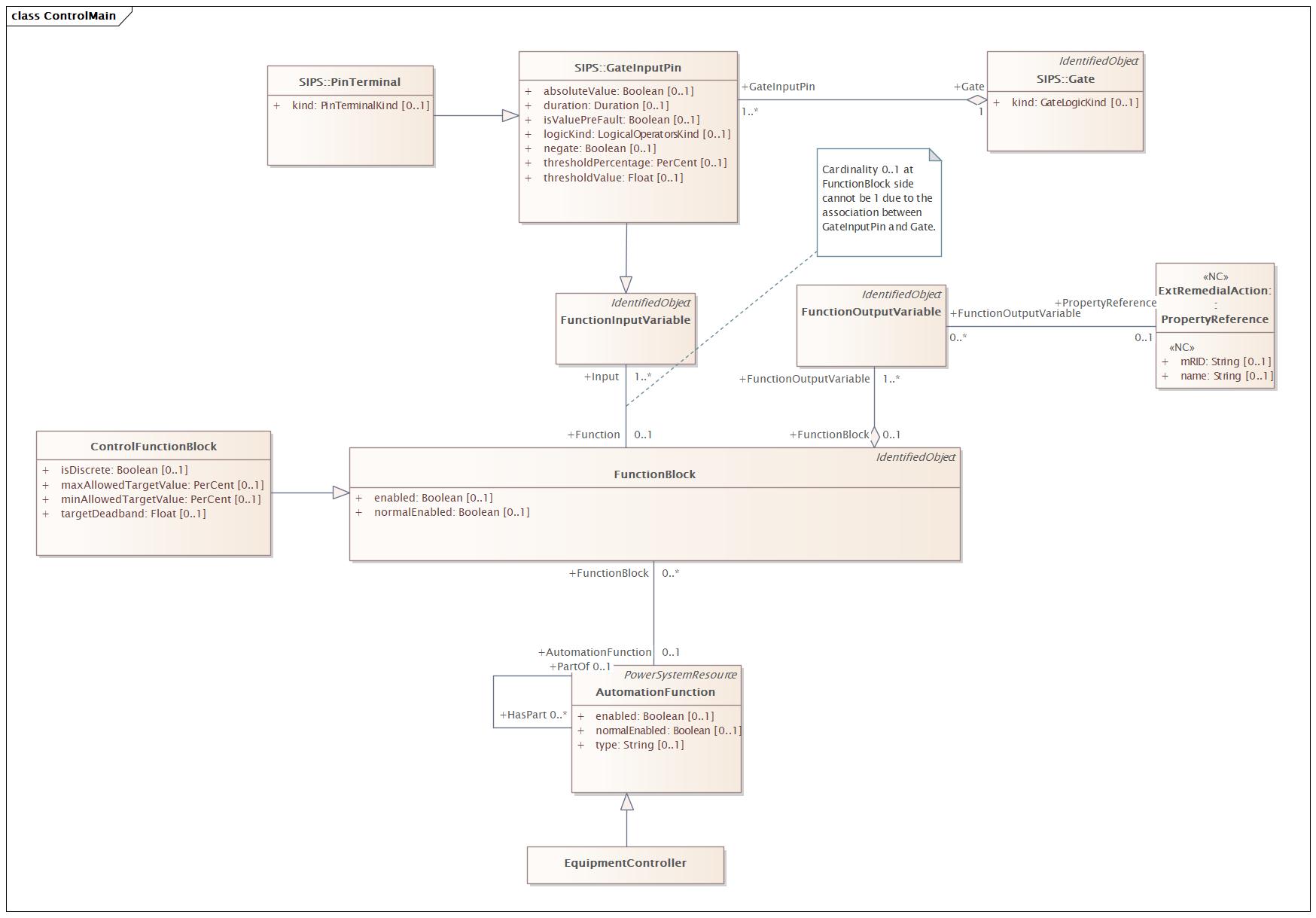
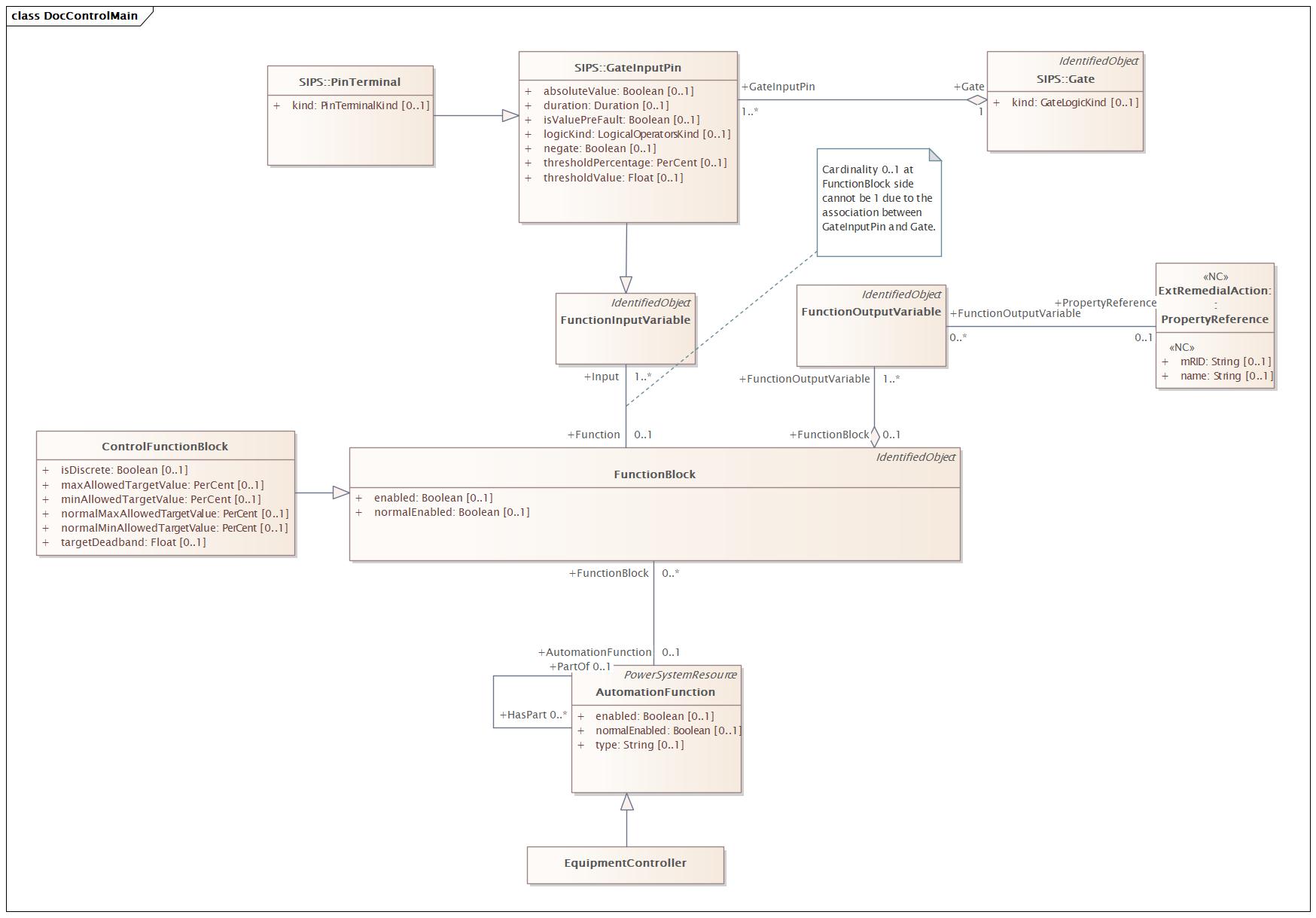
|
Name |
ControlMain |
DocControlMain |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-13 22:21:48 |
2024-12-06 19:43:32 |
|
Name |
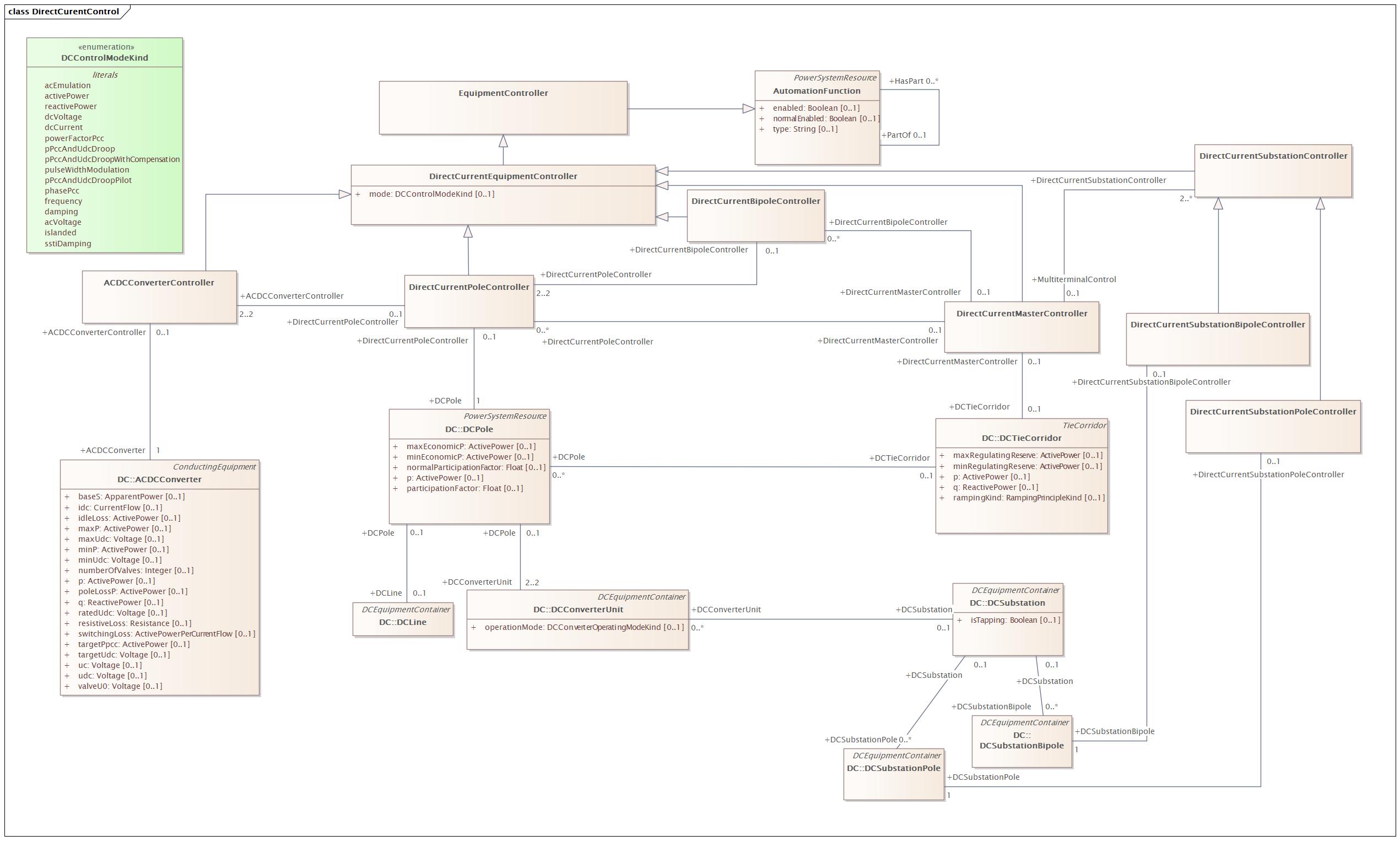
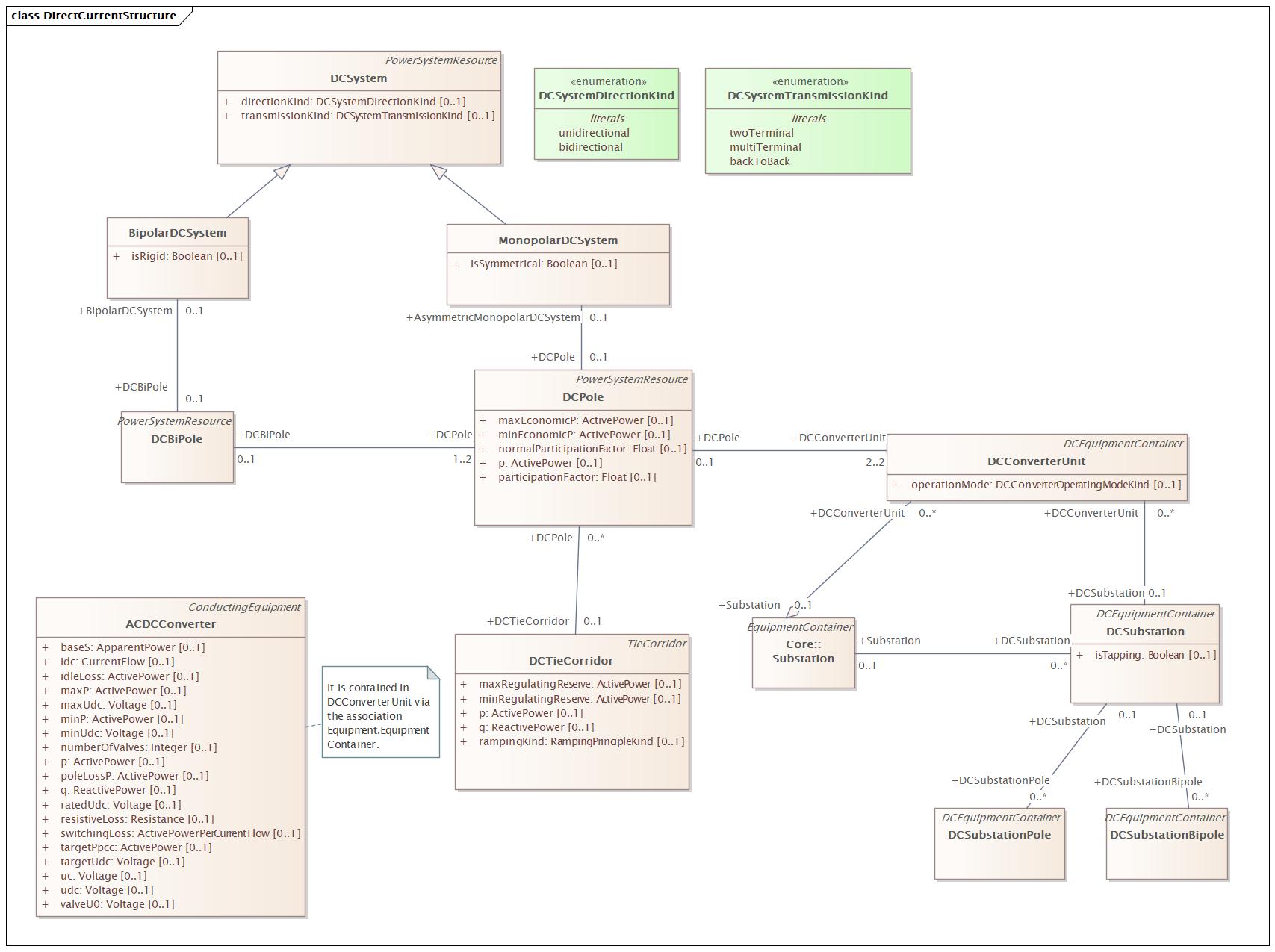
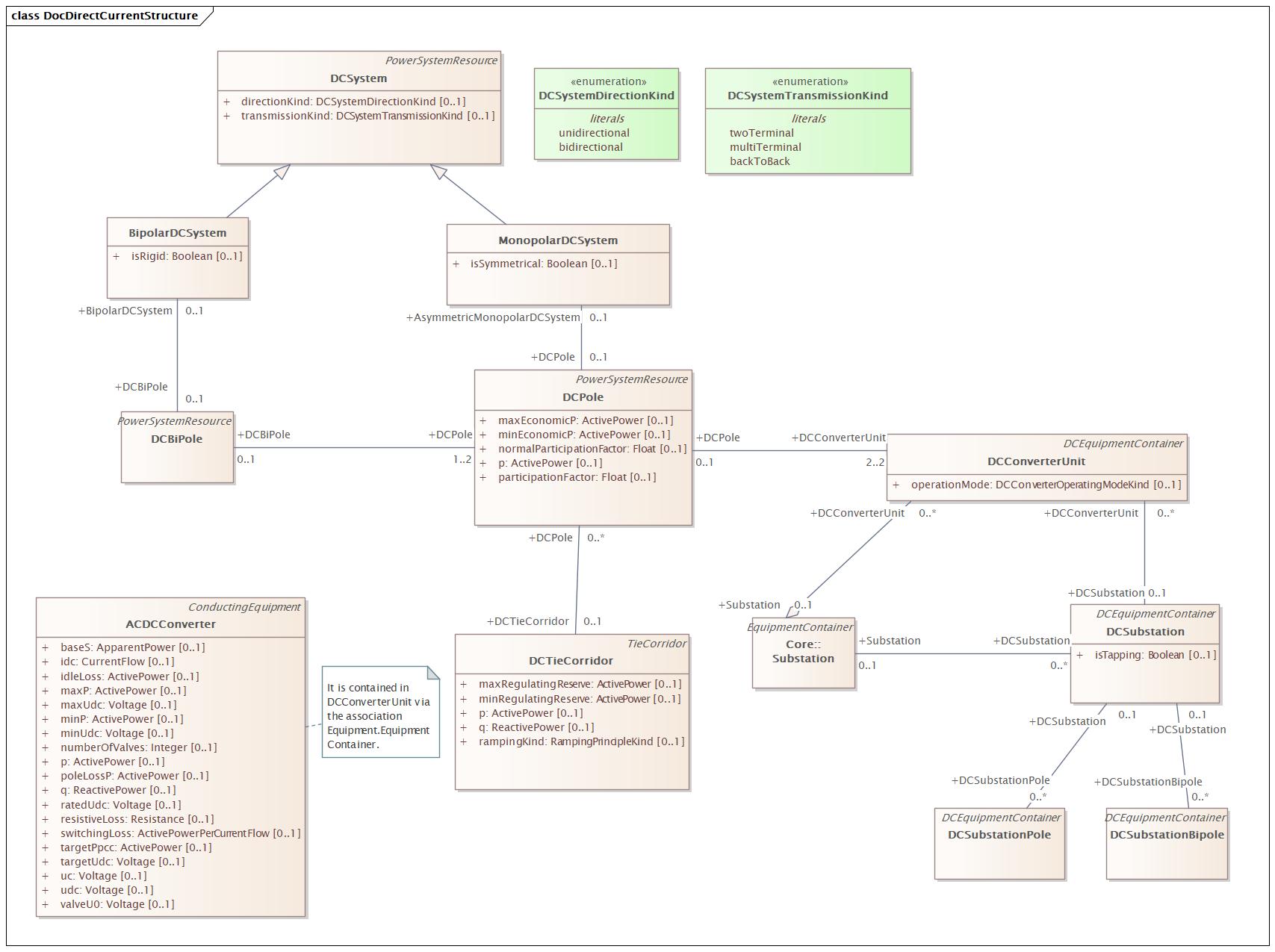
DirectCurentControl |
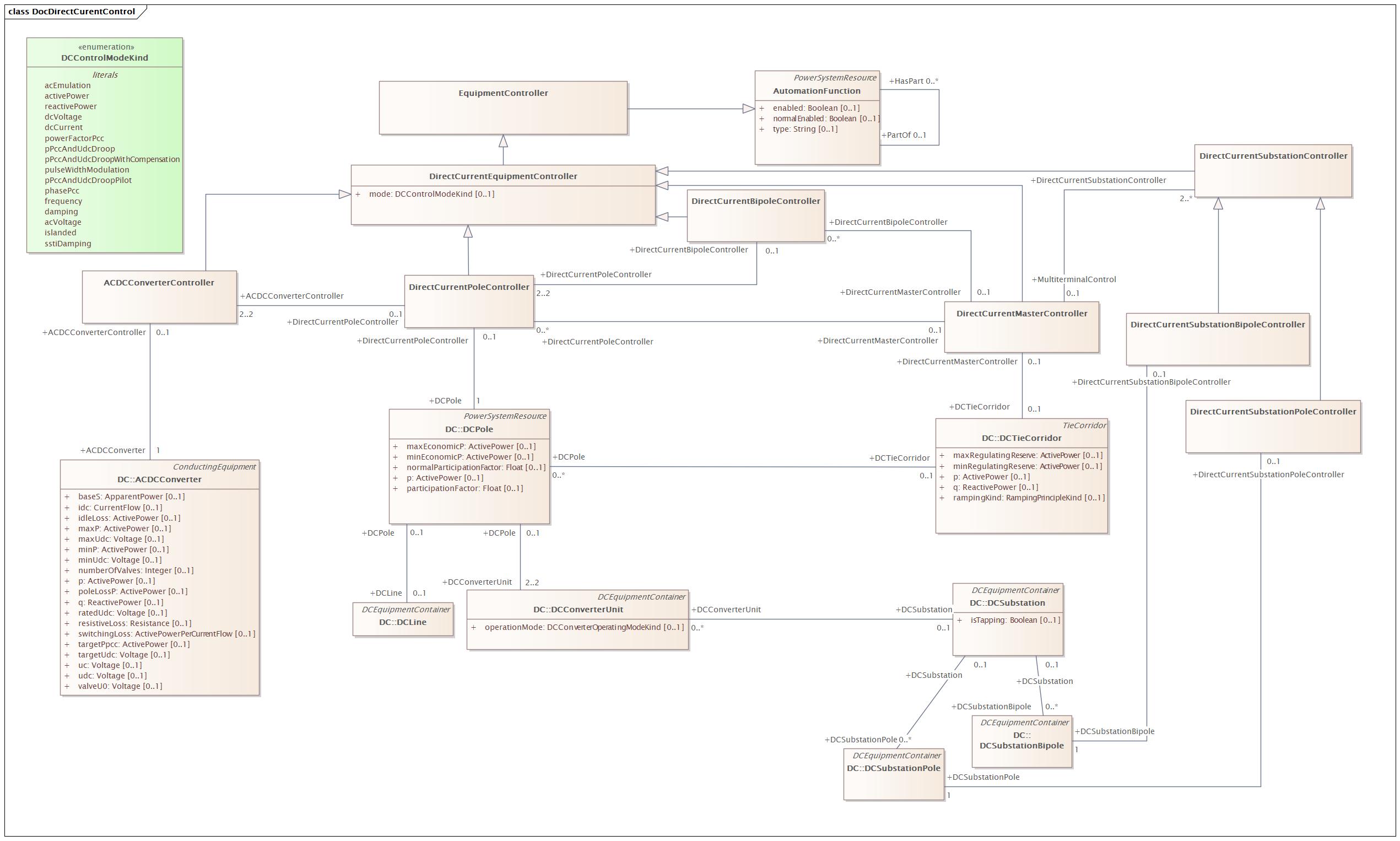
DocDirectCurentControl |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-13 22:20:45 |
2024-12-06 19:43:15 |
|
Name |
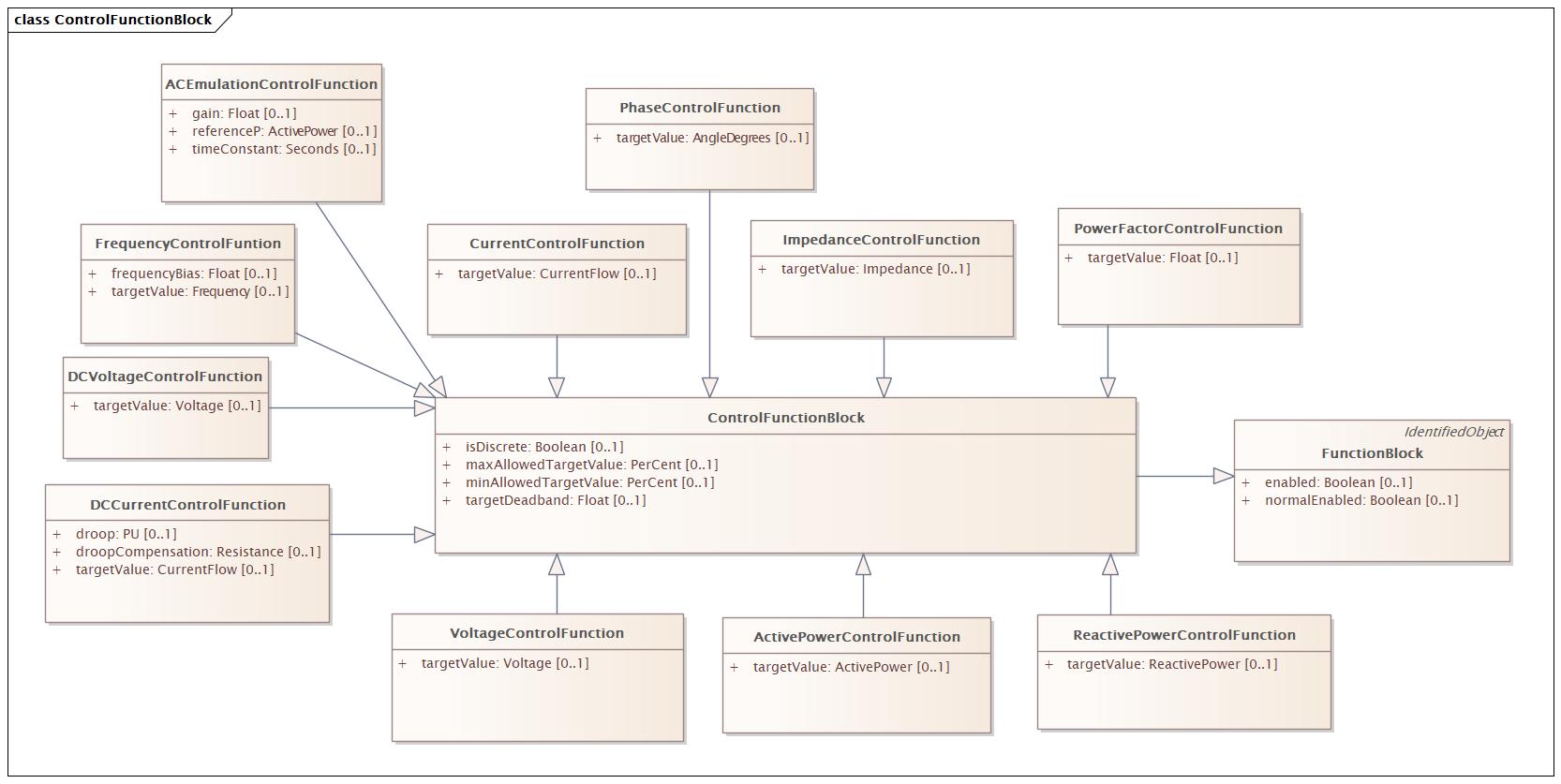
ControlFunctionBlock |
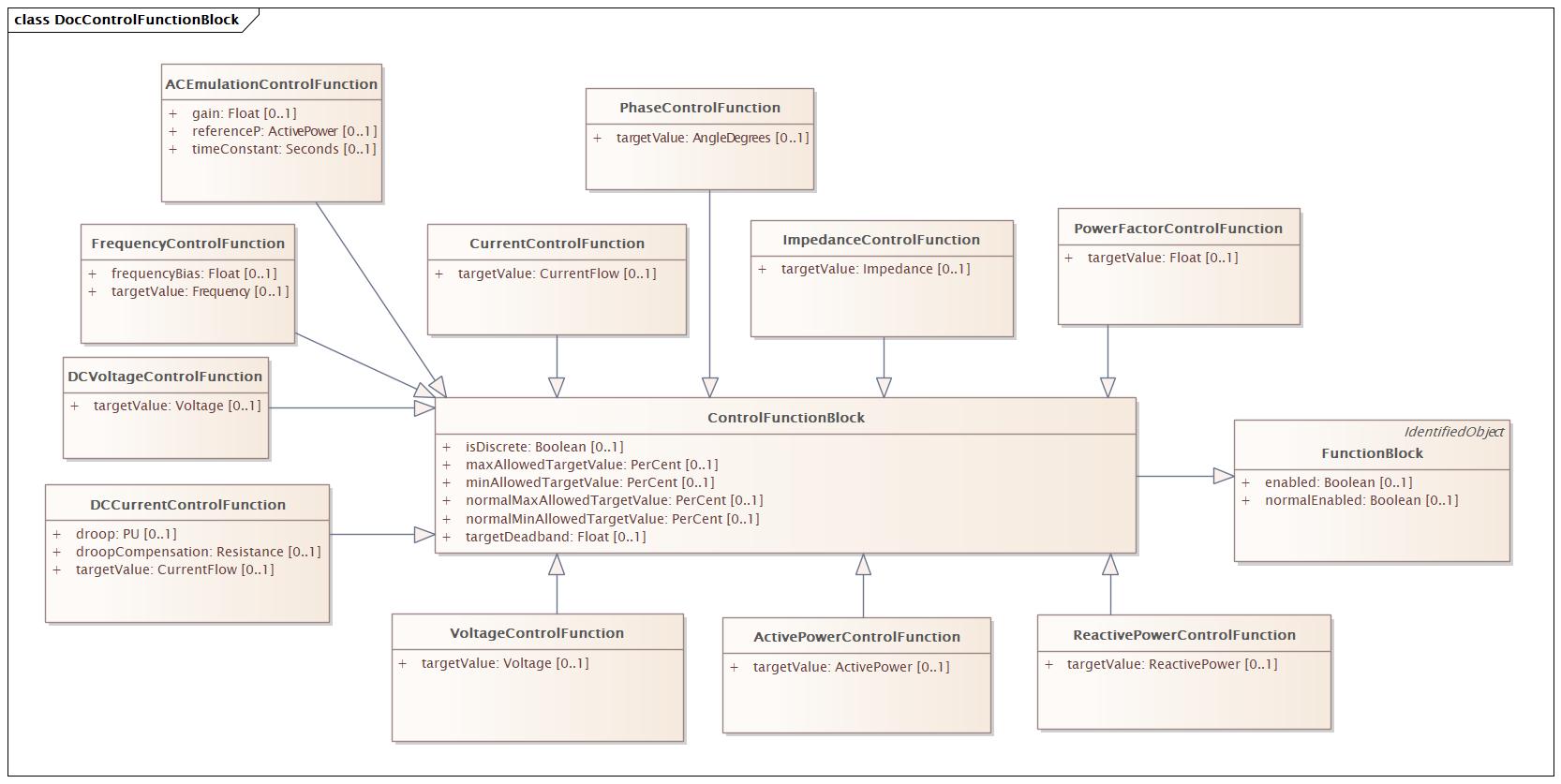
DocControlFunctionBlock |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Changed Classes:
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
aggregate |
Attribute 'aggregate' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
The aggregate flag provides an alternative way of representing an aggregated (equivalent) element. It is applicable in cases when the dedicated classes for equivalent equipment do not have all of the attributes necessary to represent the required level of detail. In case the flag is set to “true” the single instance of equipment represents multiple pieces of equipment that have been modelled together as an aggregate equivalent obtained by a network reduction procedure. Examples would be power transformers or synchronous machines operating in parallel modelled as a single aggregate power transformer or aggregate synchronous machine. The attribute is not used for EquivalentBranch, EquivalentShunt, EquivalentInjection and ExternalNetworkInjection. |
aggregate |
Attribute 'aggregate' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
The aggregate flag provides an alternative way of representing an aggregated (equivalent) element. It is applicable in cases when the dedicated classes for equivalent equipment do not have all of the attributes necessary to represent the required level of detail. In case the flag is set to "true" the single instance of equipment represents multiple pieces of equipment that have been modelled together as an aggregate equivalent obtained by a network reduction procedure. Examples would be power transformers or synchronous machines operating in parallel modelled as a single aggregate power transformer or aggregate synchronous machine. The attribute is not used for EquivalentBranch, EquivalentShunt, EquivalentInjection and ExternalNetworkInjection. |
||||||||||||||
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 11:52:25 |
2024-12-06 19:44:06 |
|
Name |
Datatypes |
DocDatatypes |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 11:52:59 |
2024-12-06 19:44:16 |
|
Name |
Reporting |
DocReporting |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-13 22:24:15 |
2024-12-06 19:43:47 |
|
Name |
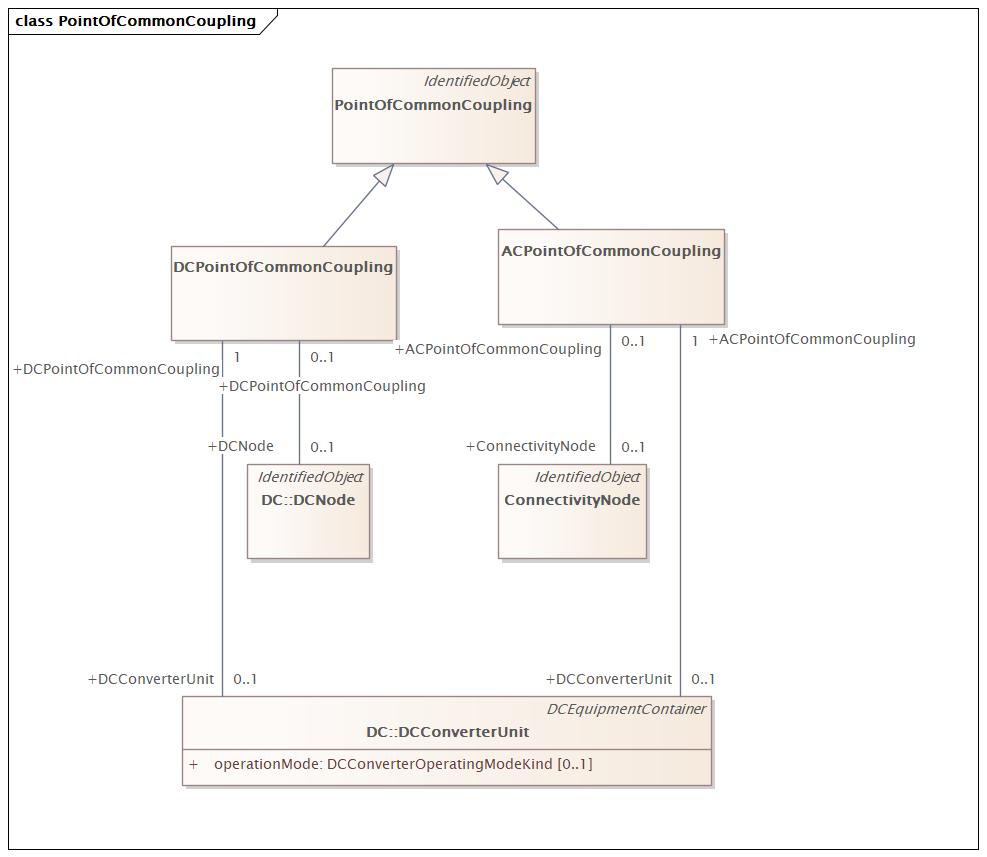
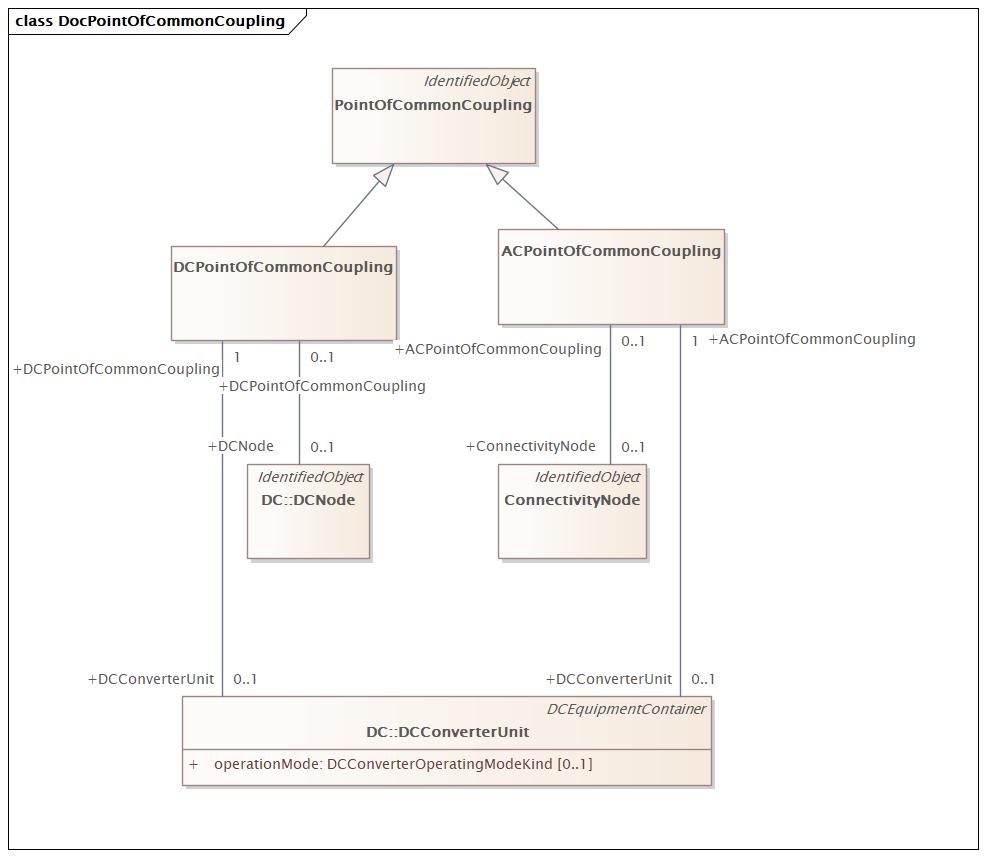
PointOfCommonCoupling |
DocPointOfCommonCoupling |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
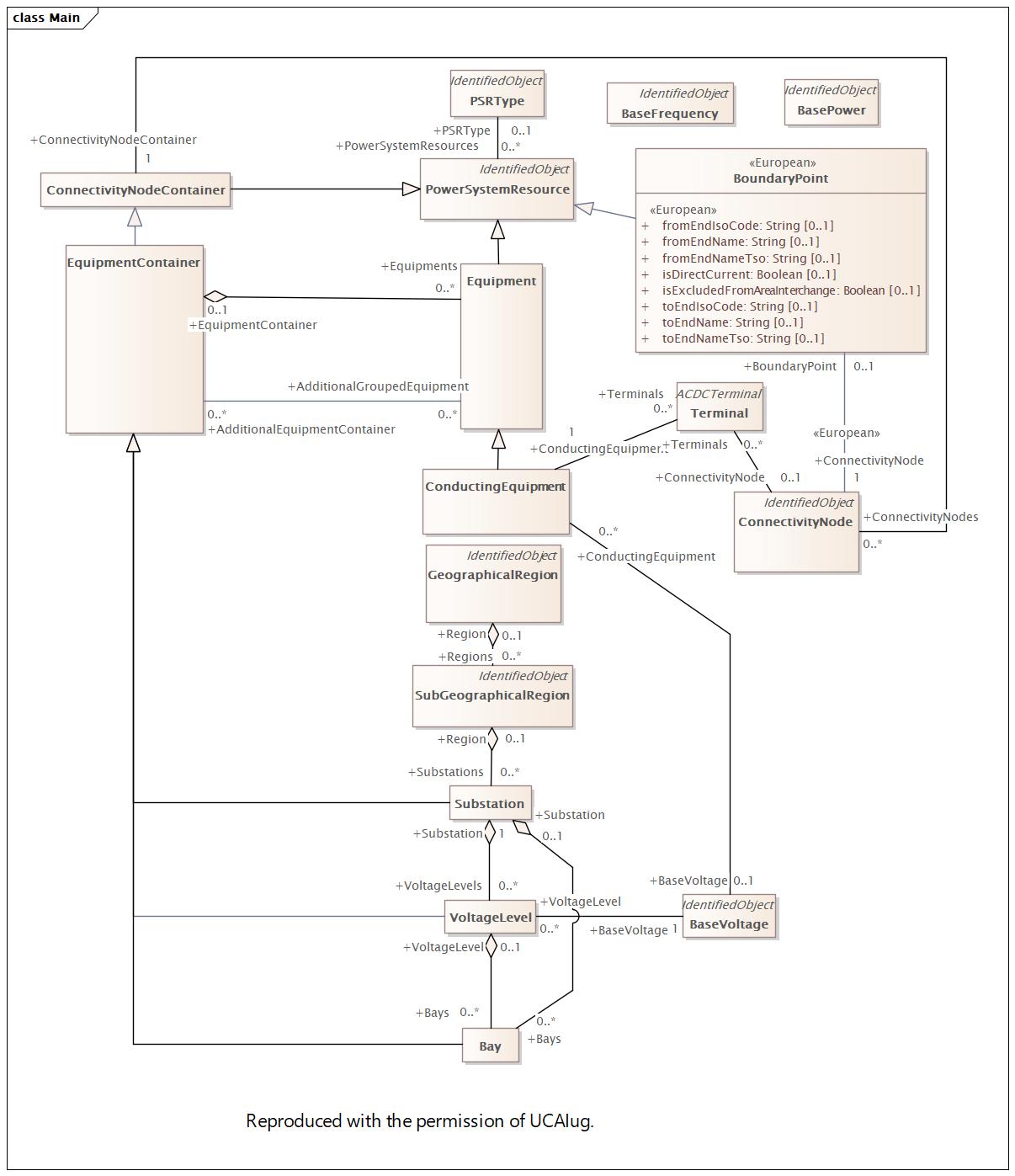
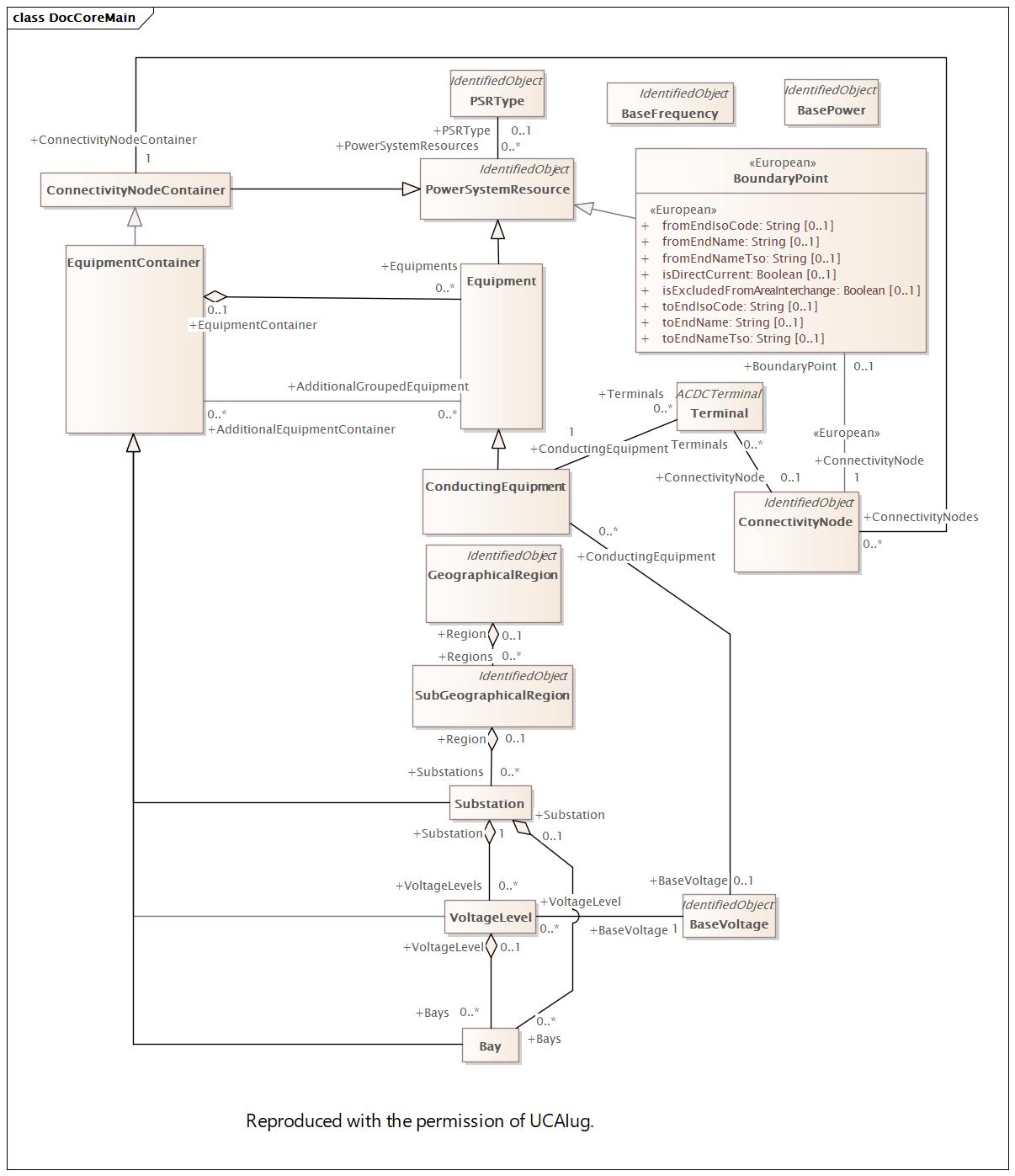
2023-10-24 06:07:21 |
2024-12-06 10:44:14 |
|
Name |
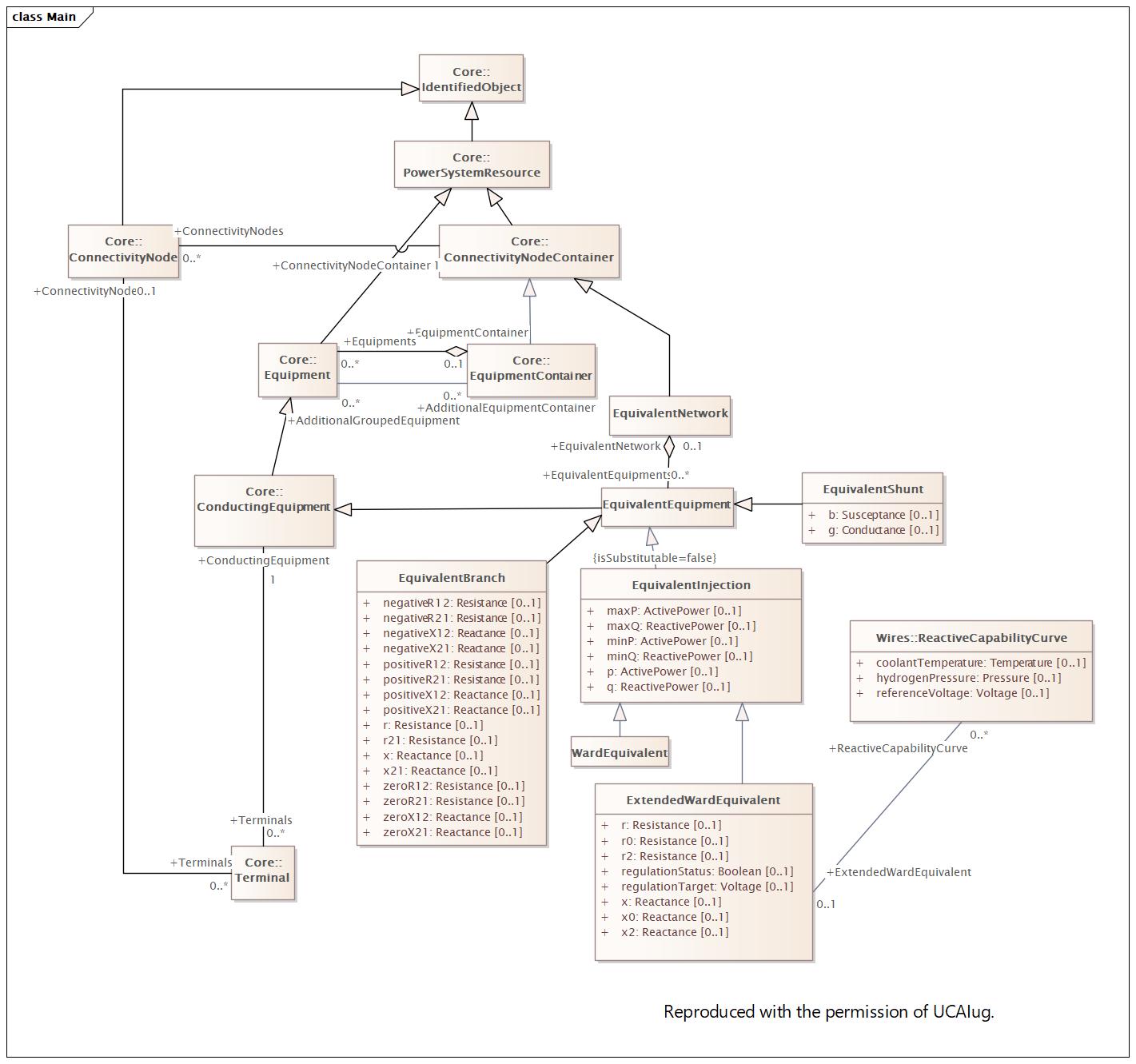
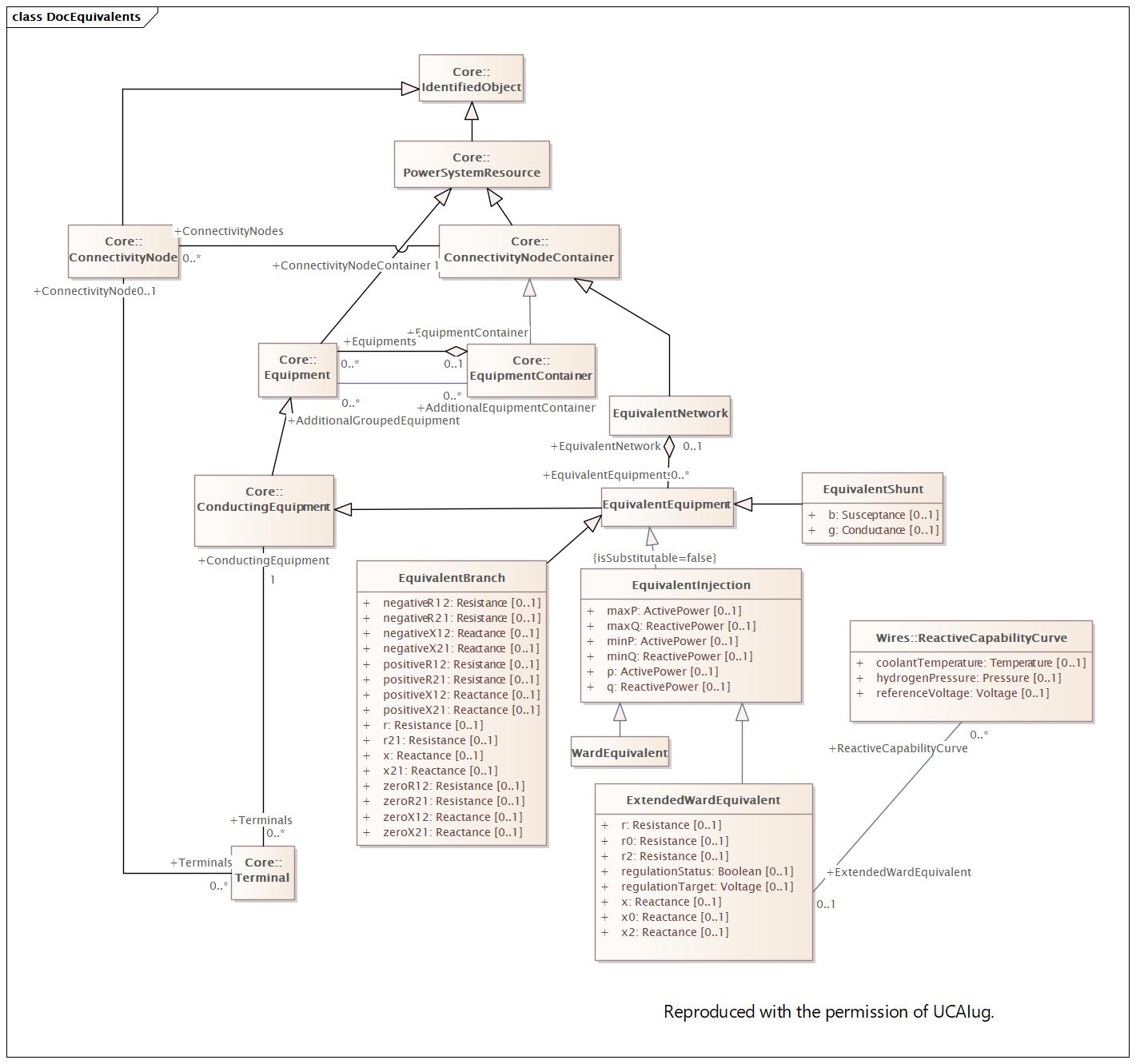
Main |
DocCoreMain |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-06-05 21:49:25 |
2024-12-06 19:43:53 |
|
Name |
NamesAndIdentity |
DocNamesAndIdentity |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 11:52:39 |
2024-12-06 19:44:11 |
|
Name |
FeederContainment |
DocFeederContainment |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-21 10:11:41 |
2024-12-06 19:44:00 |
|
Name |
CurveSchedule |
DocCurveSchedule |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 11:53:19 |
2024-12-06 19:44:27 |
|
Name |
OperatingShare |
DocOperatingShare |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Changed Classes:
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ISK |
Attribute 'ISK' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Icelandic króna. |
ISK |
Attribute 'ISK' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Icelandic krona. |
||||||||||||||
|
PYG |
Attribute 'PYG' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Paraguayan guaraní. |
PYG |
Attribute 'PYG' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Paraguayan guarani. |
||||||||||||||
|
STD |
Attribute 'STD' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
São Tomé and Príncipe dobra. |
STD |
Attribute 'STD' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Sao Tome and Principe dobra. |
||||||||||||||
|
VEF |
Attribute 'VEF' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Venezuelan bolívar fuerte. |
VEF |
Attribute 'VEF' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Venezuelan bolivar fuerte. |
||||||||||||||
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Notes |
The derived units defined for usage in the CIM. In some cases, the derived unit is equal to an SI unit. Whenever possible, the standard derived symbol is used instead of the formula for the derived unit. For example, the unit symbol Farad is defined as "F" instead of "CPerV". In cases where a standard symbol does not exist for a derived unit, the formula for the unit is used as the unit symbol. For example, density does not have a standard symbol and so it is represented as "kgPerm3". With the exception of the "kg", which is an SI unit, the unit symbols do not contain multipliers and therefore represent the base derived unit to which a multiplier can be applied as a whole. Every unit symbol is treated as an unparseable text as if it were a single-letter symbol. The meaning of each unit symbol is defined by the accompanying descriptive text and not by the text contents of the unit symbol.To allow the widest possible range of serializations without requiring special character handling, several substitutions are made which deviate from the format described in IEC 80000-1. The division symbol "/" is replaced by the letters "Per". Exponents are written in plain text after the unit as "m3" instead of being formatted as "m" with a superscript of 3 or introducing a symbol as in "m^3". The degree symbol "°" is replaced with the letters "deg". Any clarification of the meaning for a substitution is included in the description for the unit symbol.Non-SI units are included in list of unit symbols to allow sources of data to be correctly labelled with their non-SI units (for example, a GPS sensor that is reporting numbers that represent feet instead of meters). This allows software to use the unit symbol information correctly convert and scale the raw data of those sources into SI-based units. The integer values are used for harmonization with IEC 61850. |
The derived units defined for usage in the CIM. In some cases, the derived unit is equal to an SI unit. Whenever possible, the standard derived symbol is used instead of the formula for the derived unit. For example, the unit symbol Farad is defined as "F" instead of "CPerV". In cases where a standard symbol does not exist for a derived unit, the formula for the unit is used as the unit symbol. For example, density does not have a standard symbol and so it is represented as "kgPerm^3". With the exception of the "kg", which is an SI unit, the unit symbols do not contain multipliers and therefore represent the base derived unit to which a multiplier can be applied as a whole. Every unit symbol is treated as an unparseable text as if it were a single-letter symbol. The meaning of each unit symbol is defined by the accompanying descriptive text and not by the text contents of the unit symbol.To allow the widest possible range of serializations without requiring special character handling, several substitutions are made which deviate from the format described in IEC 80000-1. The division symbol "/" is replaced by the letters "Per". Exponents are written in plain text after the unit as "m^3". The letters "deg" are used instead of the degree symbol. Any clarification of the meaning for a substitution is included in the description for the unit symbol.Non-SI units are included in list of unit symbols to allow sources of data to be correctly labelled with their non-SI units (for example, a GPS sensor that is reporting numbers that represent feet instead of meters). This allows software to use the unit symbol information correctly convert and scale the raw data of those sources into SI-based units. The integer values are used for harmonization with IEC 61850. |
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
A2 |
Attribute 'A2' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Amperes squared (A²). |
A2 |
Attribute 'A2' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Amperes squared (A^2). |
||||||||||||||
|
A2s |
Attribute 'A2s' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Ampere squared time in square amperes (A²s). |
A2s |
Attribute 'A2s' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Ampere squared time in square amperes (A^2*s). |
||||||||||||||
|
APerA |
Attribute 'APerA' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Current, ratio of amperages. Note: Users may need to supply a prefix such as ‘m’ to show rates such as ‘mA/A’. |
APerA |
Attribute 'APerA' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Current, ratio of amperages. |
||||||||||||||
|
APerm |
Attribute 'APerm' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
A/m, magnetic field strength, amperes per metre. |
APerm |
Attribute 'APerm' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Amperes per metre (A/m), magnetic field strength. |
||||||||||||||
|
As |
Attribute 'As' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Ampere seconds (A·s). |
As |
Attribute 'As' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Ampere seconds (A*s). |
||||||||||||||
|
C |
Attribute 'C' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Electric charge in coulombs (A·s). |
C |
Attribute 'C' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Electric charge in coulombs (A*s). |
||||||||||||||
|
G |
Attribute 'G' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Magnetic flux density, gausses (1 G = 10-4 T). |
G |
Attribute 'G' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Magnetic flux density, gausses (1 G = 10e-4*T). |
||||||||||||||
|
HzPerHz |
Attribute 'HzPerHz' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Frequency, rate of frequency change. Note: Users may need to supply a prefix such as ‘m’ to show rates such as ‘mHz/Hz’. |
HzPerHz |
Attribute 'HzPerHz' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Frequency, rate of frequency change. |
||||||||||||||
|
J |
Attribute 'J' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Energy in joules (N·m = C·V = W·s). |
J |
Attribute 'J' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Energy in joules (N*m = C*V = W*s). |
||||||||||||||
|
JPerkg |
Attribute 'JPerkg' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Specific energy, Joules / kg. |
JPerkg |
Attribute 'JPerkg' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Specific energy, J/kg. |
||||||||||||||
|
N |
Attribute 'N' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Force in newtons (kg·m/s²). |
N |
Attribute 'N' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Force in newtons (kg*m/s^2). |
||||||||||||||
|
Oe |
Attribute 'Oe' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Magnetic field in oersteds, (1 Oe = (103/4p) A/m). |
Oe |
Attribute 'Oe' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Magnetic field in oersteds, (1 Oe = (10^3/(4*pi)) A/m = 79.57747 A/m). |
||||||||||||||
|
Pa |
Attribute 'Pa' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Pressure in pascals (N/m²). Note: the absolute or relative measurement of pressure is implied with this entry. See below for more explicit forms. |
Pa |
Attribute 'Pa' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Pressure in pascals (N/m^2). Note: the absolute or relative measurement of pressure is implied with this entry. See below for more explicit forms. |
||||||||||||||
|
T |
Attribute 'T' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Magnetic flux density in teslas (Wb/m2). |
T |
Attribute 'T' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Magnetic flux density in teslas (Wb/m^2). |
||||||||||||||
|
V2 |
Attribute 'V2' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Volt squared (W²/A²). |
V2 |
Attribute 'V2' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Volt squared (W^2/A^2). |
||||||||||||||
|
VAr |
Attribute 'VAr' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Reactive power in volt amperes reactive. The “reactive” or “imaginary” component of electrical power (VIsin(phi)). (See also real power and apparent power).Note: Different meter designs use different methods to arrive at their results. Some meters may compute reactive power as an arithmetic value, while others compute the value vectorially. The data consumer should determine the method in use and the suitability of the measurement for the intended purpose. |
VAr |
Attribute 'VAr' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Reactive power in volt amperes reactive. The "reactive" or "imaginary" component of electrical power (V*I*sin(phi)). (See also real power and apparent power).Note: Different meter designs use different methods to arrive at their results. Some meters may compute reactive power as an arithmetic value, while others compute the value vectorially. The data consumer should determine the method in use and the suitability of the measurement for the intended purpose. |
||||||||||||||
|
VPerV |
Attribute 'VPerV' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Voltage, ratio of voltages. Note: Users may need to supply a prefix such as ‘m’ to show rates such as ‘mV/V’. |
VPerV |
Attribute 'VPerV' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Voltage, ratio of voltages. |
||||||||||||||
|
W |
Attribute 'W' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Real power in watts (J/s). Electrical power may have real and reactive components. The real portion of electrical power (I²R or VIcos(phi)), is expressed in Watts. See also apparent power and reactive power. |
W |
Attribute 'W' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Real power in watts (J/s). Electrical power may have real and reactive components. The real portion of electrical power (I^2*R or V*I*cos(phi)), is expressed in Watts. See also apparent power and reactive power. |
||||||||||||||
|
WPerW |
Attribute 'WPerW' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Signal Strength, ratio of power. Note: Users may need to supply a prefix such as ‘m’ to show rates such as ‘mW/W’. |
WPerW |
Attribute 'WPerW' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Signal Strength, ratio of power. |
||||||||||||||
|
Wb |
Attribute 'Wb' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Magnetic flux in webers (V·s). |
Wb |
Attribute 'Wb' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Magnetic flux in webers (V*s). |
||||||||||||||
|
count |
Attribute 'count' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Amount of substance, Counter value. |
count |
Attribute 'count' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Amount of substance, counter value. |
||||||||||||||
|
dB |
Attribute 'dB' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Sound pressure level in decibels. Note: multiplier “d” is included in this unit symbol for compatibility with IEC 61850-7-3. |
dB |
Attribute 'dB' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Sound pressure level in decibels. Note: multiplier "d" is included in this unit symbol for compatibility with IEC 61850-7-3. |
||||||||||||||
|
dBm |
Attribute 'dBm' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Power level (logarithmic ratio of signal strength , Bel-mW), normalized to 1mW. Note: multiplier “d” is included in this unit symbol for compatibility with IEC 61850-7-3. |
dBm |
Attribute 'dBm' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Power level (logarithmic ratio of signal strength , Bel-mW), normalized to 1 mW. Note: multiplier "d" is included in this unit symbol for compatibility with IEC 61850-7-3. |
||||||||||||||
|
degC |
Attribute 'degC' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Relative temperature in degrees Celsius.In the SI unit system the symbol is °C. Electric charge is measured in coulomb that has the unit symbol C. To distinguish degree Celsius from coulomb the symbol used in the UML is degC. The reason for not using °C is that the special character ° is difficult to manage in software. |
degC |
Attribute 'degC' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Relative temperature in degrees Celsius (degC). |
||||||||||||||
|
gPerg |
Attribute 'gPerg' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Concentration, The ratio of the mass of a solute divided by the mass of the solution. Note: Users may need use a prefix such a ‘µ’ to express a quantity such as ‘µg/g’. |
gPerg |
Attribute 'gPerg' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Concentration, The ratio of the mass of a solute divided by the mass of the solution. |
||||||||||||||
|
gal |
Attribute 'gal' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Volume in gallons, US gallon (1 gal = 231 in3 = 128 fl ounce). |
gal |
Attribute 'gal' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Volume in gallons, US gallon (1 gal = 231 in^3 = 128 fl ounce). |
||||||||||||||
|
kat |
Attribute 'kat' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Catalytic activity, katal = mol / s. |
kat |
Attribute 'kat' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Catalytic activity, katal = mol/s. |
||||||||||||||
|
kg |
Attribute 'kg' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Mass in kilograms. Note: multiplier “k” is included in this unit symbol for compatibility with IEC 61850-7-3. |
kg |
Attribute 'kg' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Mass in kilograms. Note: multiplier "k" is included in this unit symbol for compatibility with IEC 61850-7-3. |
||||||||||||||
|
kgPerJ |
Attribute 'kgPerJ' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Weight per energy in kilograms per joule (kg/J). Note: multiplier “k” is included in this unit symbol for compatibility with IEC 61850-7-3. |
kgPerJ |
Attribute 'kgPerJ' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Weight per energy in kilograms per joule (kg/J). Note: multiplier "k" is included in this unit symbol for compatibility with IEC 61850-7-3. |
||||||||||||||
|
kgPerm |
Attribute 'kgPerm' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Mass per length in kilogram/metres (kg/m). Note: multiplier “k” is included in this unit symbol for compatibility with mass datatype. |
kgPerm |
Attribute 'kgPerm' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Mass per length in kilogram/metres (kg/m). Note: multiplier "k" is included in this unit symbol for compatibility with mass datatype. |
||||||||||||||
|
kgPerm3 |
Attribute 'kgPerm3' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Density in kilogram/cubic metres (kg/m³). Note: multiplier “k” is included in this unit symbol for compatibility with IEC 61850-7-3. |
kgPerm3 |
Attribute 'kgPerm3' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Density in kilogram/cubic metres (kg/m^3). Note: multiplier "k" is included in this unit symbol for compatibility with IEC 61850-7-3. |
||||||||||||||
|
kgm |
Attribute 'kgm' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Moment of mass in kilogram metres (kg·m) (first moment of mass). Note: multiplier “k” is included in this unit symbol for compatibility with IEC 61850-7-3. |
kgm |
Attribute 'kgm' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Moment of mass in kilogram metres (kg*m) (first moment of mass). Note: multiplier "k" is included in this unit symbol for compatibility with IEC 61850-7-3. |
||||||||||||||
|
kgm2 |
Attribute 'kgm2' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Moment of mass in kilogram square metres (kg·m²) (Second moment of mass, commonly called the moment of inertia). Note: multiplier “k” is included in this unit symbol for compatibility with IEC 61850-7-3. |
kgm2 |
Attribute 'kgm2' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Moment of mass in kilogram square metres (kg*m^2) (Second moment of mass, commonly called the moment of inertia). Note: multiplier "k" is included in this unit symbol for compatibility with IEC 61850-7-3. |
||||||||||||||
|
l |
Attribute 'l' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Volume in litres, litre = dm3 = m3/1000. |
l |
Attribute 'l' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Volume in litres, litre = dm^3 = m^3/1000. |
||||||||||||||
|
lPerl |
Attribute 'lPerl' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Concentration, The ratio of the volume of a solute divided by the volume of the solution. Note: Users may need use a prefix such a ‘µ’ to express a quantity such as ‘µL/L’. |
lPerl |
Attribute 'lPerl' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Concentration, The ratio of the volume of a solute divided by the volume of the solution. |
||||||||||||||
|
lm |
Attribute 'lm' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Luminous flux in lumens (cd·sr). |
lm |
Attribute 'lm' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Luminous flux in lumens (cd*sr). |
||||||||||||||
|
lx |
Attribute 'lx' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Illuminance in lux (lm/m²). |
lx |
Attribute 'lx' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Illuminance in lux (lm/m^2). |
||||||||||||||
|
m2 |
Attribute 'm2' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Area in square metres (m²). |
m2 |
Attribute 'm2' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Area in square metres (m^2). |
||||||||||||||
|
m2Pers |
Attribute 'm2Pers' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Viscosity in square metres / second (m²/s). |
m2Pers |
Attribute 'm2Pers' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Viscosity in square metres/second (m^2/s). |
||||||||||||||
|
m3 |
Attribute 'm3' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Volume in cubic metres (m³). |
m3 |
Attribute 'm3' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Volume in cubic metres (m^3). |
||||||||||||||
|
m3Pers |
Attribute 'm3Pers' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Volumetric flow rate in cubic metres per second (m³/s). |
m3Pers |
Attribute 'm3Pers' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Volumetric flow rate in cubic metres per second (m^3/s). |
||||||||||||||
|
mPerm3 |
Attribute 'mPerm3' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Fuel efficiency in metres per cubic metres (m/m³). |
mPerm3 |
Attribute 'mPerm3' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Fuel efficiency in metres per cubic metres (m/m^3). |
||||||||||||||
|
mPers2 |
Attribute 'mPers2' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Acceleration in metres per second squared (m/s²). |
mPers2 |
Attribute 'mPers2' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Acceleration in metres per second squared (m/s^2). |
||||||||||||||
|
molPerm3 |
Attribute 'molPerm3' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Concentration, The amount of substance concentration, (c), the amount of solvent in moles divided by the volume of solution in m³. |
molPerm3 |
Attribute 'molPerm3' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Concentration, The amount of substance concentration, (c), the amount of solvent in moles divided by the volume of solution in m^3. |
||||||||||||||
|
sPers |
Attribute 'sPers' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Time, Ratio of time. Note: Users may need to supply a prefix such as ‘µ’ to show rates such as ‘µs/s’. |
sPers |
Attribute 'sPers' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Time, Ratio of time. |
||||||||||||||
|
sr |
Attribute 'sr' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Solid angle in steradians (m2/m2). |
sr |
Attribute 'sr' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Solid angle in steradians (m^2/m^2). |
||||||||||||||
|
tonne |
Attribute 'tonne' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Mass in tons, “tonne” or “metric ton” (1000 kg = 1 Mg). |
tonne |
Attribute 'tonne' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Mass in tons, "tonne" or "metric ton" (1000 kg = 1 Mg). |
||||||||||||||
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 11:47:48 |
2024-12-06 19:44:49 |
|
Name |
EnumeratedUnitDatatypes |
DocEnumeratedUnitDatatypes |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 11:50:21 |
2024-12-06 19:44:34 |
|
Name |
CombinedElectricalDatatypes |
DocCombinedElectricalDatatypes |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 11:47:26 |
2024-12-06 19:44:45 |
|
Name |
ElectricityDatatypes |
DocElectricityDatatypes |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 11:49:28 |
2024-12-06 19:44:58 |
|
Name |
MonetaryDatatypes |
DocMonetaryDatatypes |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-06-05 21:44:56 |
2024-12-06 19:44:39 |
|
Name |
BasicDatatypes |
DocBasicDatatypes |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 11:49:47 |
2024-12-06 19:45:08 |
|
Name |
TimeDatatypes |
DocTimeDatatypes |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-02-04 06:39:22 |
2024-12-06 19:44:54 |
|
Name |
GeneralDatatypes |
DocGeneralDatatypes |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Changed Classes:
Links:
Association:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Alias |
| |
|
Direction |
|
Unspecified |
|
IsLeaf |
|
false |
|
IsRoot |
|
false |
|
Notes |
| |
|
Source Linked Feature |
| |
|
Stereotype |
| |
|
Target Linked Feature |
| |
|
Type |
|
Association |
|
Baseline Model |
|
Destination Model |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Source Role End Changes |
|
Target Role End Changes |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Association:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Alias |
| |
|
Direction |
|
Unspecified |
|
IsLeaf |
|
false |
|
IsRoot |
|
false |
|
Notes |
| |
|
Source Linked Feature |
| |
|
Stereotype |
| |
|
Target Linked Feature |
| |
|
Type |
|
Association |
|
Baseline Model |
|
Destination Model |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Source Role End Changes |
|
Target Role End Changes |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
phaseSide1 |
Attribute 'phaseSide1' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Phase of this SwitchPhase on the side with terminal sequence number equal to 1. Should be a phase contained in that terminal’s phases attribute. |
phaseSide1 |
Attribute 'phaseSide1' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Phase of this SwitchPhase on the side with terminal sequence number equal to 1. Should be a phase contained in that terminal's phases attribute. |
||||||||||||||
|
phaseSide2 |
Attribute 'phaseSide2' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Phase of this SwitchPhase on the side with terminal sequence number equal to 2. Should be a phase contained in that terminal’s Terminal.phases attribute. |
phaseSide2 |
Attribute 'phaseSide2' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Phase of this SwitchPhase on the side with terminal sequence number equal to 2. Should be a phase contained in that terminal's Terminal.phases attribute. |
||||||||||||||
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
xMax |
Attribute 'xMax' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
The reactance depends on the tap position according to a "u" shaped curve. The maximum reactance (xMax) appears at the low and high tap positions. Depending on the “u” curve the attribute can be either higher or lower than PowerTransformerEnd.x. |
xMax |
Attribute 'xMax' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
The reactance depends on the tap position according to a "u" shaped curve. The maximum reactance (xMax) appears at the low and high tap positions. Depending on the "u" curve the attribute can be either higher or lower than PowerTransformerEnd.x. |
||||||||||||||
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
fromPhase |
Attribute 'fromPhase' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Refer to the class description. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
toPhase |
Attribute 'toPhase' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Refer to the class description. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Notes |
This class represents the external network and is used for IEC 60909 calculations. It is only used if EquivalentInjection cannot provide the details required by IEC 60909 on short circuit equivalent of an external network. |
This class represents the external network for use in power flow and short-circuit calculations.In the power flow domain the external network is modelled as a power injection with power limits and a power-frequency bias. For short-circuit calculations the external network is modelled as the “network feeders” element defined in section 6.2 of IEC60909-0:2016. Boolean flag ikSecond allows short-circuit calculations using the superposition method to detect that the maximum and minimum initial symmetrical short-circuit currents have to be corrected for the fact that they were calculated according the IEC60909-0 method. |
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ikSecond |
Attribute 'ikSecond' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Indicates whether initial symmetrical short-circuit current and power have been calculated according to IEC (Ik"). Used only if short circuit calculations are done according to superposition method. |
ikSecond |
Attribute 'ikSecond' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Indicates whether the maximum and minimum initial symmetrical short-circuit currents (Ik” max and Ik” min) have been calculated according to the IEC 60909-0 method. Is only used in short-circuit calculations done according to the superposition method. |
||||||||||||||
|
maxInitialSymShCCurrent |
Attribute 'maxInitialSymShCCurrent' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Maximum initial symmetrical short-circuit currents (Ik" max) in A (Ik" = Sk"/(SQRT(3) Un)). Used for short circuit data exchange according to IEC 60909. |
maxInitialSymShCCurrent |
Attribute 'maxInitialSymShCCurrent' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Maximum initial symmetrical short-circuit current (Ik" max) in A. Ik” is defined in clause 3.5 of IEC 60909-0:2016. |
||||||||||||||
|
maxQ |
Attribute 'maxQ' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Maximum reactive power limit. It is used for modelling of infeed for load flow exchange and not for short circuit modelling. |
maxQ |
Attribute 'maxQ' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Maximum reactive power of the injection. Used for modelling of infeed for load flow exchange. Not used for short-circuit modelling. |
||||||||||||||
|
maxR0ToX0Ratio |
Attribute 'maxR0ToX0Ratio' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Maximum ratio of zero sequence resistance of Network Feeder to its zero sequence reactance (R(0)/X(0) max). Used for short circuit data exchange according to IEC 60909. |
maxR0ToX0Ratio |
Attribute 'maxR0ToX0Ratio' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Maximum ratio of zero sequence resistance to zero sequence reactance (R(0)/X(0) max). R0 and X0 are the real and imaginary parts of the zero sequence short-circuit impedance Z0 defined in clause 3.19.3 of IEC 60909-0:2016. |
||||||||||||||
|
maxR1ToX1Ratio |
Attribute 'maxR1ToX1Ratio' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Maximum ratio of positive sequence resistance of Network Feeder to its positive sequence reactance (R(1)/X(1) max). Used for short circuit data exchange according to IEC 60909. |
maxR1ToX1Ratio |
Attribute 'maxR1ToX1Ratio' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Maximum ratio of positive sequence resistance to positive sequence reactance (R(1)/X(1) max). R1 and X1 are the real and imaginary parts of the positive sequence short-circuit impedance Z1 defined in clause 3.19.1 of IEC 60909-0:2016. |
||||||||||||||
|
maxZ0ToZ1Ratio |
Attribute 'maxZ0ToZ1Ratio' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Maximum ratio of zero sequence impedance to its positive sequence impedance (Z(0)/Z(1) max). Used for short circuit data exchange according to IEC 60909. |
maxZ0ToZ1Ratio |
Attribute 'maxZ0ToZ1Ratio' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Maximum ratio of zero sequence impedance to its positive sequence impedance (Z(0)/Z(1) max). Z0 is the zero sequence short-circuit impedance defined in clause 3.19.3 of IEC 60909-0:2016. Z1 is the positive sequence short-circuit impedance defined in clause 3.19.1 of IEC 60909-0:2016. |
||||||||||||||
|
minInitialSymShCCurrent |
Attribute 'minInitialSymShCCurrent' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Minimum initial symmetrical short-circuit currents (Ik" min) in A (Ik" = Sk"/(SQRT(3) Un)). Used for short circuit data exchange according to IEC 60909. |
minInitialSymShCCurrent |
Attribute 'minInitialSymShCCurrent' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Minimum initial symmetrical short-circuit current (Ik" min) in A. Ik” is defined in clause 3.5 of IEC 60909-0:2016. |
||||||||||||||
|
minQ |
Attribute 'minQ' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Minimum reactive power limit. It is used for modelling of infeed for load flow exchange and not for short circuit modelling. |
minQ |
Attribute 'minQ' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Minimum reactive power of the injection. Used for modelling of infeed for load flow exchange. Not used for short-circuit modelling. |
||||||||||||||
|
minR0ToX0Ratio |
Attribute 'minR0ToX0Ratio' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Indicates whether initial symmetrical short-circuit current and power have been calculated according to IEC (Ik"). Used for short circuit data exchange according to IEC 60909. |
minR0ToX0Ratio |
Attribute 'minR0ToX0Ratio' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Minimum ratio of zero sequence resistance to zero sequence reactance (R(0)/X(0) min). R0 and X0 are the real and imaginary parts of the zero sequence short-circuit impedance Z0 defined in clause 3.19.3 of IEC 60909-0:2016. |
||||||||||||||
|
minR1ToX1Ratio |
Attribute 'minR1ToX1Ratio' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Minimum ratio of positive sequence resistance of Network Feeder to its positive sequence reactance (R(1)/X(1) min). Used for short circuit data exchange according to IEC 60909. |
minR1ToX1Ratio |
Attribute 'minR1ToX1Ratio' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Minimum ratio of positive sequence resistance to positive sequence reactance (R(1)/X(1) min). R1 and X1 are the real and imaginary parts of the positive sequence short-circuit impedance Z1 defined in clause 3.19.1 of IEC 60909-0:2016. |
||||||||||||||
|
minZ0ToZ1Ratio |
Attribute 'minZ0ToZ1Ratio' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Minimum ratio of zero sequence impedance to its positive sequence impedance (Z(0)/Z(1) min). Used for short circuit data exchange according to IEC 60909. |
minZ0ToZ1Ratio |
Attribute 'minZ0ToZ1Ratio' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Minimum ratio of zero sequence impedance to its positive sequence impedance (Z(0)/Z(1) min). Z0 is the zero sequence short-circuit impedance defined in clause 3.19.3 of IEC 60909-0:2016. Z1 is the positive sequence short-circuit impedance defined in clause 3.19.1 of IEC 60909-0:2016. |
||||||||||||||
|
voltageFactor |
Attribute 'voltageFactor' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Voltage factor in pu, which was used to calculate short-circuit current Ik" and power Sk". Used only if short circuit calculations are done according to superposition method. |
voltageFactor |
Attribute 'voltageFactor' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Voltage factor (c) in pu which has been used to calculate the maximum and minimum initial symmetrical short-circuit currents (Ik” max and Ik” min). Is only used in short-circuit calculations done according to the superposition method. The voltage factor is defined in clause 3.15 of IEC 60909-0:2016. |
||||||||||||||
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
xMax |
Attribute 'xMax' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
The reactance depends on the tap position according to a "u" shaped curve. The maximum reactance (xMax) appears at the low and high tap positions. Depending on the “u” curve the attribute can be either higher or lower than PowerTransformerEnd.x. |
xMax |
Attribute 'xMax' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
The reactance depends on the tap position according to a "u" shaped curve. The maximum reactance (xMax) appears at the low and high tap positions. Depending on the "u" curve the attribute can be either higher or lower than PowerTransformerEnd.x. |
||||||||||||||
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:00:00 |
2024-12-06 19:46:19 |
|
Name |
VoltageControl |
DocVoltageControl |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2023-10-08 08:19:31 |
2024-12-06 19:45:41 |
|
Name |
LineModel |
DocLineModel |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:00:00 |
2024-12-06 19:46:22 |
|
Name |
WiresPhaseModel |
DocWiresPhaseModel |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 11:54:01 |
2024-12-06 19:45:31 |
|
Name |
EarthFaultCompensator |
DocEarthFaultCompensator |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 11:55:55 |
2024-12-06 19:45:45 |
|
Name |
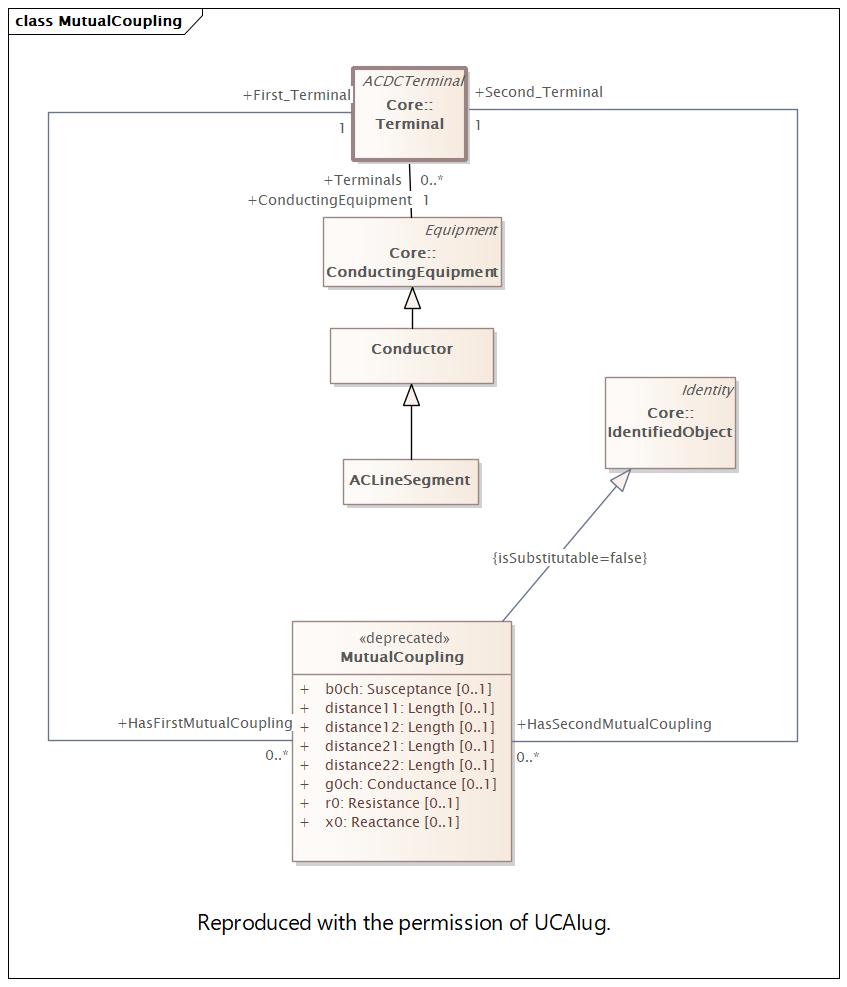
MutualCoupling |
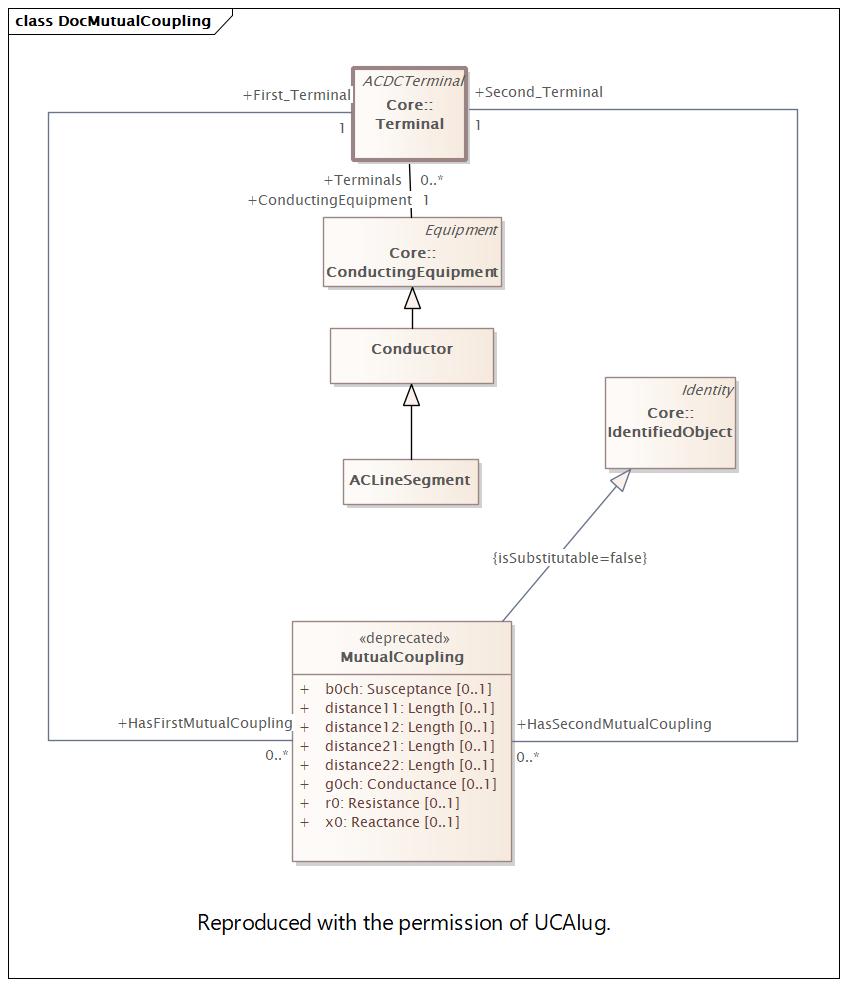
DocMutualCoupling |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 11:56:50 |
2024-12-06 19:45:52 |
|
Name |
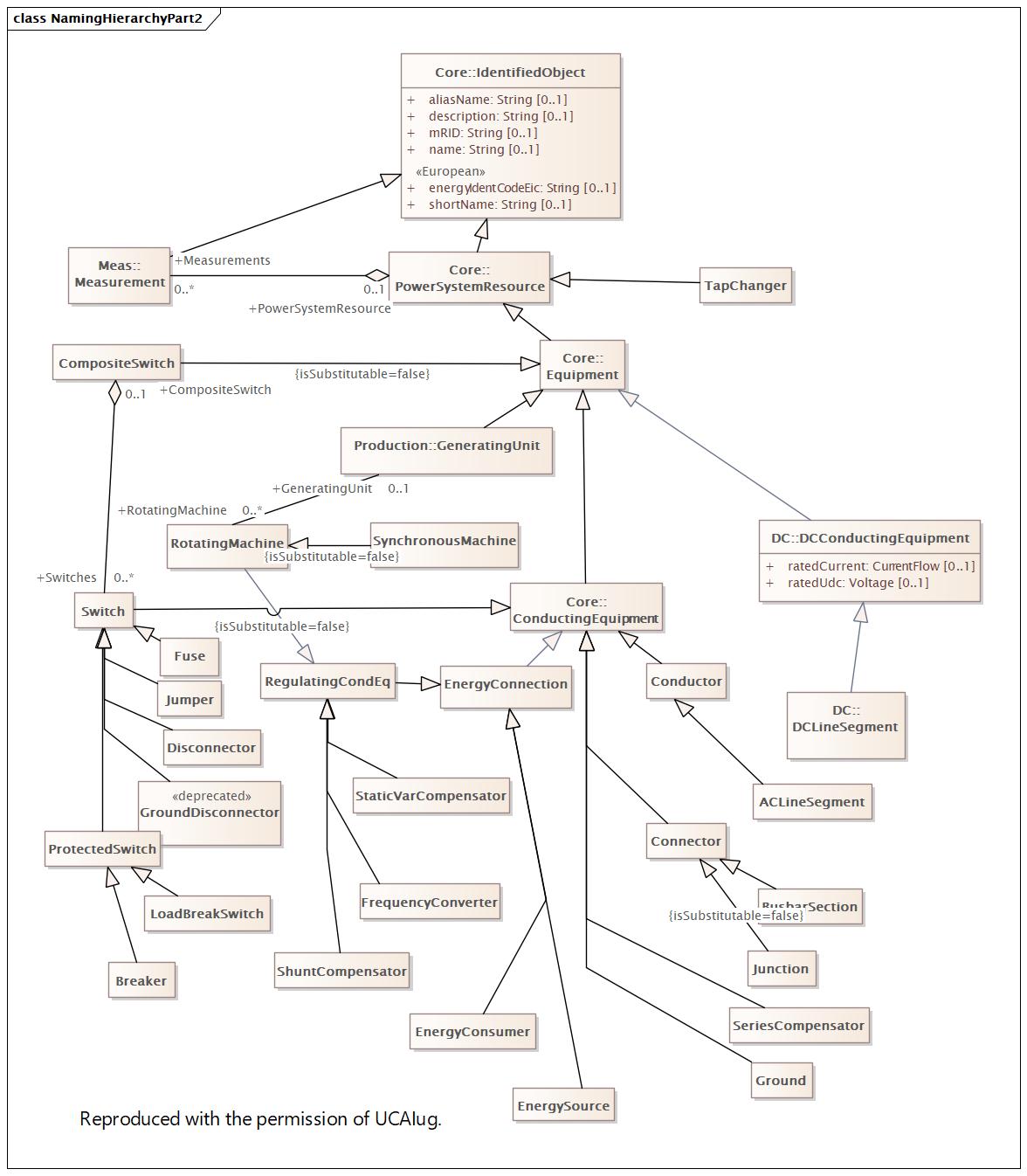
NamingHierarchyPart2 |
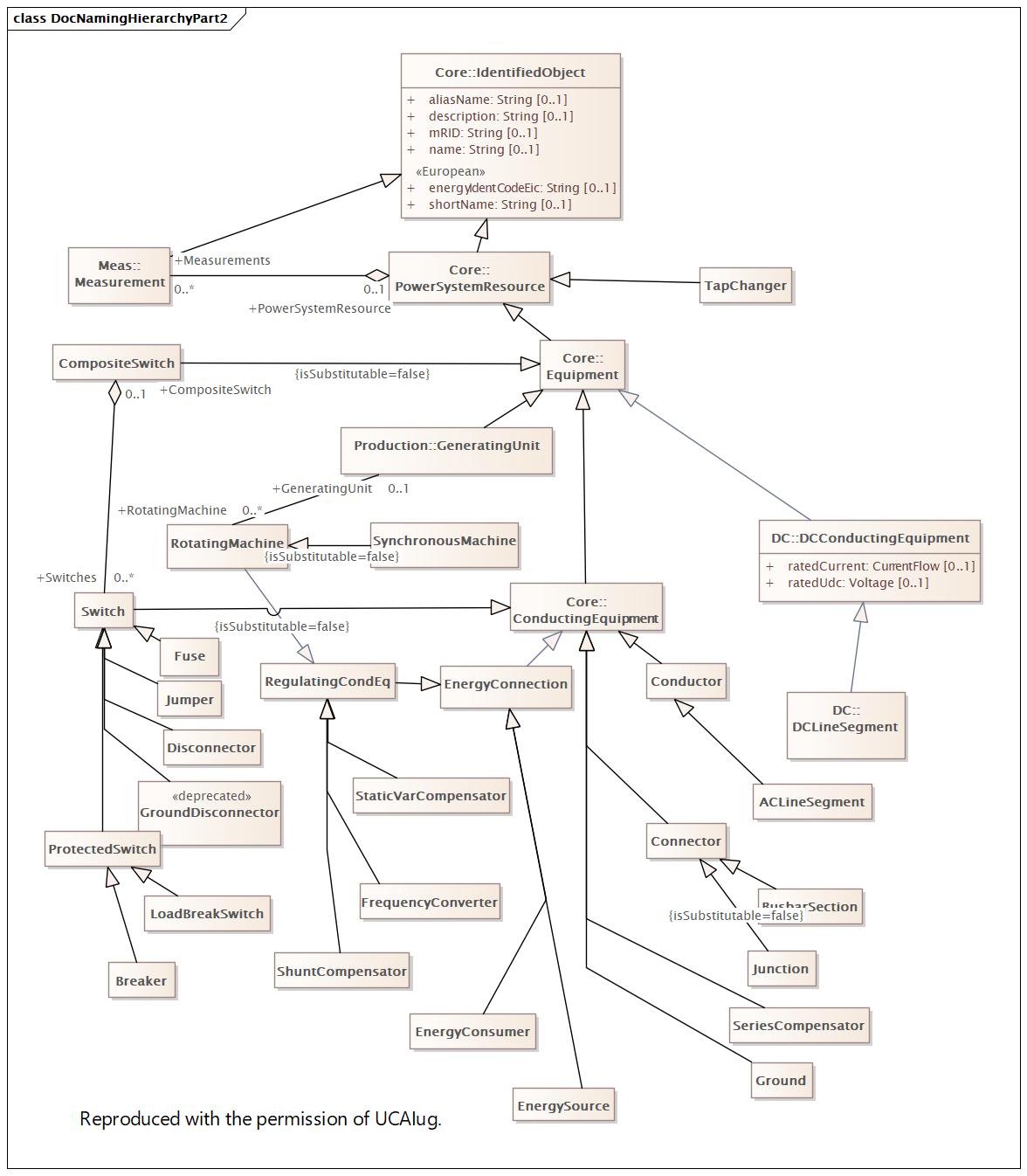
DocNamingHierarchyPart2 |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-06-04 21:06:59 |
2024-12-06 19:46:11 |
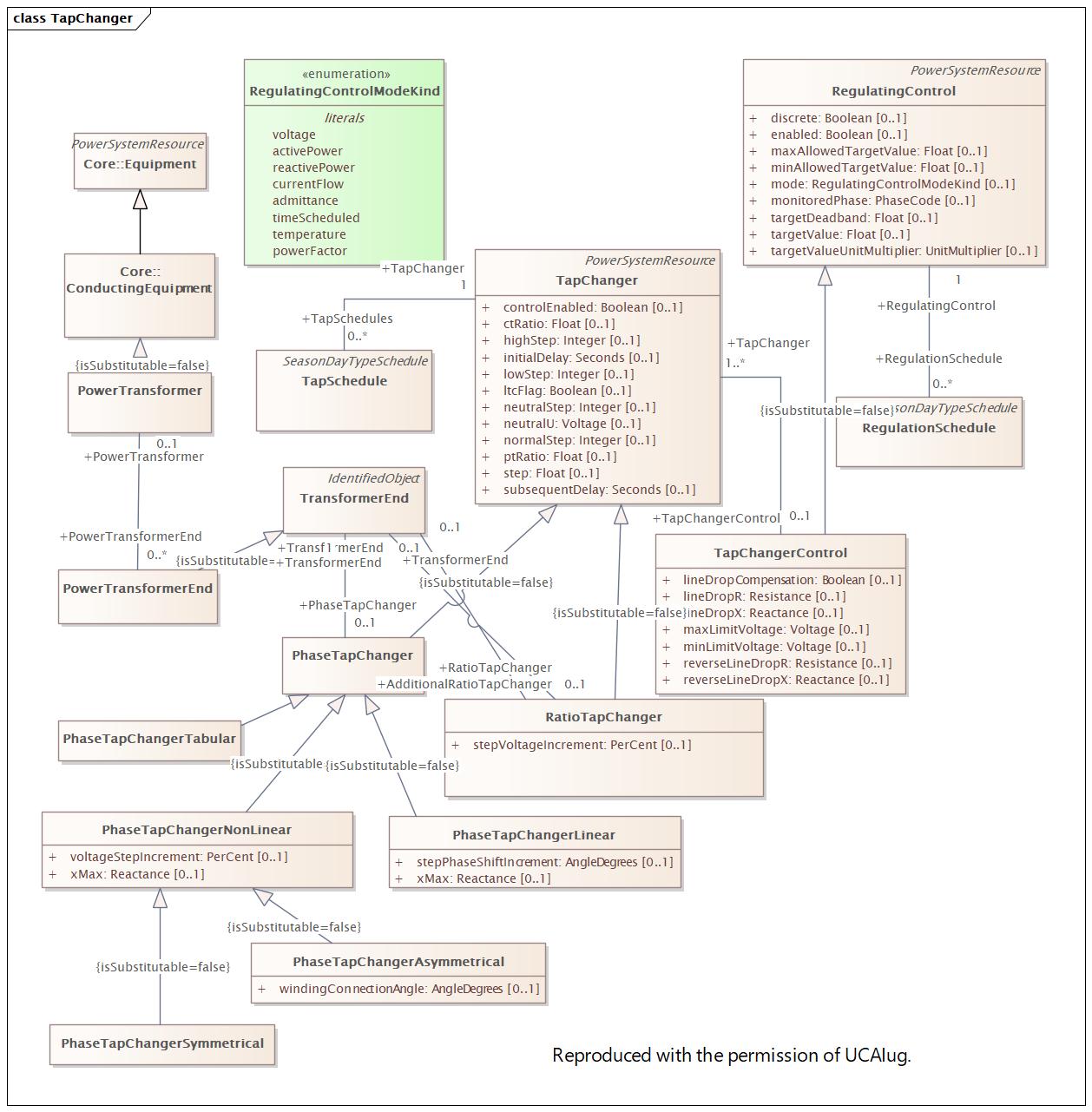
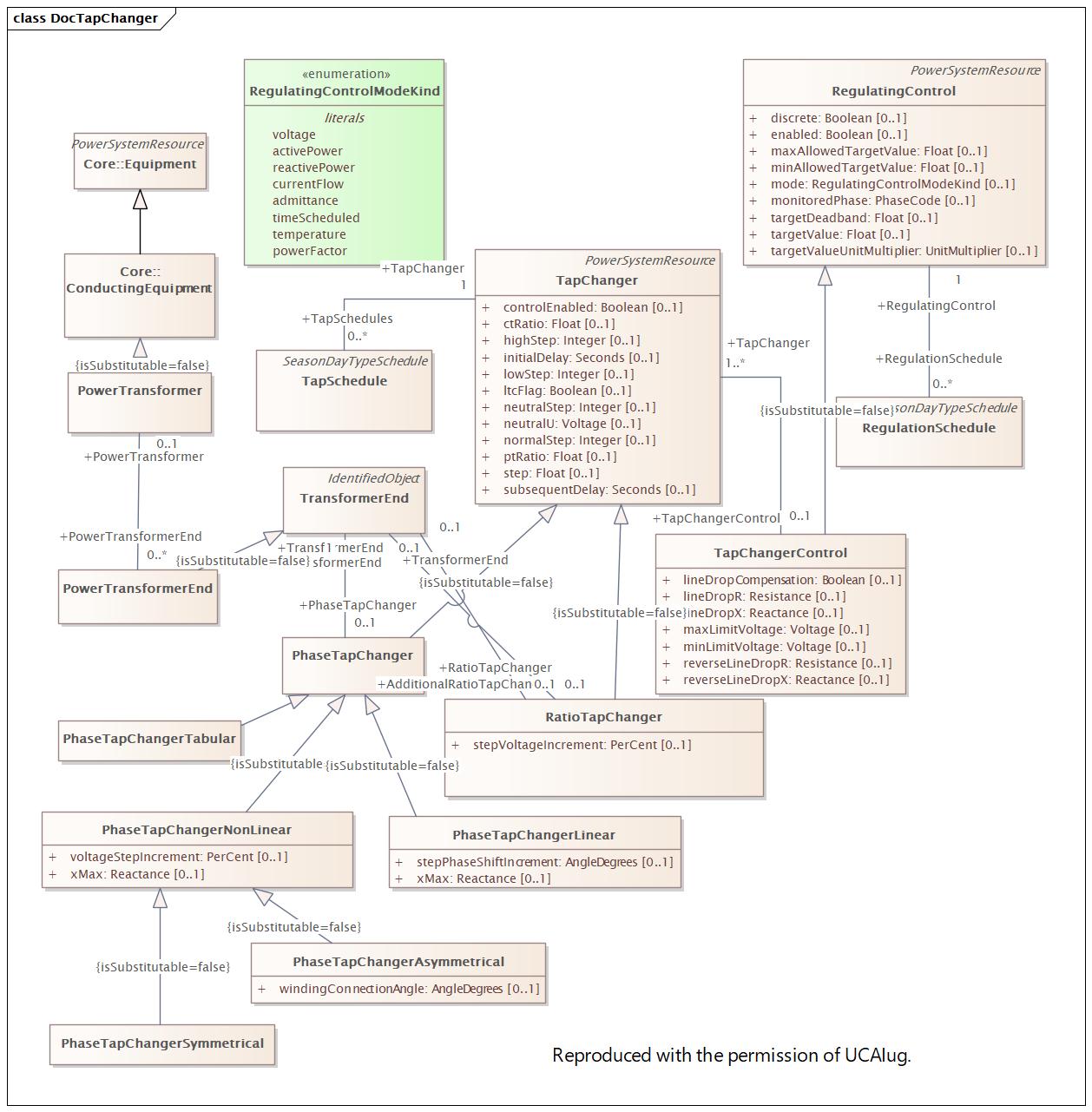
|
Name |
TapChanger |
DocTapChanger |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
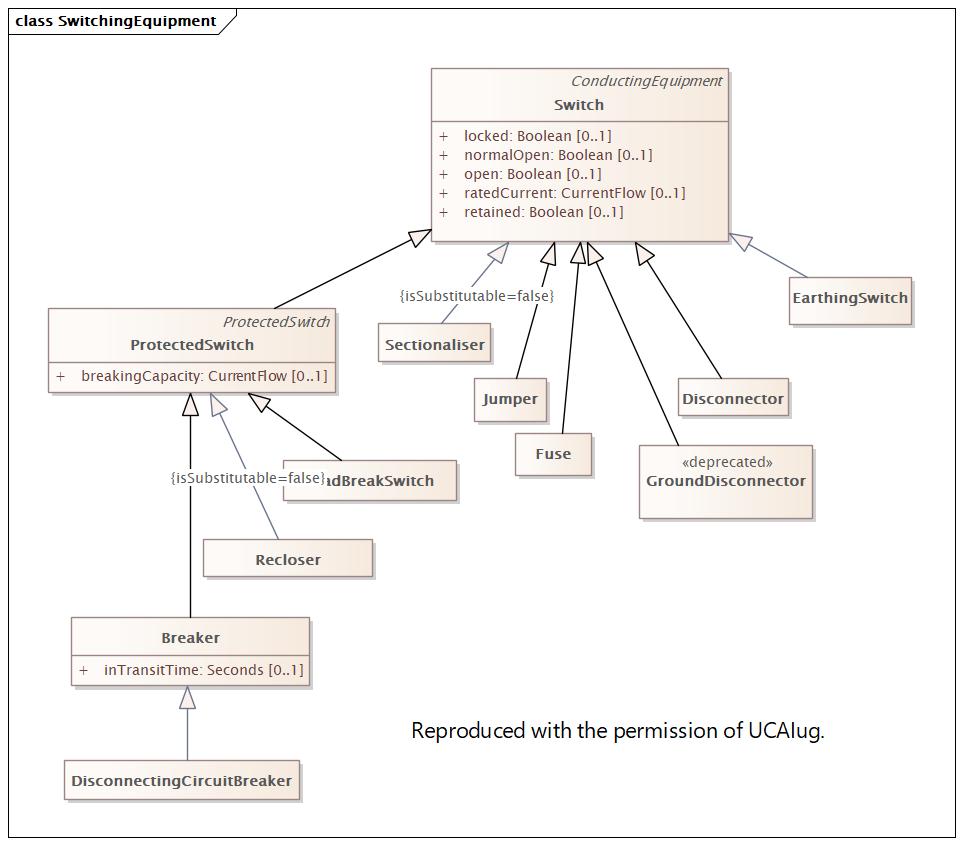
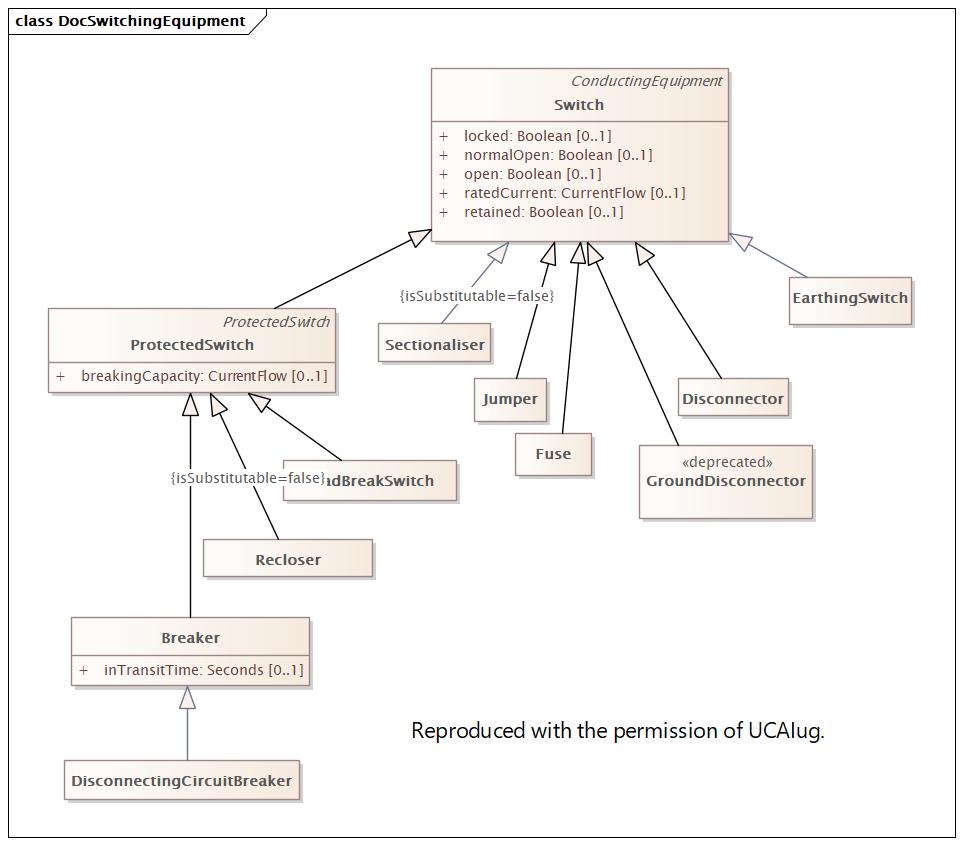
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-18 03:53:58 |
2024-12-06 19:46:07 |
|
Name |
SwitchingEquipment |
DocSwitchingEquipment |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 11:54:39 |
2024-12-06 19:45:17 |
|
Name |
CutsAndJumpers |
DocCutsAndJumpers |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2023-02-19 08:04:55 |
2024-12-06 19:46:04 |
|
Name |
ShuntCompensator |
DocShuntCompensator |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:00:00 |
2024-12-06 19:46:00 |
|
Name |
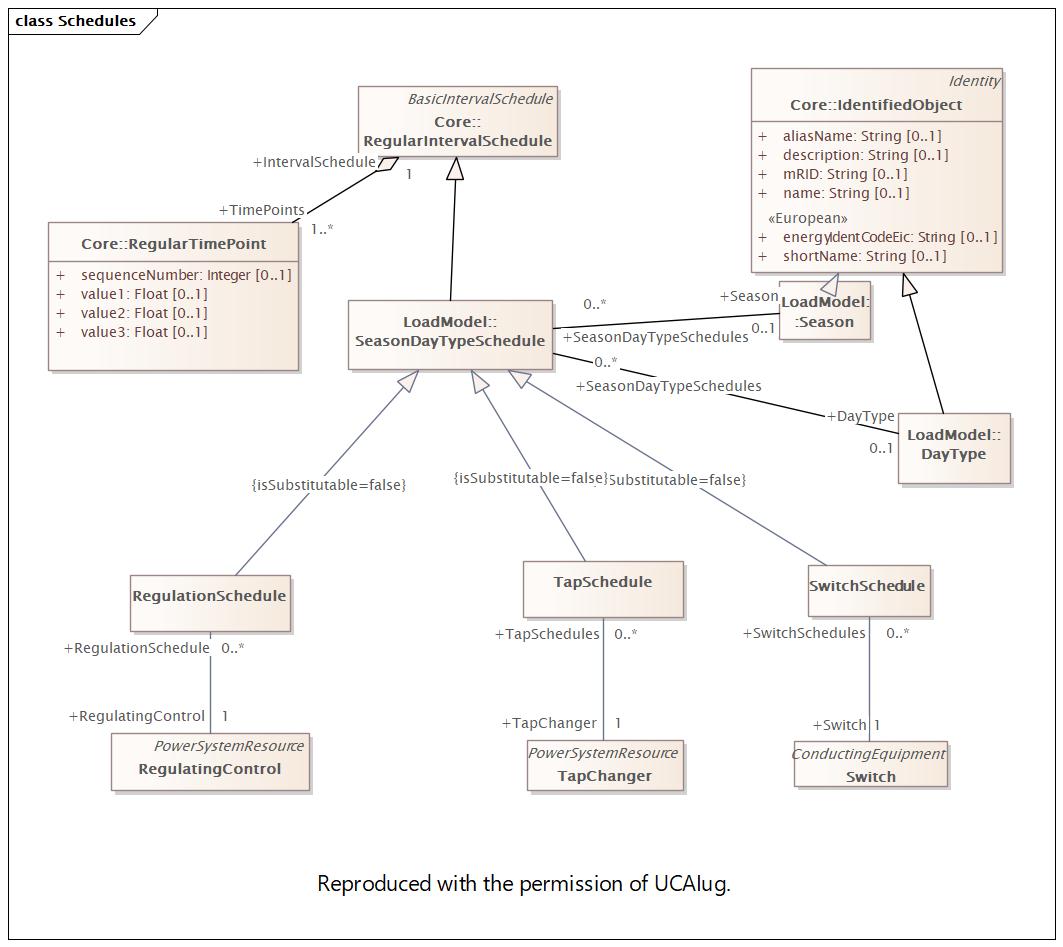
Schedules |
DocSchedules |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 11:57:14 |
2024-12-06 19:45:49 |
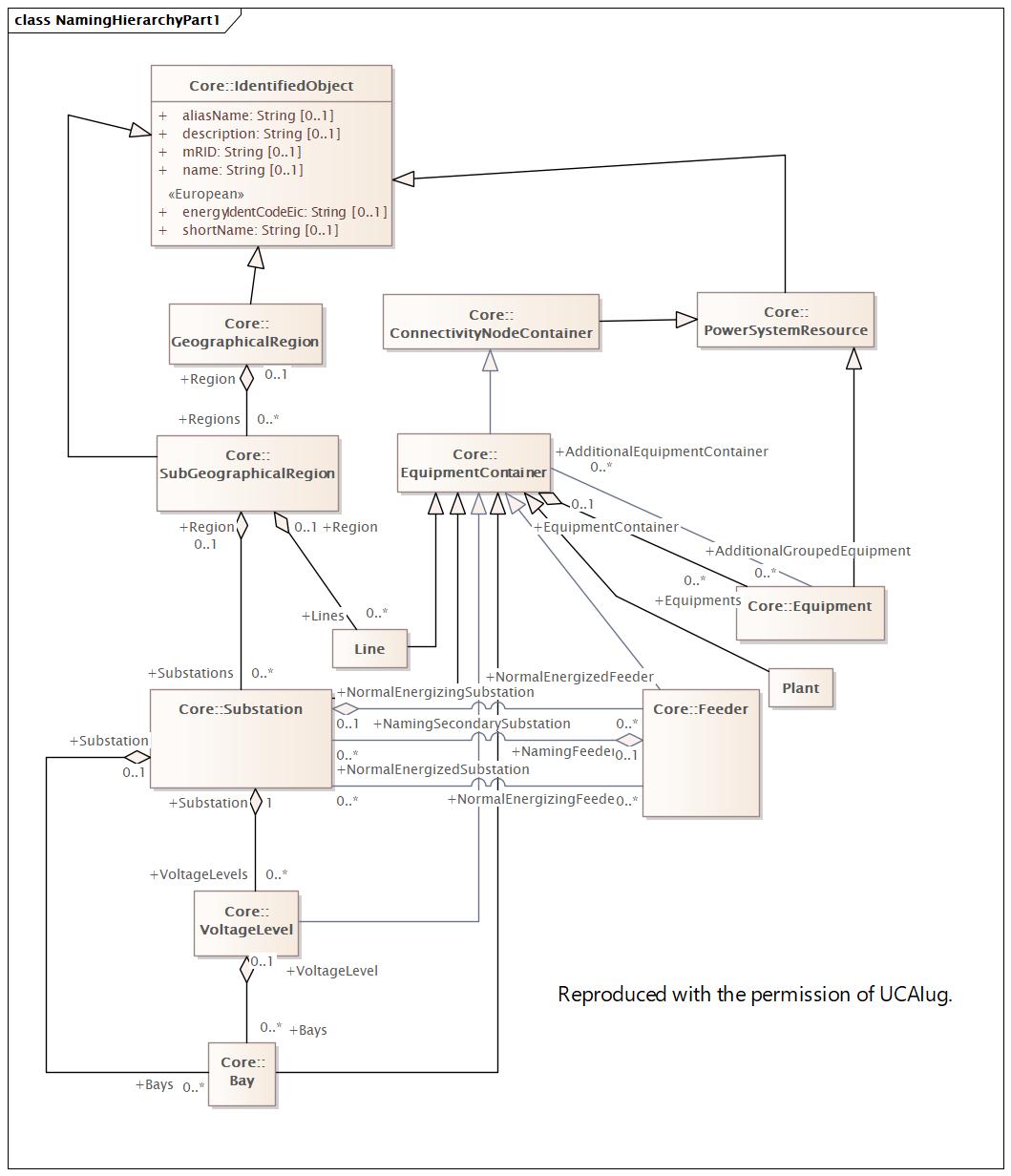
|
Name |
NamingHierarchyPart1 |
DocNamingHierarchyPart1 |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2023-02-11 09:32:13 |
2024-12-06 19:46:27 |
|
Name |
Transformer |
DocTransformer |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-06-05 23:06:39 |
2024-12-06 19:46:15 |
|
Name |
TapChangerTabular |
DocTapChangerTabular |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2023-02-06 23:10:10 |
2024-12-06 19:45:56 |
|
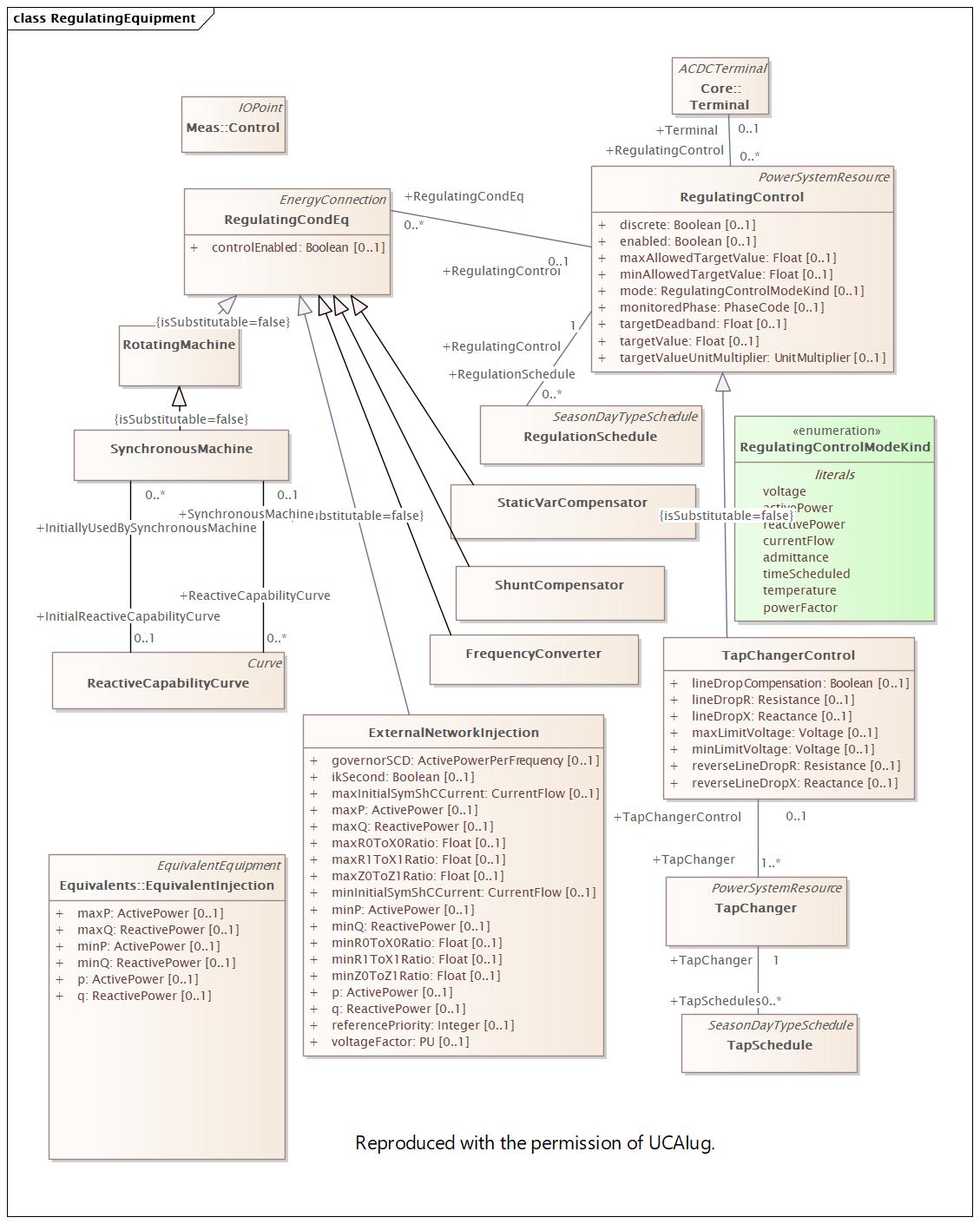
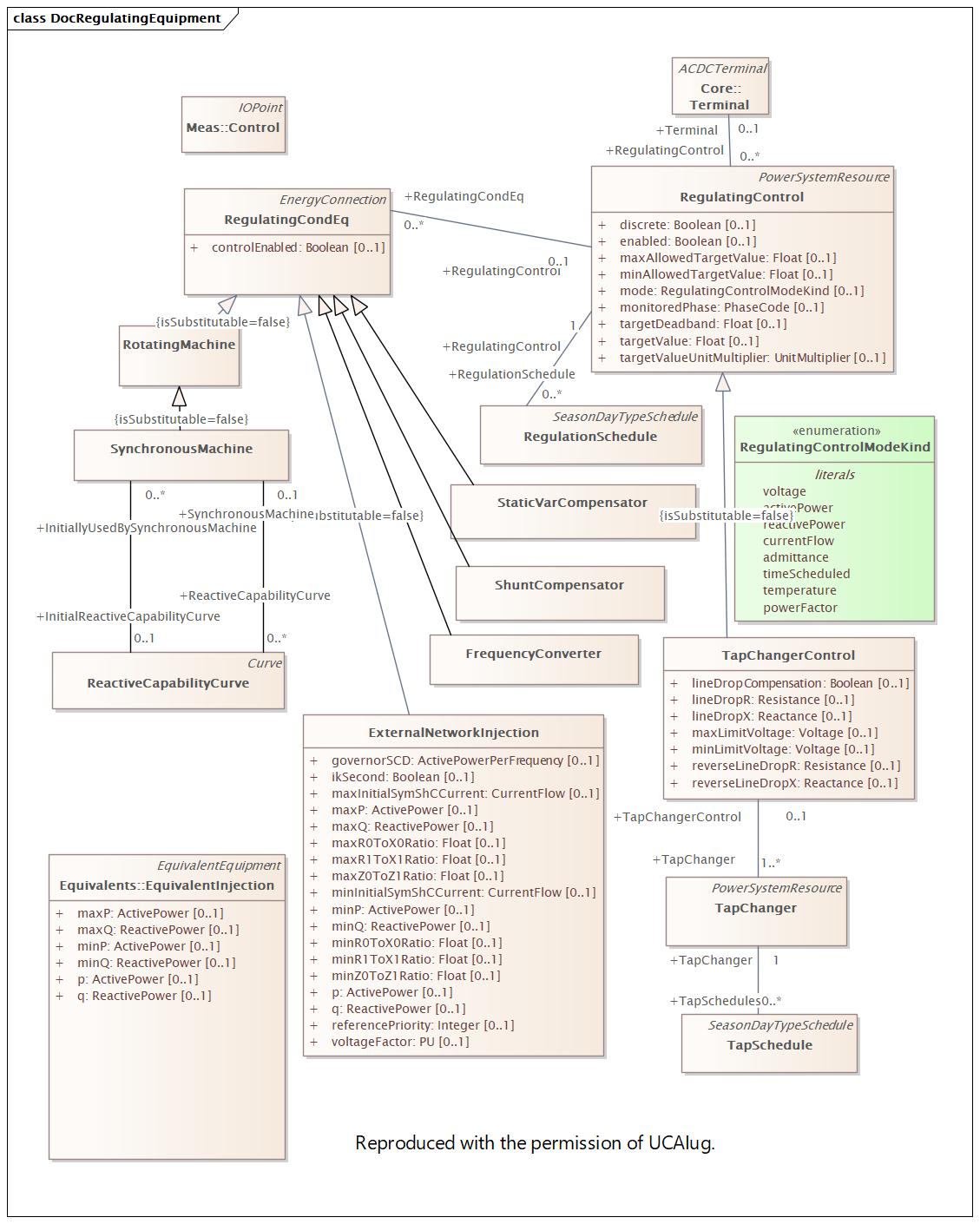
Name |
RegulatingEquipment |
DocRegulatingEquipment |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
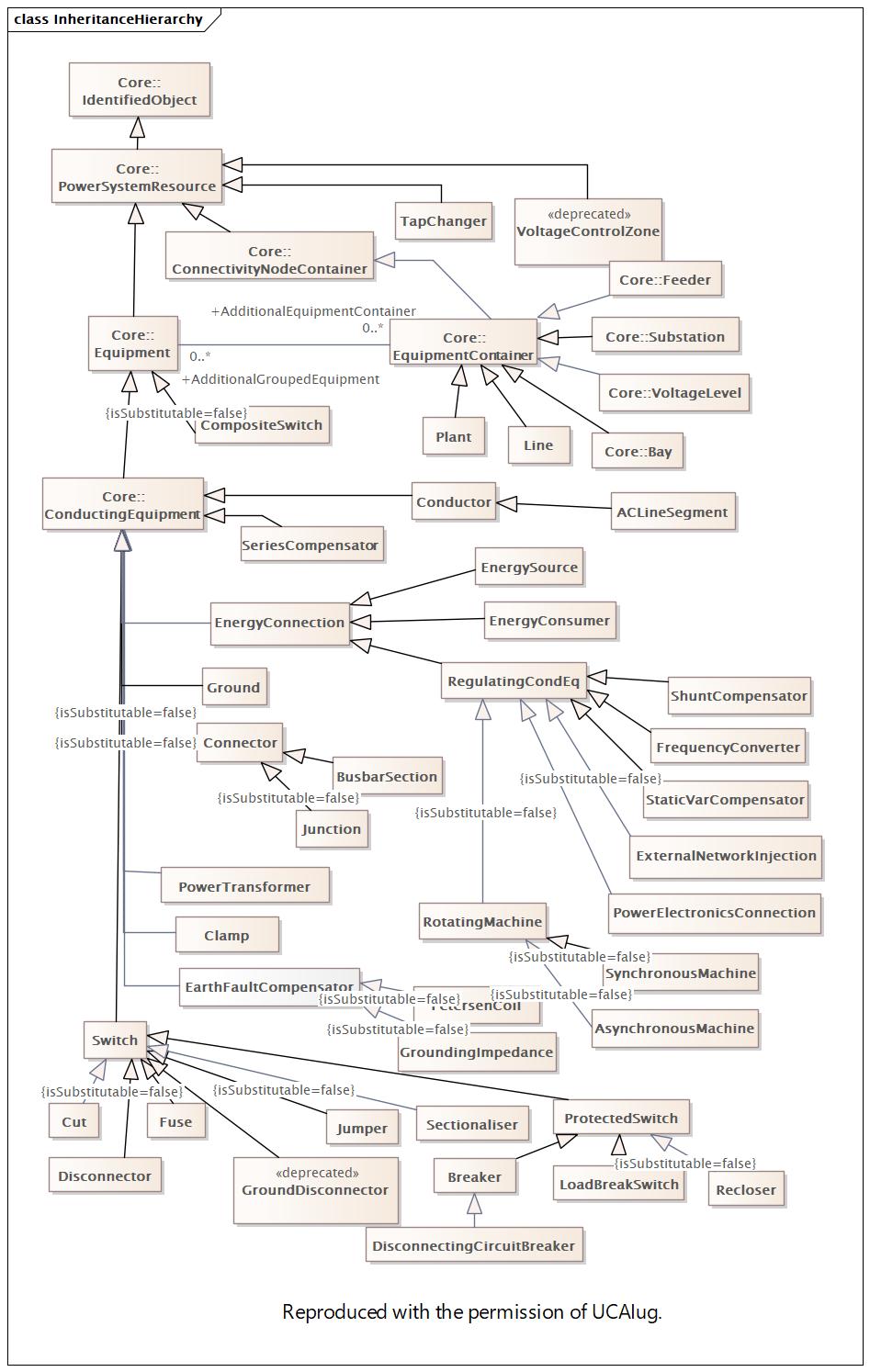
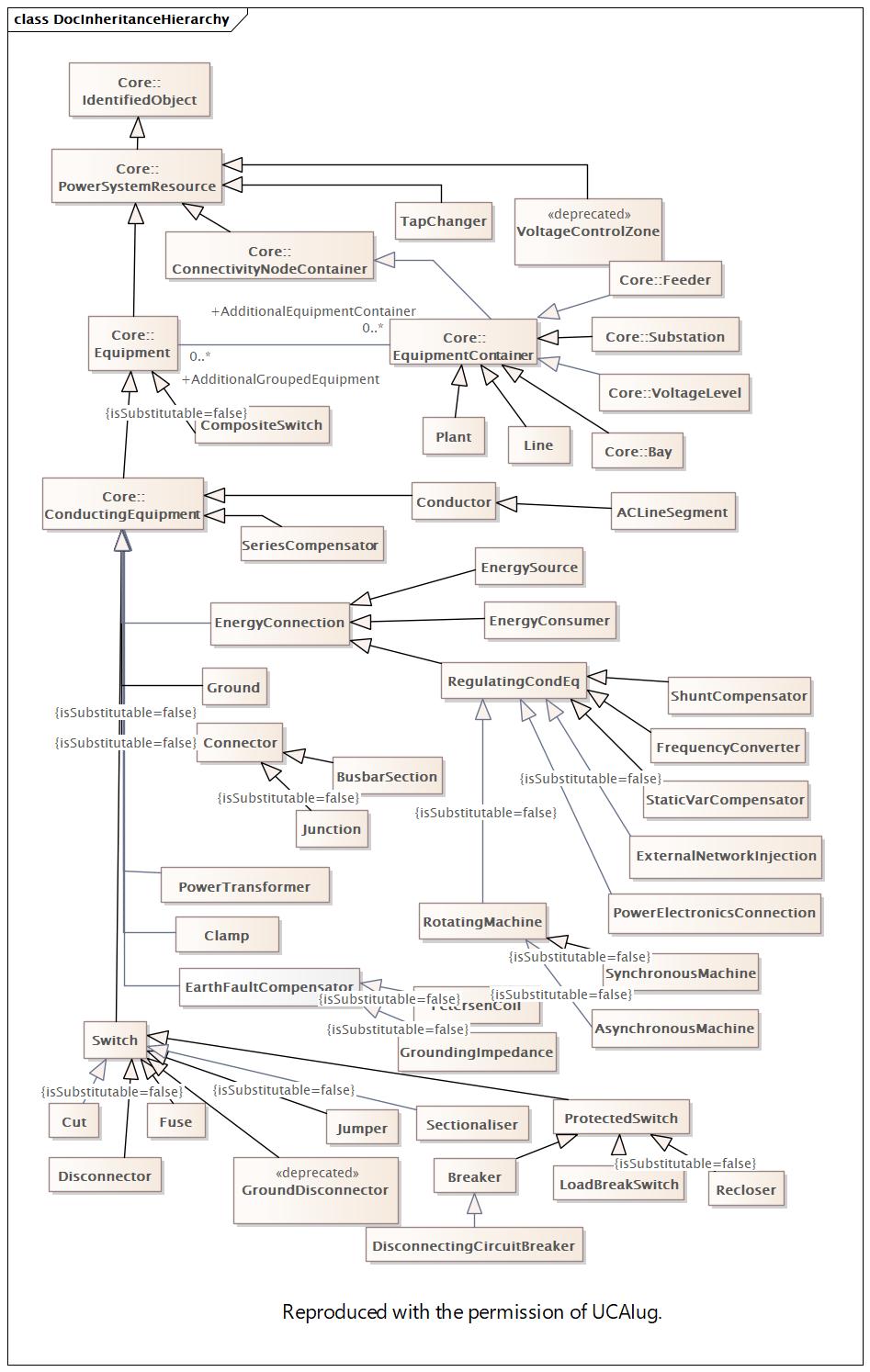
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 11:55:15 |
2024-12-06 19:45:36 |
|
Name |
InheritanceHierarchy |
DocInheritanceHierarchy |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 11:54:21 |
2024-12-06 19:45:24 |
|
Name |
Datatypes |
DocDatatypes |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:00:30 |
2024-12-06 19:46:41 |
|
Name |
Main |
DocLoad |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:01:42 |
2024-12-06 19:47:18 |
|
Name |
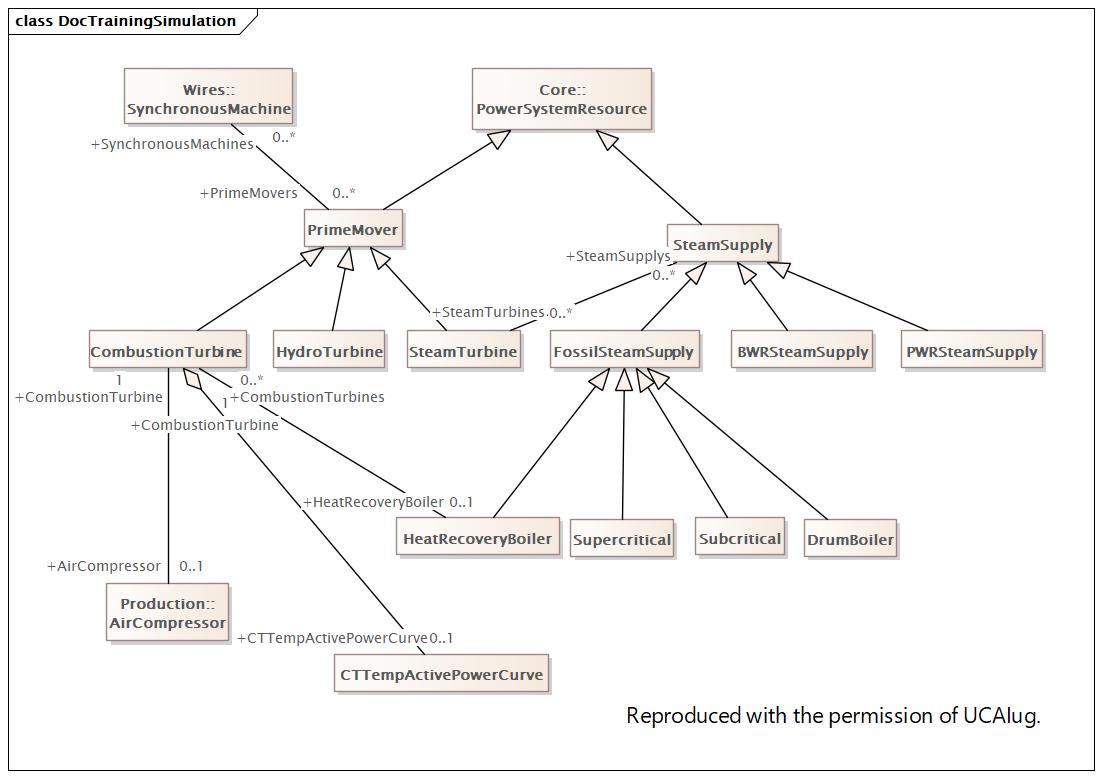
Main |
DocTrainingSimulation |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:01:14 |
2024-12-06 19:47:26 |
|
Name |
Datatypes |
DocDatatypes |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:07:01 |
2024-12-06 19:47:34 |
|
Name |
PowerElectronics |
DocPowerElectronics |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:06:40 |
2024-12-06 19:47:45 |
|
Name |
Nuclear |
DocNuclear |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-08 21:03:49 |
2024-12-06 19:47:56 |
|
Name |
Hydro |
DocHydro |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2023-10-24 06:14:29 |
2024-12-06 19:47:48 |
|
Name |
Main |
DocMain |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:02:16 |
2024-12-06 19:48:01 |
|
Name |
Thermal |
DocThermal |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-13 22:25:58 |
2024-12-06 19:47:41 |
|
Name |
Production |
DocProduction |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:06:11 |
2024-12-06 19:47:52 |
|
Name |
Datatypes |
DocDatatypes |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Package 'Generation' has no changes to the classes it contains.
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:00:59 |
2024-12-06 19:47:00 |
|
Name |
Main |
DocGeneration |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
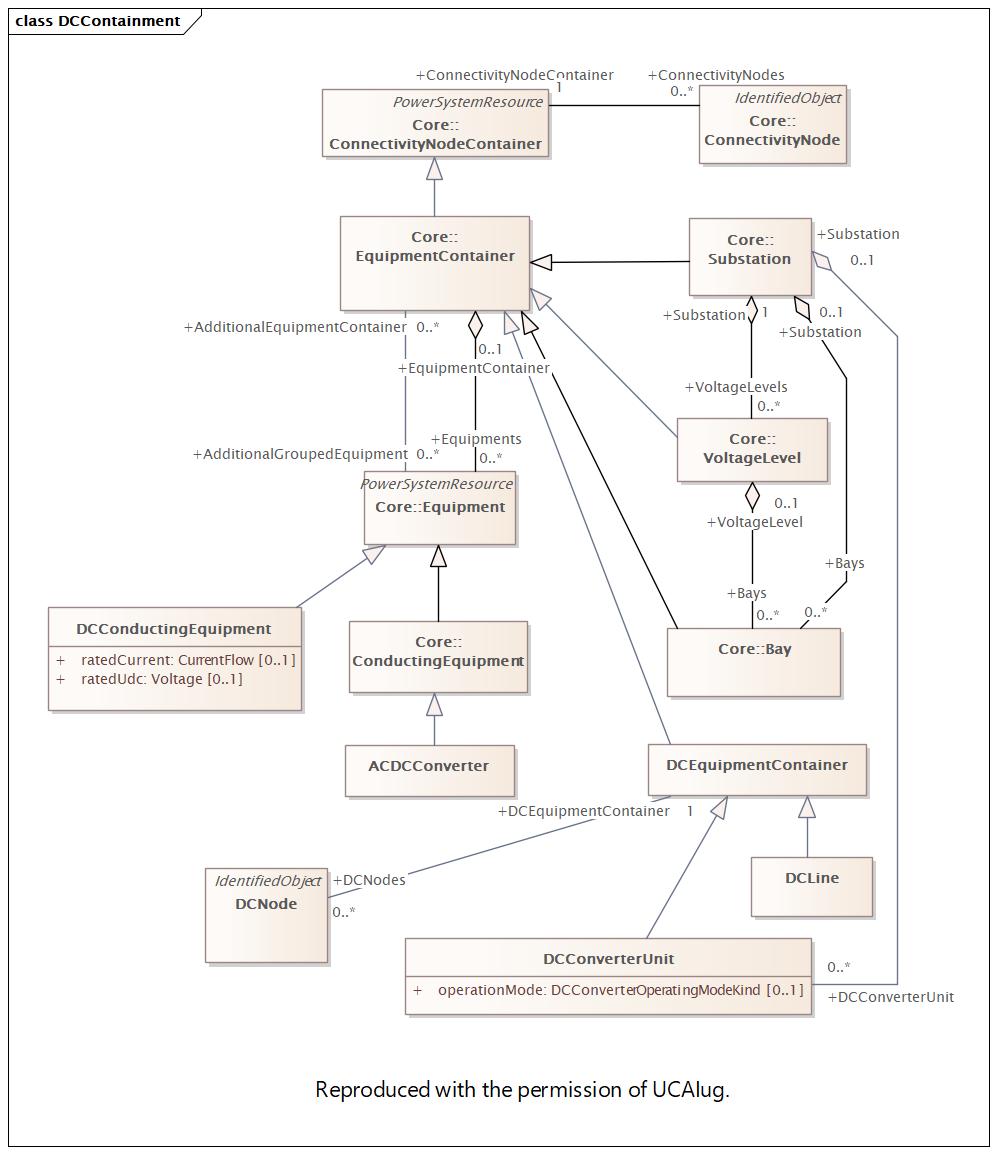
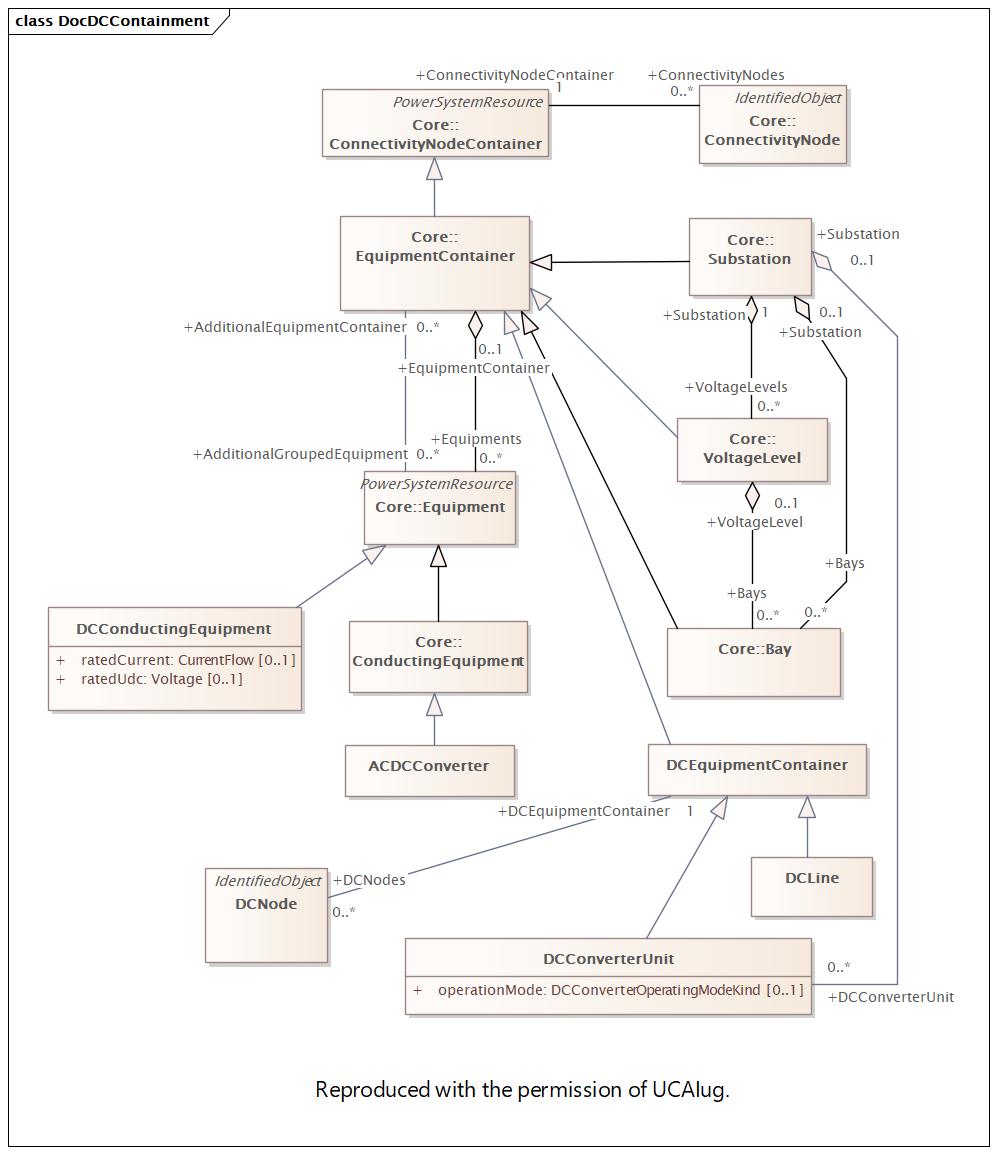
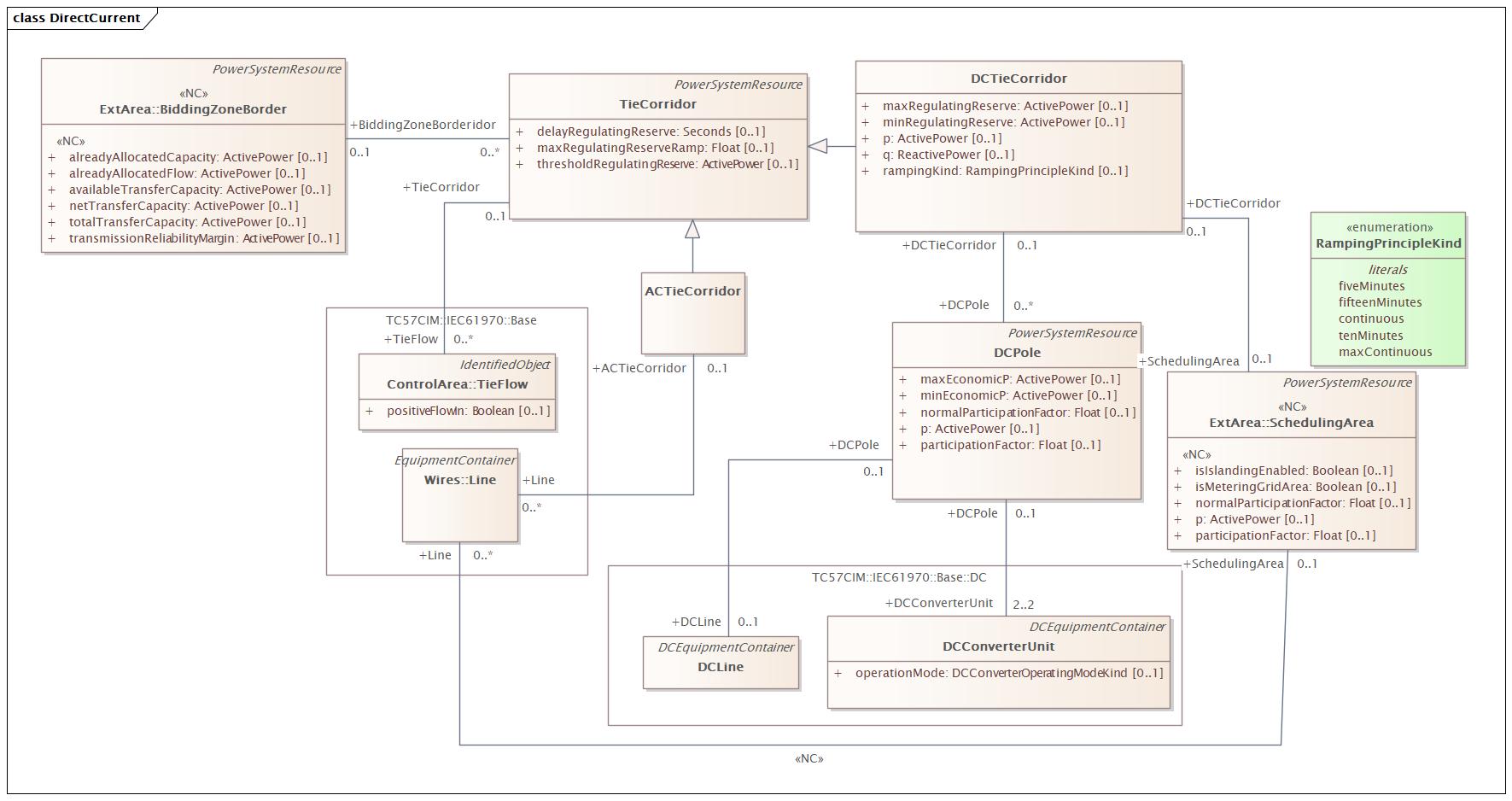
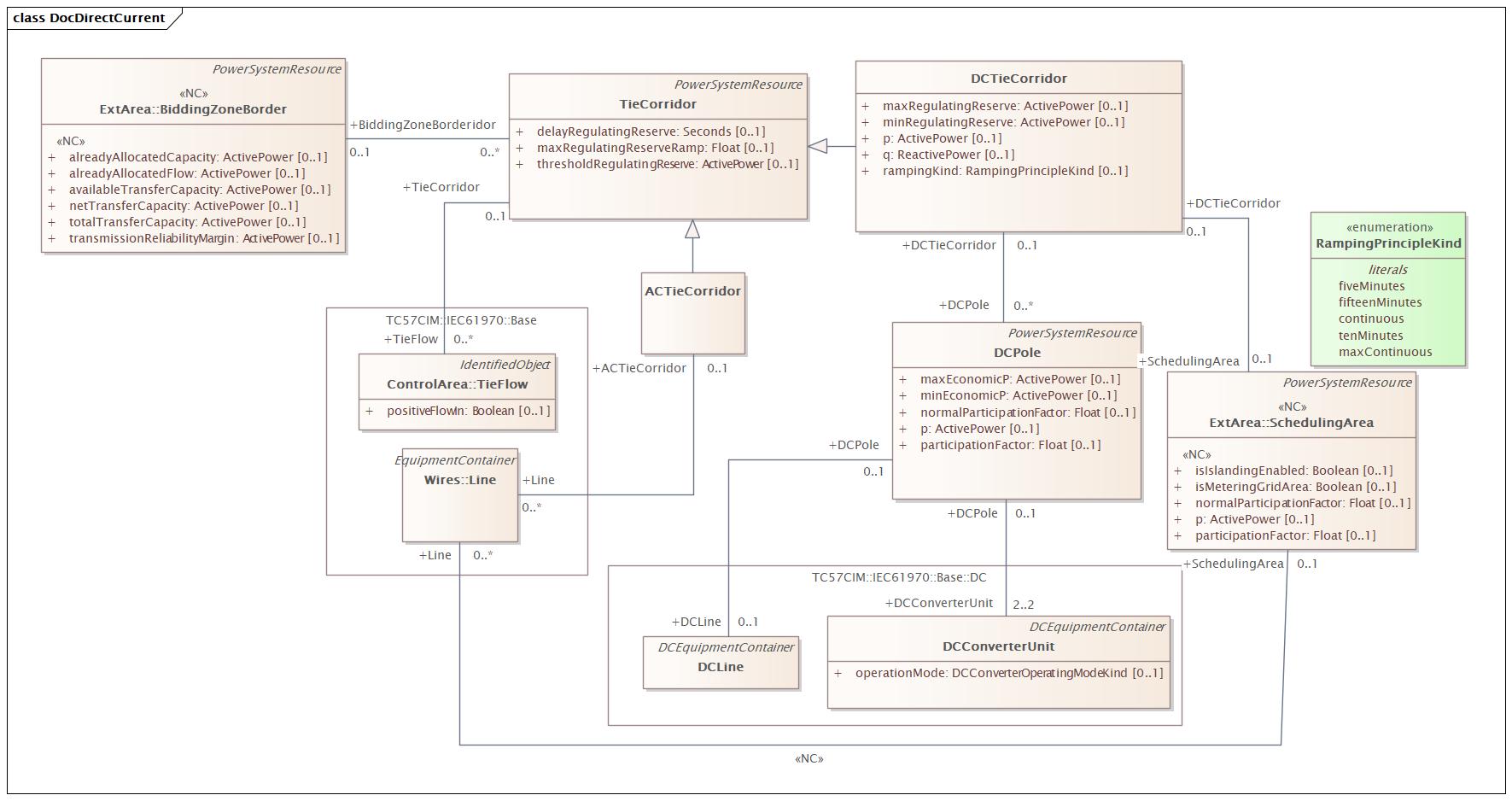
Package 'DocDC' has no changes to the classes it contains.
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2023-02-11 07:30:49 |
2024-12-06 19:50:04 |
|
Name |
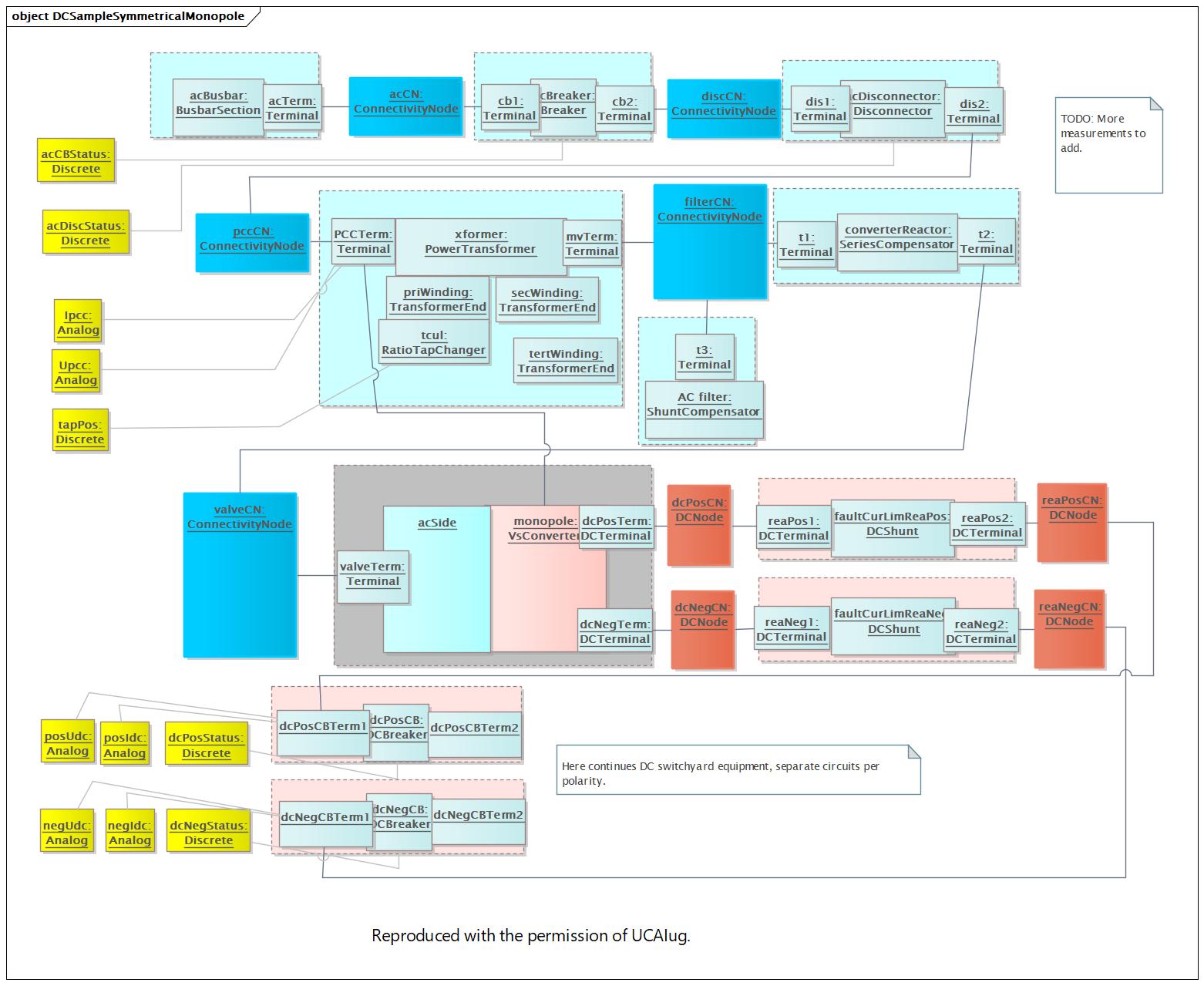
DCSampleSymmetricalMonopole |
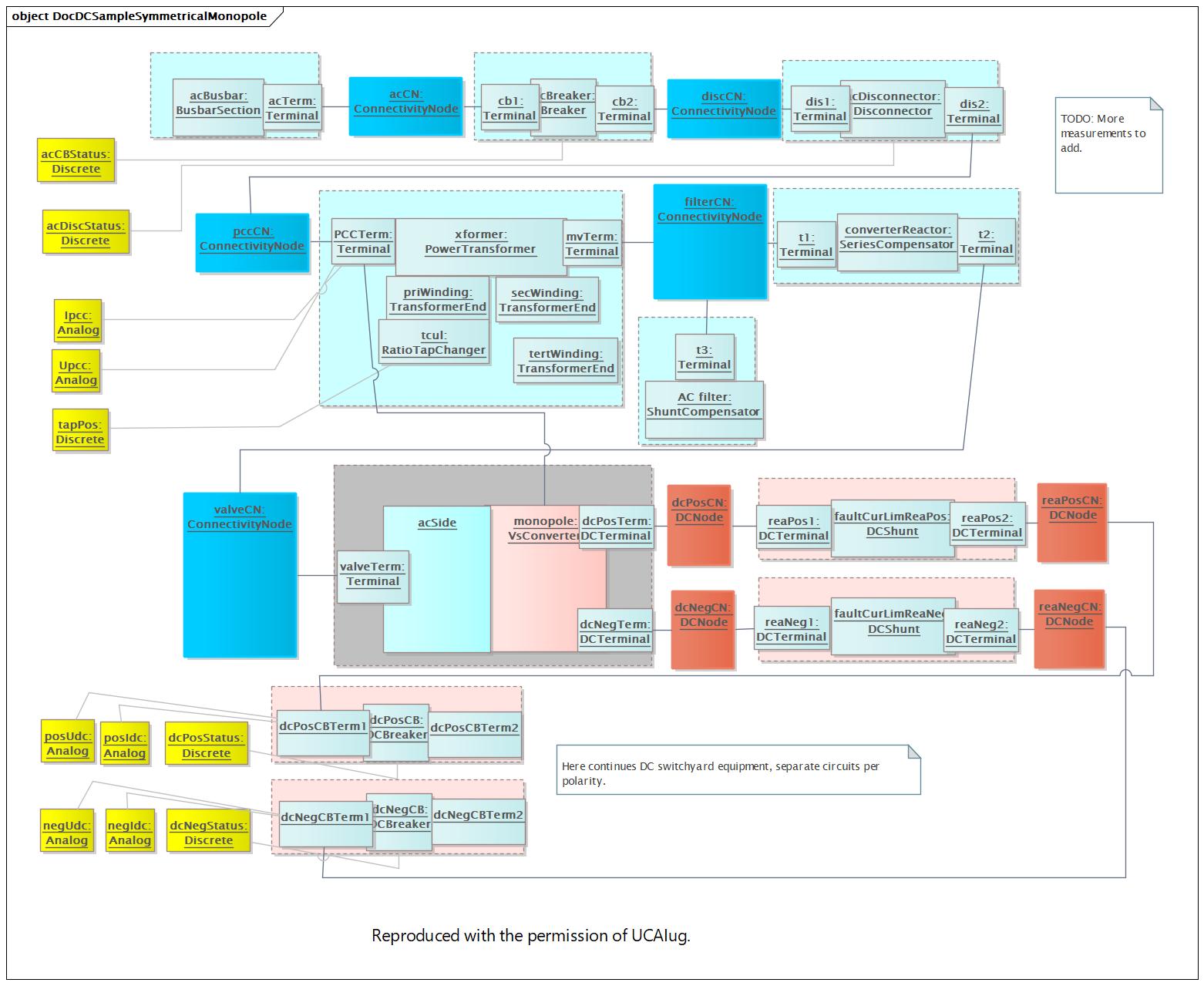
DocDCSampleSymmetricalMonopole |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2023-02-11 07:30:37 |
2024-12-06 19:49:59 |
|
Name |
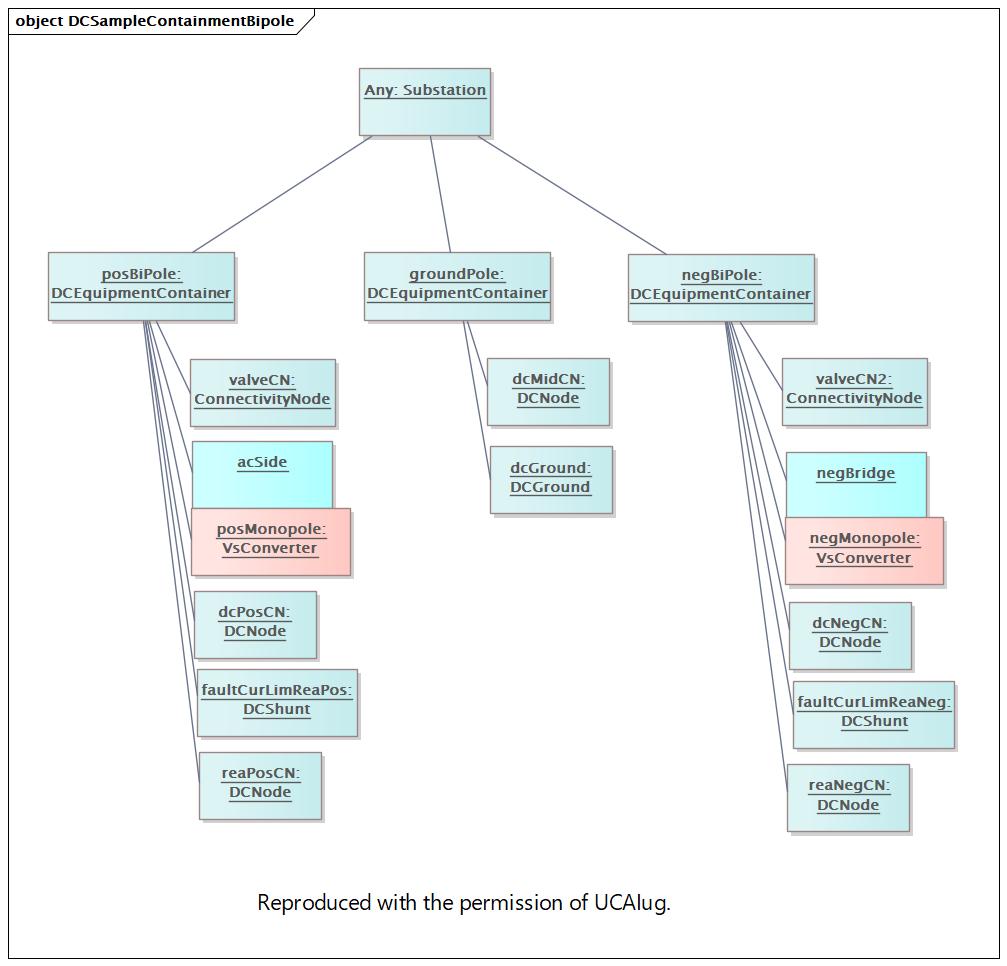
DCSampleContainmentBipole |
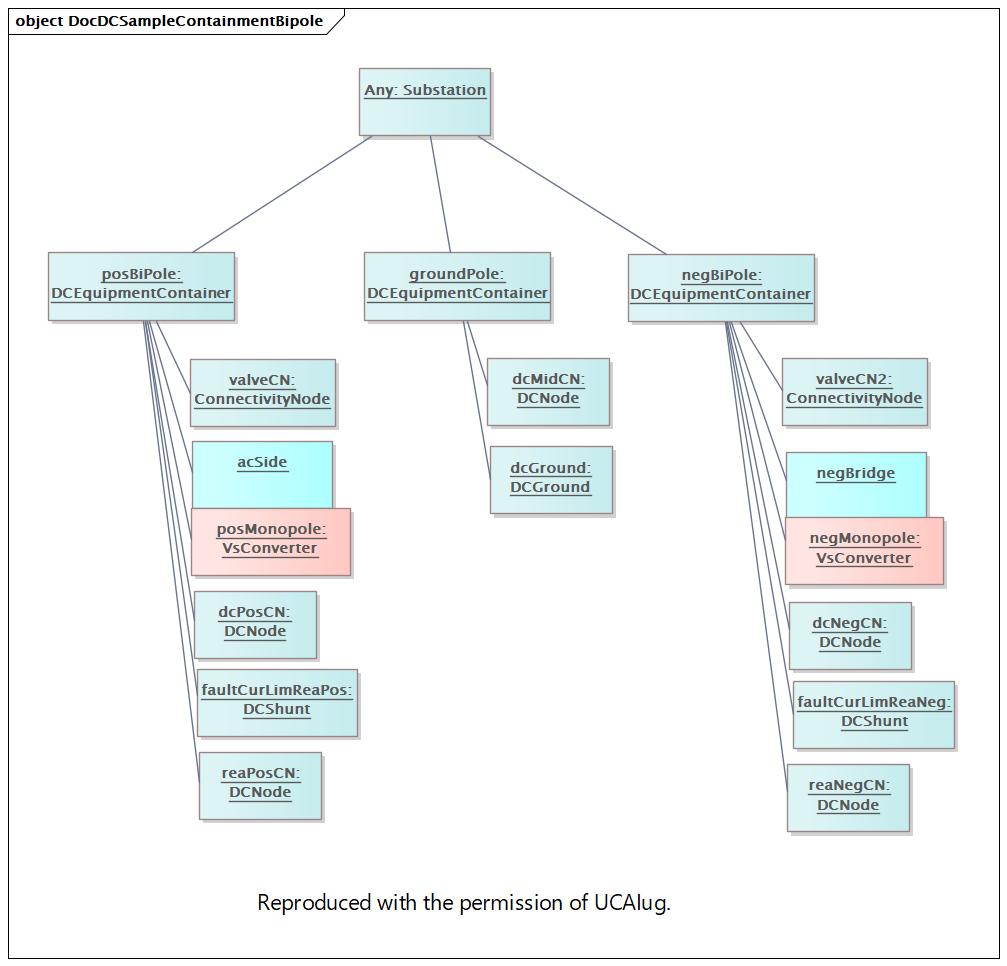
DocDCSampleContainmentBipole |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2023-02-11 07:30:17 |
2024-12-06 19:49:56 |
|
Name |
DCContainmentSymmetricalMonopole |
DocDCContainmentSymmetricalMonopole |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2023-02-11 07:30:58 |
2024-12-06 19:50:07 |
|
Name |
DCSampleAsymmetricalMonopole |
DocDCSampleAsymmetricalMonopole |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2023-02-11 07:31:10 |
2024-12-06 19:50:12 |
|
Name |
DCSampleBipole |
DocDCSampleBipole |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Changed Classes:
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
polarity |
Attribute 'polarity' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Represents the normal network polarity condition. Depending on the converter configuration the value shall be set as follows:- For a monopole with two converter terminals use DCPolarityKind “positive” and “negative”.- For a bi-pole or symmetric monopole with three converter terminals use DCPolarityKind “positive”, “middle” and “negative”. |
polarity |
Attribute 'polarity' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Represents the normal network polarity condition. Depending on the converter configuration the value shall be set as follows:- For a monopole with two converter terminals use DCPolarityKind "positive" and "negative".- For a bi-pole or symmetric monopole with three converter terminals use DCPolarityKind "positive", "middle" and "negative". |
||||||||||||||
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
idc |
Attribute 'idc' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Converter DC current, also called Id. It is converter’s state variable, result from power flow. |
idc |
Attribute 'idc' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Converter DC current, also called Id. It is converter's state variable, result from power flow. |
||||||||||||||
|
idleLoss |
Attribute 'idleLoss' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Active power loss in pole at no power transfer. It is the converter’s configuration data used in power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
idleLoss |
Attribute 'idleLoss' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Active power loss in pole at no power transfer. It is the converter's configuration data used in power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
||||||||||||||
|
maxUdc |
Attribute 'maxUdc' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
The maximum voltage on the DC side at which the converter should operate. It is the converter’s configuration data used in power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
maxUdc |
Attribute 'maxUdc' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
The maximum voltage on the DC side at which the converter should operate. It is the converter's configuration data used in power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
||||||||||||||
|
minUdc |
Attribute 'minUdc' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
The minimum voltage on the DC side at which the converter should operate. It is the converter’s configuration data used in power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
minUdc |
Attribute 'minUdc' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
The minimum voltage on the DC side at which the converter should operate. It is the converter's configuration data used in power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
||||||||||||||
|
poleLossP |
Attribute 'poleLossP' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
The active power loss at a DC Pole = idleLoss + switchingLoss*|Idc| + resitiveLoss*Idc^2.For lossless operation Pdc=Pac.For rectifier operation with losses Pdc=Pac-lossP.For inverter operation with losses Pdc=Pac+lossP.It is converter’s state variable used in power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
poleLossP |
Attribute 'poleLossP' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
The active power loss at a DC Pole = idleLoss + switchingLoss*|Idc| + resitiveLoss*Idc^2.For lossless operation Pdc=Pac.For rectifier operation with losses Pdc=Pac-lossP.For inverter operation with losses Pdc=Pac+lossP.It is converter's state variable used in power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
||||||||||||||
|
ratedUdc |
Attribute 'ratedUdc' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Rated converter DC voltage, also called UdN. The attribute shall be a positive value. It is the converter’s configuration data used in power flow. For instance a bipolar DC link with value 200 kV has a 400kV difference between the dc lines. |
ratedUdc |
Attribute 'ratedUdc' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Rated converter DC voltage, also called UdN. The attribute shall be a positive value. It is the converter's configuration data used in power flow. For instance a bipolar DC link with value 200 kV has a 400kV difference between the dc lines. |
||||||||||||||
|
resistiveLoss |
Attribute 'resistiveLoss' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
It is the converter’s configuration data used in power flow. Refer to poleLossP. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
resistiveLoss |
Attribute 'resistiveLoss' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
It is the converter's configuration data used in power flow. Refer to poleLossP. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
||||||||||||||
|
uc |
Attribute 'uc' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Line-to-line converter voltage, the voltage at the AC side of the valve. It is converter’s state variable, result from power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
uc |
Attribute 'uc' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Line-to-line converter voltage, the voltage at the AC side of the valve. It is converter's state variable, result from power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
||||||||||||||
|
udc |
Attribute 'udc' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Converter voltage at the DC side, also called Ud. It is converter’s state variable, result from power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
udc |
Attribute 'udc' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Converter voltage at the DC side, also called Ud. It is converter's state variable, result from power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
||||||||||||||
|
valveU0 |
Attribute 'valveU0' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Valve threshold voltage, also called Uvalve. Forward voltage drop when the valve is conducting. Used in loss calculations, i.e. the switchLoss depend on numberOfValves * valveU0. |
valveU0 |
Attribute 'valveU0' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Valve threshold voltage, also called Uvalve. Forward voltage drop when the valve is conducting. Used in loss calculations, i.e. the switchLoss depend on numberOfValves*valveU0. |
||||||||||||||
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
alpha |
Attribute 'alpha' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Firing angle that determines the DC voltage at the converter DC terminal. Typical value between 10 degrees and 18 degrees for a rectifier. It is converter’s state variable, result from power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
alpha |
Attribute 'alpha' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Firing angle that determines the DC voltage at the converter DC terminal. Typical value between 10 degrees and 18 degrees for a rectifier. It is converter's state variable, result from power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
||||||||||||||
|
gamma |
Attribute 'gamma' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Extinction angle. It is used to limit the DC voltage at the inverter if needed. Typical value between 17 degrees and 20 degrees for an inverter. It is converter’s state variable, result from power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
gamma |
Attribute 'gamma' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Extinction angle. It is used to limit the DC voltage at the inverter if needed. Typical value between 17 degrees and 20 degrees for an inverter. It is converter's state variable, result from power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
||||||||||||||
|
maxAlpha |
Attribute 'maxAlpha' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Maximum firing angle. It is the converter’s configuration data used in power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
maxAlpha |
Attribute 'maxAlpha' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Maximum firing angle. It is the converter's configuration data used in power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
||||||||||||||
|
maxGamma |
Attribute 'maxGamma' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Maximum extinction angle. It is the converter’s configuration data used in power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
maxGamma |
Attribute 'maxGamma' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Maximum extinction angle. It is the converter's configuration data used in power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
||||||||||||||
|
maxIdc |
Attribute 'maxIdc' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
The maximum direct current (Id) on the DC side at which the converter should operate. It is the converter’s configuration data use in power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
maxIdc |
Attribute 'maxIdc' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
The maximum direct current (Id) on the DC side at which the converter should operate. It is the converter's configuration data use in power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
||||||||||||||
|
minAlpha |
Attribute 'minAlpha' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Minimum firing angle. It is the converter’s configuration data used in power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
minAlpha |
Attribute 'minAlpha' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Minimum firing angle. It is the converter's configuration data used in power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
||||||||||||||
|
minGamma |
Attribute 'minGamma' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Minimum extinction angle. It is the converter’s configuration data used in power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
minGamma |
Attribute 'minGamma' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Minimum extinction angle. It is the converter's configuration data used in power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
||||||||||||||
|
minIdc |
Attribute 'minIdc' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
The minimum direct current (Id) on the DC side at which the converter should operate. It is the converter’s configuration data used in power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
minIdc |
Attribute 'minIdc' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
The minimum direct current (Id) on the DC side at which the converter should operate. It is the converter's configuration data used in power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
||||||||||||||
|
operatingMode |
Attribute 'operatingMode' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Indicates whether the DC pole is operating as an inverter or as a rectifier. It is converter’s control variable used in power flow. |
operatingMode |
Attribute 'operatingMode' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Indicates whether the DC pole is operating as an inverter or as a rectifier. It is converter's control variable used in power flow. |
||||||||||||||
|
ratedIdc |
Attribute 'ratedIdc' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Rated converter DC current, also called IdN. The attribute shall be a positive value. It is the converter’s configuration data used in power flow. |
ratedIdc |
Attribute 'ratedIdc' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Rated converter DC current, also called IdN. The attribute shall be a positive value. It is the converter's configuration data used in power flow. |
||||||||||||||
|
targetAlpha |
Attribute 'targetAlpha' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Target firing angle. It is converter’s control variable used in power flow. It is only applicable for rectifier control. Allowed values are within the range minAlpha<=targetAlpha<=maxAlpha. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
targetAlpha |
Attribute 'targetAlpha' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Target firing angle. It is converter's control variable used in power flow. It is only applicable for rectifier control. Allowed values are within the range minAlpha<=targetAlpha<=maxAlpha. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
||||||||||||||
|
targetGamma |
Attribute 'targetGamma' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Target extinction angle. It is converter’s control variable used in power flow. It is only applicable for inverter control. Allowed values are within the range minGamma<=targetGamma<=maxGamma. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
targetGamma |
Attribute 'targetGamma' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Target extinction angle. It is converter's control variable used in power flow. It is only applicable for inverter control. Allowed values are within the range minGamma<=targetGamma<=maxGamma. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
||||||||||||||
|
targetIdc |
Attribute 'targetIdc' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
DC current target value. It is converter’s control variable used in power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
targetIdc |
Attribute 'targetIdc' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
DC current target value. It is converter's control variable used in power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
||||||||||||||
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
delta |
Attribute 'delta' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Angle between VsConverter.uv and ACDCConverter.uc. It is converter’s state variable used in power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value or zero. |
delta |
Attribute 'delta' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Angle between VsConverter.uv and ACDCConverter.uc. It is converter's state variable used in power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value or zero. |
||||||||||||||
|
droop |
Attribute 'droop' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Droop constant. The pu value is obtained as D [kV/MW] x Sb / Ubdc. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
droop |
Attribute 'droop' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Droop constant. The pu value is obtained as D [kV/MW] * Sb / Ubdc. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
||||||||||||||
|
maxModulationIndex |
Attribute 'maxModulationIndex' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
The maximum quotient between the AC converter voltage (Uc) and DC voltage (Ud). A factor typically less than 1. It is converter’s configuration data used in power flow. |
maxModulationIndex |
Attribute 'maxModulationIndex' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
The maximum quotient between the AC converter voltage (Uc) and DC voltage (Ud). A factor typically less than 1. It is converter's configuration data used in power flow. |
||||||||||||||
|
maxValveCurrent |
Attribute 'maxValveCurrent' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
The maximum current through a valve. It is converter’s configuration data. |
maxValveCurrent |
Attribute 'maxValveCurrent' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
The maximum current through a valve. It is converter's configuration data. |
||||||||||||||
|
targetQpcc |
Attribute 'targetQpcc' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Reactive power injection target in AC grid, at point of common coupling. Load sign convention is used, i.e. positive sign means flow out from a node. |
targetQpcc |
Attribute 'targetQpcc' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Reactive power injection target in AC grid, at point of common coupling. Load sign convention is used, i.e. positive sign means flow out from a node. |
||||||||||||||
|
uv |
Attribute 'uv' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Line-to-line voltage on the valve side of the converter transformer. It is converter’s state variable, result from power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
uv |
Attribute 'uv' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Line-to-line voltage on the valve side of the converter transformer. It is converter's state variable, result from power flow. The attribute shall be a positive value. |
||||||||||||||
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-13 22:28:10 |
2024-12-06 19:49:34 |
|
Name |
DirectCurrentEquipment |
DocDirectCurrentEquipment |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:08:19 |
2024-12-06 19:49:16 |
|
Name |
DCLineModel |
DocDCLineModel |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2023-02-06 21:40:51 |
2024-12-06 19:49:12 |
|
Name |
DCEquipment |
DocDocDCEquipment |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-08 20:55:54 |
2024-12-06 19:49:02 |
|
Name |
DCContainment |
DocDCContainment |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-13 22:27:27 |
2024-12-06 19:49:39 |
|
Name |
DirectCurrent |
DocDirectCurrent |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-02-04 07:40:41 |
2024-12-06 19:49:45 |
|
Name |
ACDCConnectivityModel |
DocACDCConnectivityModel |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2023-02-07 20:35:19 |
2024-12-06 19:49:20 |
|
Name |
ACDCConverter |
DocACDCConverter |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-13 22:27:41 |
2024-12-06 19:49:29 |
|
Name |
DirectCurrentStructure |
DocDirectCurrentStructure |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Changed Classes:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Notes |
This class represents networks that have been equivalized using either the ward or extended ward method. |
This class represents networks that have been equivalized using either the Ward or extended Ward method. A Ward equivalent is a combination of an impedance load and a PQ load. An extended Ward equivalent is a combination of an impedance load, a PQ load and as voltage source with an internal impedance. |
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
maxQ |
Attribute 'maxQ' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Maximum reactive power of the injection. Used for modelling of infeed for load flow exchange. Not used for short circuit modelling. If maxQ and minQ are not used ReactiveCapabilityCurve can be used. |
maxQ |
Attribute 'maxQ' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Maximum reactive power of the injection. Used for modelling of infeed for load flow exchange. Not used for short-circuit modelling. If maxQ and minQ are not used ReactiveCapabilityCurve can be used. |
||||||||||||||
|
minQ |
Attribute 'minQ' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Minimum reactive power of the injection. Used for modelling of infeed for load flow exchange. Not used for short circuit modelling. If maxQ and minQ are not used ReactiveCapabilityCurve can be used. |
minQ |
Attribute 'minQ' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Minimum reactive power of the injection. Used for modelling of infeed for load flow exchange. Not used for short-circuit modelling. If maxQ and minQ are not used ReactiveCapabilityCurve can be used. |
||||||||||||||
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
r |
Attribute 'r' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Positive sequence resistance. Used to represent Extended-Ward (IEC 60909).Usage : Extended-Ward is a result of network reduction prior to the data exchange. |
r |
Attribute 'r' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Positive sequence resistance. Used to represent (extended) Ward equivalent. |
||||||||||||||
|
r0 |
Attribute 'r0' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Zero sequence resistance. Used to represent Extended-Ward (IEC 60909).Usage : Extended-Ward is a result of network reduction prior to the data exchange. |
r0 |
Attribute 'r0' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Zero sequence resistance. Used to represent (extended) Ward equivalent. |
||||||||||||||
|
r2 |
Attribute 'r2' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Negative sequence resistance. Used to represent Extended-Ward (IEC 60909).Usage : Extended-Ward is a result of network reduction prior to the data exchange. |
r2 |
Attribute 'r2' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Negative sequence resistance. Used to represent (extended) Ward equivalent. |
||||||||||||||
|
x |
Attribute 'x' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Positive sequence reactance. Used to represent Extended-Ward (IEC 60909).Usage : Extended-Ward is a result of network reduction prior to the data exchange. |
x |
Attribute 'x' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Positive sequence reactance. Used to represent (extended) Ward equivalent. |
||||||||||||||
|
x0 |
Attribute 'x0' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Zero sequence reactance. Used to represent Extended-Ward (IEC 60909).Usage : Extended-Ward is a result of network reduction prior to the data exchange. |
x0 |
Attribute 'x0' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Zero sequence reactance. Used to represent (extended) Ward equivalent. |
||||||||||||||
|
x2 |
Attribute 'x2' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Negative sequence reactance. Used to represent Extended-Ward (IEC 60909).Usage : Extended-Ward is a result of network reduction prior to the data exchange. |
x2 |
Attribute 'x2' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Negative sequence reactance. Used to represent (extended) Ward equivalent. |
||||||||||||||
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-06-05 22:25:21 |
2024-12-06 19:50:32 |
|
Name |
Main |
DocEquivalents |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:12:57 |
2024-12-06 19:50:40 |
|
Name |
AuxiliaryEquipment |
DocAuxiliaryEquipment |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:13:51 |
2024-12-06 19:50:54 |
|
Name |
Measurement |
DocMeasurement |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:14:01 |
2024-12-06 19:50:51 |
|
Name |
Datatypes |
DocDatatypes |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:13:37 |
2024-12-06 19:50:57 |
|
Name |
MeasurementInheritance |
DocMeasurementInheritance |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:13:19 |
2024-12-06 19:51:00 |
|
Name |
Quality |
DocQuality |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:14:19 |
2024-12-06 19:50:47 |
|
Name |
Control |
DocControl |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:15:05 |
2024-12-06 19:51:10 |
|
Name |
Main |
DocTopology |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:14:39 |
2024-12-06 19:51:17 |
|
Name |
TopologyReporting |
DocTopologyReporting |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Changed Classes:
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
orientation |
Attribute 'orientation' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Coordinate system orientation of the diagram. A positive orientation gives standard “right-hand” orientation, with negative orientation indicating a “left-hand” orientation. For 2D diagrams, a positive orientation will result in X values increasing from left to right and Y values increasing from bottom to top. A negative orientation gives the “left-hand” orientation (favoured by computer graphics displays) with X values increasing from left to right and Y values increasing from top to bottom. |
orientation |
Attribute 'orientation' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Coordinate system orientation of the diagram. A positive orientation gives standard "right-hand" orientation, with negative orientation indicating a "left-hand" orientation. For 2D diagrams, a positive orientation will result in X values increasing from left to right and Y values increasing from bottom to top. A negative orientation gives the "left-hand" orientation (favoured by computer graphics displays) with X values increasing from left to right and Y values increasing from top to bottom. |
||||||||||||||
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:15:30 |
2024-12-06 19:51:23 |
|
Name |
DiagramLayout |
DocDiagramLayout |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-13 22:31:59 |
2024-12-06 19:51:35 |
|
Name |
SSSC |
DocSSSC |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-13 22:31:28 |
2024-12-06 19:51:30 |
|
Name |
FACTS |
DocFACTS |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:15:50 |
2024-12-06 19:51:46 |
|
Name |
BranchGroup |
DocBranchGroup |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-08 21:05:48 |
2024-12-06 19:51:43 |
|
Name |
OperationalLimits |
DocOperationalLimits |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2023-10-08 06:39:35 |
2024-12-06 19:51:53 |
|
Name |
ControlArea |
DocControlArea |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:17:11 |
2024-12-06 19:51:57 |
|
Name |
ControlAreaInheritance |
DocControlAreaInheritance |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:16:54 |
2024-12-06 19:52:01 |
|
Name |
Datatypes |
DocDatatypes |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:17:35 |
2024-12-06 19:52:10 |
|
Name |
Contingency |
DocContingency |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-02-04 07:32:25 |
2024-12-06 19:52:17 |
|
Name |
StateVariables |
DocStateVariables |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Added Classes:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Abstract |
|
false |
|
Alias |
| |
|
Author |
|
tviegut |
|
Cardinality |
| |
|
Classifier |
| |
|
Complexity |
|
1 |
|
Concurrency |
| |
|
GenFile |
| |
|
GenType |
|
Java |
|
IsLeaf |
|
false |
|
IsRoot |
|
false |
|
IsSpec |
|
false |
|
Keywords |
| |
|
Multiplicity |
| |
|
Name |
|
NumericOperation |
|
Notes |
|
Class to represent a numerical operation. |
|
ParentPackage |
|
62361Draft |
|
Persistence |
| |
|
Phase |
|
1.0 |
|
Scope |
|
public |
|
Status |
|
Proposed |
|
Stereotype |
| |
|
Style |
| |
|
Type |
|
Class |
|
Version |
|
1.0 |
|
Visibility |
|
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
numericOperationType |
Attribute 'numericOperationType' Metadata:
|
1..1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Links:
Generalization:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Alias |
| |
|
Direction |
|
Source -> Destination |
|
Name |
| |
|
Notes |
| |
|
Stereotype |
| |
|
Type |
|
Generalization |
|
Baseline Model |
|
Destination Model |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Source Role End Changes |
|
Target Role End Changes |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Abstract |
|
false |
|
Alias |
| |
|
Author |
|
tviegut |
|
Cardinality |
| |
|
Classifier |
| |
|
Complexity |
|
1 |
|
Concurrency |
| |
|
GenFile |
| |
|
GenType |
|
Java |
|
IsLeaf |
|
false |
|
IsRoot |
|
false |
|
IsSpec |
|
false |
|
Keywords |
| |
|
Multiplicity |
| |
|
Name |
|
ConstantFunctionBlock |
|
Notes |
|
Class to define a function block containing a constant value. A FunctionBlockType should be associated along with a FunctionLogicDescription with an specified language attribute. The typeConstant attribute should be aligned with available data types in the chosen programing language. |
|
ParentPackage |
|
62361Draft |
|
Persistence |
| |
|
Phase |
|
1.0 |
|
Scope |
|
public |
|
Status |
|
Proposed |
|
Stereotype |
| |
|
Style |
| |
|
Type |
|
Class |
|
Version |
|
1.0 |
|
Visibility |
|
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
nameConstant |
Attribute 'nameConstant' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Name of the constant. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
typeConstant |
Attribute 'typeConstant' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Defined the data type of the value in this constant. Should be aligned with available data types in the chosen programing language. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
valueConstant |
Attribute 'valueConstant' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Value attached to the constant. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Links:
Generalization:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Alias |
| |
|
Direction |
|
Source -> Destination |
|
Name |
| |
|
Notes |
| |
|
Stereotype |
| |
|
Type |
|
Generalization |
|
Baseline Model |
|
Destination Model |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Source Role End Changes |
|
Target Role End Changes |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Abstract |
|
false |
|
Alias |
| |
|
Author |
|
tviegut |
|
Cardinality |
| |
|
Classifier |
| |
|
Complexity |
|
1 |
|
Concurrency |
| |
|
GenFile |
| |
|
GenType |
|
Java |
|
IsLeaf |
|
false |
|
IsRoot |
|
false |
|
IsSpec |
|
false |
|
Keywords |
| |
|
Multiplicity |
| |
|
Name |
|
DelayTimer |
|
Notes |
|
Class to define a DelayTimer. Behavior matches that of the On Delay Timer and Off Delay Timer standard function blocks from IEC 61131-3. |
|
ParentPackage |
|
62361Draft |
|
Persistence |
| |
|
Phase |
|
1.0 |
|
Scope |
|
public |
|
Status |
|
Proposed |
|
Stereotype |
| |
|
Style |
| |
|
Type |
|
Class |
|
Version |
|
1.0 |
|
Visibility |
|
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
delay |
Attribute 'delay' Metadata:
|
1..1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
onDelayTimer |
Attribute 'onDelayTimer' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Set to True (or leave undefined) to tell if the timer's output is to be turned ON after delay. Otherwise, assume the timer's output is to be turned OFF after the delay. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Links:
Generalization:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Alias |
| |
|
Direction |
|
Source -> Destination |
|
Name |
| |
|
Notes |
| |
|
Stereotype |
| |
|
Type |
|
Generalization |
|
Baseline Model |
|
Destination Model |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Source Role End Changes |
|
Target Role End Changes |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Abstract |
|
false |
|
Alias |
| |
|
Author |
|
tviegut |
|
Cardinality |
| |
|
Classifier |
| |
|
Complexity |
|
1 |
|
Concurrency |
| |
|
GenFile |
| |
|
GenType |
|
Java |
|
IsLeaf |
|
false |
|
IsRoot |
|
false |
|
IsSpec |
|
false |
|
Keywords |
| |
|
Multiplicity |
| |
|
Name |
|
UpDownCounter |
|
Notes |
|
Class to define a rising or falling edge counter. Similar to the CTU and CTD standard function blocks from IEC 61131-3. |
|
ParentPackage |
|
62361Draft |
|
Persistence |
| |
|
Phase |
|
1.0 |
|
Scope |
|
public |
|
Status |
|
Proposed |
|
Stereotype |
| |
|
Style |
| |
|
Type |
|
Class |
|
Version |
|
1.0 |
|
Visibility |
|
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
counterLimitValue |
Attribute 'counterLimitValue' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
The highest value the counter can go to. Similar to the PV input for CTU or CTD in IEC 61131-3. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
risingEdge |
Attribute 'risingEdge' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Set to True (or leave undefined) to model a rising edge counter. Otherwise, this is a falling edge counter. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Links:
Generalization:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Alias |
| |
|
Direction |
|
Source -> Destination |
|
Name |
| |
|
Notes |
| |
|
Stereotype |
| |
|
Type |
|
Generalization |
|
Baseline Model |
|
Destination Model |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Source Role End Changes |
|
Target Role End Changes |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Abstract |
|
false |
|
Alias |
| |
|
Author |
|
tviegut |
|
Cardinality |
| |
|
Classifier |
| |
|
Complexity |
|
1 |
|
Concurrency |
| |
|
GenFile |
| |
|
GenType |
|
Java |
|
IsLeaf |
|
false |
|
IsRoot |
|
false |
|
IsSpec |
|
false |
|
Keywords |
| |
|
Multiplicity |
| |
|
Name |
|
FlipFlop |
|
Notes |
|
Class to define a Flipflop. Behavior matches that of the SR or RS Bistable standard function blocks from IEC 61131-3. |
|
ParentPackage |
|
62361Draft |
|
Persistence |
| |
|
Phase |
|
1.0 |
|
Scope |
|
public |
|
Status |
|
Proposed |
|
Stereotype |
| |
|
Style |
| |
|
Type |
|
Class |
|
Version |
|
1.0 |
|
Visibility |
|
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
setDominant |
Attribute 'setDominant' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Set to True (or leave undefined) to model a Set-dominant bi-stable. Otherwise, this is a Reset-dominant bi-stable. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Links:
Generalization:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Alias |
| |
|
Direction |
|
Source -> Destination |
|
Name |
| |
|
Notes |
| |
|
Stereotype |
| |
|
Type |
|
Generalization |
|
Baseline Model |
|
Destination Model |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Source Role End Changes |
|
Target Role End Changes |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Abstract |
|
false |
|
Alias |
| |
|
Author |
|
tviegut |
|
Cardinality |
| |
|
Classifier |
| |
|
Complexity |
|
1 |
|
Concurrency |
| |
|
GenFile |
| |
|
GenType |
|
Java |
|
IsLeaf |
|
false |
|
IsRoot |
|
false |
|
IsSpec |
|
false |
|
Keywords |
| |
|
Multiplicity |
| |
|
Name |
|
EdgeDetector |
|
Notes |
|
Class to define an Edge detector. Similar to the R_TRIG and F_TRIG standard function blocks from IEC 61131-3. |
|
ParentPackage |
|
62361Draft |
|
Persistence |
| |
|
Phase |
|
1.0 |
|
Scope |
|
public |
|
Status |
|
Proposed |
|
Stereotype |
| |
|
Style |
| |
|
Type |
|
Class |
|
Version |
|
1.0 |
|
Visibility |
|
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
risingEdge |
Attribute 'risingEdge' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Set to True (or leave undefined) to model a rising edge detector. Otherwise, this is a falling edge detector. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Links:
Generalization:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Alias |
| |
|
Direction |
|
Source -> Destination |
|
Name |
| |
|
Notes |
| |
|
Stereotype |
| |
|
Type |
|
Generalization |
|
Baseline Model |
|
Destination Model |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Source Role End Changes |
|
Target Role End Changes |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Changed Classes:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ParentPackage |
62351Draft |
62361Draft |
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
Modelica |
Attribute 'Modelica' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Modelica is an object-oriented, declarative, multi-domain modeling language for component-oriented modeling of complex systems, e.g., systems containing mechanical, electrical, electronic, hydraulic, thermal, control, electric power or process-oriented subcomponents. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
PLCopen |
Attribute 'PLCopen' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
PLCopen as defined within IEC 61131-3. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
StructuredText |
Attribute 'StructuredText' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
StructuredText |
Attribute 'StructuredText' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
StructuredText (ST or STX) as defined within IEC 61131-3. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ParentPackage |
62351Draft |
62361Draft |
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
kind |
Attribute 'kind' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
gateLogicType |
Attribute 'gateLogicType' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Type of boolean gate. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ParentPackage |
62351Draft |
62361Draft |
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ParentPackage |
62351Draft |
62361Draft |
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
kind |
Attribute 'kind' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
operationType |
Attribute 'operationType' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Type of logic operation. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ParentPackage |
62351Draft |
62361Draft |
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ParentPackage |
62351Draft |
62361Draft |
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ParentPackage |
62351Draft |
62361Draft |
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
programLanguage |
Attribute 'programLanguage' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
The programming language used to define the input types, output types and declaration of this function. |
language |
Attribute 'language' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
The programming language used to define the input types, output types and declaration of this function. |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
otherProgramLanguage |
Attribute 'otherProgramLanguage' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
To be used when the programLanguage attribute is in the options defined in ProgrammingLanguageKind. |
otherLanguage |
Attribute 'otherLanguage' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
To be used when the programmingLanguage attribute is in the options defined in ProgrammingLanguageKind. |
||||||||||||||||||||
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ParentPackage |
62351Draft |
62361Draft |
Package '62361Draft' has no changes to the diagrams it contains.
Added Classes:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Abstract |
|
false |
|
Alias |
| |
|
Author |
|
dozdt00 |
|
Cardinality |
| |
|
Classifier |
| |
|
Complexity |
|
1 |
|
Concurrency |
| |
|
GenFile |
| |
|
GenType |
|
Java |
|
IsLeaf |
|
false |
|
IsRoot |
|
false |
|
IsSpec |
|
false |
|
Keywords |
| |
|
Multiplicity |
| |
|
Name |
|
GroundDistanceProtectionFunctionBlock |
|
Notes |
|
This class represents a function for ground distance protection. |
|
ParentPackage |
|
Protection |
|
Persistence |
| |
|
Phase |
|
1.0 |
|
Scope |
|
public |
|
Status |
|
Proposed |
|
Stereotype |
| |
|
Style |
| |
|
Type |
|
Class |
|
Version |
|
1.0 |
|
Visibility |
|
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
residualCompensationFactorAngle |
Attribute 'residualCompensationFactorAngle' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
This attribute represents the angle of the mutual coupling compensation factor. It can be mapped onto "K0FactAng" of PDIS in IEC 61850-7-4 Ed. 2.1. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
residualCompensationFactorMagnitude |
Attribute 'residualCompensationFactorMagnitude' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
This attribute represents the magnitude of the mutual coupling compensation factor. It can be mapped onto "K0Fact" of PDIS in IEC 61850-7-4 Ed. 2.1. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Links:
Generalization:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Alias |
| |
|
Direction |
|
Source -> Destination |
|
Name |
| |
|
Notes |
| |
|
Stereotype |
| |
|
Type |
|
Generalization |
|
Baseline Model |
|
Destination Model |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Source Role End Changes |
|
Target Role End Changes |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Abstract |
|
false |
|
Alias |
| |
|
Author |
|
tviegut |
|
Cardinality |
| |
|
Classifier |
| |
|
Complexity |
|
1 |
|
Concurrency |
| |
|
GenFile |
| |
|
GenType |
|
Java |
|
IsLeaf |
|
false |
|
IsRoot |
|
false |
|
IsSpec |
|
false |
|
Keywords |
| |
|
Multiplicity |
| |
|
Name |
|
ProtectionOperatingQuantityKind |
|
Notes |
|
Enumeration to express the operating quantity that a protection or protection-related function block operates on. The items in the enumeration only make sense if the phases attribute of the function blocks is ABC. Items ‘zeroSequenceTimesThree’ and ‘negativeSequenceTimesThree’ are options that some relays typically use to skip a division by three in the component calculation. |
|
ParentPackage |
|
Protection |
|
Persistence |
| |
|
Phase |
|
1.0 |
|
Scope |
|
public |
|
Status |
|
Proposed |
|
Stereotype |
|
enumeration |
|
Style |
| |
|
Type |
|
Class |
|
Version |
|
1.0 |
|
Visibility |
|
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
maxPhase |
Attribute 'maxPhase' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Maximum of ABC phase quantities. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
maxPhasePhase |
Attribute 'maxPhasePhase' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Maximum of phase-phase quantities (AB, BC, CA). Makes sense only for the over-voltage protection function block when operating over phase-phase quantities. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
minPhase |
Attribute 'minPhase' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Minimum of ABC phase quantities. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
minPhasePhase |
Attribute 'minPhasePhase' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Minimum of phase-phase quantities (AB, BC, CA). Makes sense only for the under-voltage protection function block when operating over phase-phase quantities. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
negativeSequence |
Attribute 'negativeSequence' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Negative sequence operating quantity. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
negativeSequenceTimesThree |
Attribute 'negativeSequenceTimesThree' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Operating quantity defined as 3I2 or 3V2. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
positiveSequence |
Attribute 'positiveSequence' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Positive sequence operating quantity. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
zeroSequence |
Attribute 'zeroSequence' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Zero sequence operating quantity. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
zeroSequenceTimesThree |
Attribute 'zeroSequenceTimesThree' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Operating quantity defined as 3I0 or 3V0. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Abstract |
|
false |
|
Alias |
| |
|
Author |
|
paov001 |
|
Cardinality |
| |
|
Classifier |
| |
|
Complexity |
|
1 |
|
Concurrency |
| |
|
GenFile |
| |
|
GenType |
| |
|
IsLeaf |
|
false |
|
IsRoot |
|
false |
|
IsSpec |
|
false |
|
Keywords |
| |
|
Multiplicity |
| |
|
Name |
|
PhaseCodeProtection |
|
Notes |
|
Enumeration of phase identifiers used to designate the combination of phase and/or neutral conductors measured for protection function and protection function blocks. It is a restricted subset of PhaseCode enumeration. Using the complete PhaseCode enumeration does not make sense for the protection function, e.g. ABCN. |
|
ParentPackage |
|
Protection |
|
Persistence |
| |
|
Phase |
| |
|
Scope |
|
public |
|
Status |
|
Proposed |
|
Stereotype |
|
enumeration |
|
Style |
| |
|
Type |
|
Class |
|
Version |
| |
|
Visibility |
|
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
A |
Attribute 'A' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Phase A. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
AB |
Attribute 'AB' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Phases A and B. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
ABC |
Attribute 'ABC' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Phases A, B, and C. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
B |
Attribute 'B' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Phase B. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
BC |
Attribute 'BC' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Phases B and C. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
C |
Attribute 'C' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Phase C. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
CA |
Attribute 'CA' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Phases C and A. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
N |
Attribute 'N' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Neutral phase. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
s1 |
Attribute 's1' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Secondary phase 1. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
s12 |
Attribute 's12' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Secondary phase 1 and 2. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
s2 |
Attribute 's2' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
Secondary phase 2. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Changed Classes:
Links:
Association:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Alias |
| |
|
Direction |
|
Unspecified |
|
IsLeaf |
|
false |
|
IsRoot |
|
false |
|
Notes |
| |
|
Source Linked Feature |
| |
|
Stereotype |
| |
|
Target Linked Feature |
| |
|
Type |
|
Association |
|
Baseline Model |
|
Destination Model |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Source Role End Changes |
|
Target Role End Changes |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Association:
|
Baseline Model |
|
Destination Model |
||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Source Role End Changes |
|
Target Role End Changes |
||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
fuseCurveType |
Attribute 'fuseCurveType' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Characteristic curves related to the fuse can be classified into several types, e.g. minimum melting curve, total clearing time curve. |
ATTRIBUTE REMOVED FROM MODEL |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Links:
Association:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Alias |
| |
|
Direction |
|
Unspecified |
|
IsLeaf |
|
false |
|
IsRoot |
|
false |
|
Notes |
| |
|
Source Linked Feature |
| |
|
Stereotype |
| |
|
Target Linked Feature |
| |
|
Type |
|
Association |
|
Baseline Model |
|
Destination Model |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Source Role End Changes |
|
Target Role End Changes |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Association:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Alias |
| |
|
Direction |
|
Unspecified |
|
IsLeaf |
|
false |
|
IsRoot |
|
false |
|
Notes |
| |
|
Source Linked Feature |
| |
|
Stereotype |
| |
|
Target Linked Feature |
| |
|
Type |
|
Association |
|
Baseline Model |
|
Destination Model |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Source Role End Changes |
|
Target Role End Changes |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Association:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Alias |
| |
|
Direction |
|
Unspecified |
|
IsLeaf |
|
false |
|
IsRoot |
|
false |
|
Notes |
| |
|
Source Linked Feature |
| |
|
Stereotype |
| |
|
Target Linked Feature |
| |
|
Type |
|
Association |
|
Baseline Model |
|
Destination Model |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Source Role End Changes |
|
Target Role End Changes |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Association:
|
Baseline Model |
|
Destination Model |
||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Source Role End Changes |
|
Target Role End Changes |
||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Links:
Generalization:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Alias |
| |
|
Direction |
|
Source -> Destination |
|
Name |
| |
|
Notes |
| |
|
Stereotype |
| |
|
Type |
|
Generalization |
|
Baseline Model |
|
Destination Model |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Source Role End Changes |
|
Target Role End Changes |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
phases |
Attribute 'phases' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
operatingQuantityType |
Attribute 'operatingQuantityType' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Attribute to specify an operating quantity when the phases attribute is defined as ABC. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
phases |
Attribute 'phases' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Operating phase quantities. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Links:
Association:
|
Baseline Model |
|
Destination Model |
||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Source Role End Changes |
|
Target Role End Changes |
||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
inService |
Attribute 'inService' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
This attribute represents whether the group is in-service or not. |
enabled |
Attribute 'enabled' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
This attribute represents whether the group is enabled or not. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
normallyEnabled |
Attribute 'normallyEnabled' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
True, if the protection settings group is normally enabled (active). Otherwise false. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Links:
Association:
|
Baseline Model |
|
Destination Model |
||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Source Role End Changes |
|
Target Role End Changes |
||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
phases |
Attribute 'phases' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Represents the normal network phasing condition. If the attribute is missing, three phases (ABC) shall be assumed, except for terminals of grounding classes (specializations of EarthFaultCompensator, GroundDisconnector, and Ground) which will be assumed to be N. Therefore, phase code ABCN is explicitly declared when needed, e.g. for star point grounding equipment.The phase code on terminals connecting the same ConnectivityNode or TopologicalNode as well as for equipment between two terminals shall be consistent. |
operatingQuantityType |
Attribute 'operatingQuantityType' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Attribute to specify an operating quantity when the phases attribute is defined as ABC. Required for current and voltage protection function blocks to clearly identify which quantity to operate on. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ATTRIBUTE DOES NOT EXIST |
phases |
Attribute 'phases' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Operating phase quantities. If ABC, operatingQuantityType must be specified for voltage and current elements to precise the operating quantity. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
normal |
Attribute 'normal' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
This attribute means whether the protection function block is normal status. |
ATTRIBUTE REMOVED FROM MODEL |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Links:
Generalization:
|
Source: (GroundDirectionProtectionFunctionBlock) [0] |
|
Target: (DirectionalProtectionFunctionBlock) [0] |
REMOVED FROM MODEL |
|
|
|
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
normal |
Attribute 'normal' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
This attribute means whether the protection function is normal status. |
ATTRIBUTE REMOVED FROM MODEL |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Added Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Author |
|
paov001 |
|
CreatedDate |
|
2024-11-19 16:00:53 |
|
DiagramType |
|
ClassDiagram |
|
ModifiedDate |
|
2024-12-08 16:17:36 |
|
Name |
|
DocEPRIProposedUpdates8 |
|
Notes |
| |
|
Package |
|
EAPK_3F02E213_ECF8_4f14_9AD5_D4A252FE300A |
|
ParentPackage |
|
Protection |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
Diagram 'DocEPRIProposedUpdates8' does not exist in the model. |
|
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-13 22:04:48 |
2024-12-08 16:17:36 |
|
Name |
ProtectionFunctionInheritance2 |
DocProtectionFunctionInheritance2 |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-14 09:52:46 |
2024-12-08 16:17:36 |
|
Name |
EPRIProposedUpdates1 |
DocEPRIProposedUpdates1 |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-10-18 17:07:25 |
2024-12-08 16:17:36 |
|
Name |
EPRIProposedUpdates6 |
DocEPRIProposedUpdates6 |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-13 22:00:28 |
2024-12-08 16:17:36 |
|
Name |
ProtectionCharacteristicCurve |
DocProtectionCharacteristicCurve |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-10-18 16:49:43 |
2024-12-08 16:17:36 |
|
Name |
EPRIProposedUpdates3 |
DocEPRIProposedUpdates3 |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-13 08:55:44 |
2024-12-08 16:17:36 |
|
Name |
Main |
DocMain |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-10-18 14:20:32 |
2024-12-08 16:17:36 |
|
Name |
EPRIProposedUpdates4 |
DocEPRIProposedUpdates4 |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-17 09:17:29 |
2024-12-08 16:17:36 |
|
Name |
EPRIProposedUpdates2 |
DocEPRIProposedUpdates2 |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-13 22:02:12 |
2024-12-08 16:17:36 |
|
Name |
ProtectionFunctionInheritance1 |
DocProtectionFunctionInheritance1 |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-13 08:47:56 |
2024-12-08 16:17:36 |
|
Name |
ProtectionFunctionLogicDescription |
DocProtectionFunctionLogicDescription |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-10-18 16:47:02 |
2024-12-08 16:17:36 |
|
Name |
EPRIProposedUpdates5 |
DocEPRIProposedUpdates5 |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-13 22:06:05 |
2024-12-08 16:17:36 |
|
Name |
ProtectionFunctionInheritance3 |
DocProtectionFunctionInheritance3 |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-10-18 16:05:08 |
2024-12-08 16:17:36 |
|
Name |
EPRIProposedUpdates7 |
DocEPRIProposedUpdates7 |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:18:30 |
2024-12-06 19:54:42 |
|
Name |
Faults |
DocFaults |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:18:47 |
2024-12-06 19:54:55 |
|
Name |
Main |
DocSCADA |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:18:57 |
2024-12-06 19:54:50 |
|
Name |
Datatypes |
DocDatatypes |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Package 'DocICCPConfiguration' has no changes to the classes it contains.
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:19:54 |
2024-12-06 19:55:21 |
|
Name |
ICCPExample |
DocICCPExample |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:19:17 |
2024-12-06 19:55:11 |
|
Name |
ICCP |
DocICCP |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2022-06-10 12:19:33 |
2024-12-06 19:55:08 |
|
Name |
GenericBilateralExchange |
DocGenericBilateralExchange |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-13 22:12:57 |
2024-12-06 19:55:38 |
|
Name |
TemporaryLimits |
DocTemporaryLimits |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-13 22:13:10 |
2024-12-06 19:55:43 |
|
Name |
ThermalBehaviourLimit |
DocThermalBehaviourLimit |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-13 22:16:18 |
2024-12-06 19:55:35 |
|
Name |
InfeedLimit |
DocInfeedLimit |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-13 22:29:20 |
2024-12-06 19:55:53 |
|
Name |
SIPSGate |
DocSIPSGate |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-13 22:29:13 |
2024-12-06 19:55:50 |
|
Name |
SIPS |
DocSIPS |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Package 'Base' has no changes to the classes it contains.
Package 'Base' has no changes to the diagrams it contains.
Changed Diagrams:
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Changed Classes:
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
tc |
Attribute 'tc' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Temperature control (<i>Tc</i>). Unit = °F or °C depending on parameters <i>Af1</i> and <i>Bf1</i>. |
tc |
Attribute 'tc' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Temperature control (<i>Tc</i>). Unit = degF or degC depending on parameters <i>Af1</i> and <i>Bf1</i>. |
||||||||||||||
|
tr |
Attribute 'tr' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Rated temperature (<i>Tr</i>). Unit = °C depending on parameters<i> Af1 </i>and <i>Bf1</i>. |
tr |
Attribute 'tr' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Rated temperature (<i>Tr</i>). Unit = degC depending on parameters<i> Af1 </i>and <i>Bf1</i>. |
||||||||||||||
Changed Classes:
Links:
Association:
|
Source: (UnderexcitationLimiterDynamics) [0..1] |
|
Target: (ExcitationSystemDynamics) [1] |
REMOVED FROM MODEL |
|
|
|
Changed Classes:
Links:
Association:
|
Source: (UnderexcitationLimiterDynamics) [0..1] |
|
Target: (ExcitationSystemDynamics) [1] |
REMOVED FROM MODEL |
|
|
|
Package 'StandardModels' has no changes to the diagrams it contains.
Changed Classes:
Links:
Association:
|
Source: (SignalRecorder) [0..*] |
|
Target: (RecordedSignal) [0..1] |
REMOVED FROM MODEL |
|
|
|
Changed Classes:
Links:
Association:
|
Source: (SignalRecorder) [0..*] |
|
Target: (RecordedSignal) [0..1] |
REMOVED FROM MODEL |
|
|
|
Changed Diagrams:
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Package 'Dynamics' has no changes to the classes it contains.
Package 'Dynamics' has no changes to the diagrams it contains.
Changed Classes:
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
sequenceNumber |
Attribute 'sequenceNumber' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
A chronological serial number indicating the order of the faults related to the grid disturbance. Primary faults have fault ID “1”, and secondary/latent faults have fault ID “2” or more. |
sequenceNumber |
Attribute 'sequenceNumber' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
A chronological serial number indicating the order of the faults related to the grid disturbance. Primary faults have fault ID "1", and secondary/latent faults have fault ID "2" or more. |
||||||||||||||
Package 'ExtFaultsPRA' has no changes to the classes it contains.
Package 'ExtFaultsPRA' has no changes to the diagrams it contains.
Changed Diagrams:
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Package 'ExtNetworkCodes' has no changes to the diagrams it contains.
Package 'InfExtEUNetworkCodes' has no changes to the classes it contains.
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ParentPackage |
InfENTSOEextensionsNetworkCodes |
InfExtEUNetworkCodes |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Changed Classes:
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
NegativeSequence |
Attribute 'NegativeSequence' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
ATTRIBUTE REMOVED FROM MODEL |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PositiveSequence |
Attribute 'PositiveSequence' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
ATTRIBUTE REMOVED FROM MODEL |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ZeroSequence |
Attribute 'ZeroSequence' Metadata:
|
1..1 |
ATTRIBUTE REMOVED FROM MODEL |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Package 'CoreExtension' has no changes to the diagrams it contains.
Package 'BaseExtension' has no changes to the classes it contains.
Package 'BaseExtension' has no changes to the diagrams it contains.
Package 'GridExtension' has no changes to the classes it contains.
Package 'GridExtension' has no changes to the diagrams it contains.
Package 'InfProtectionControlExtentions' has no changes to the classes it contains.
Package 'InfProtectionControlExtentions' has no changes to the diagrams it contains.
Package 'DocExtGrid' has no changes to the classes it contains.
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ParentPackage |
DocExtIEC61970 |
DocExtGrid |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ParentPackage |
DocExtIEC61970 |
DocExtGrid |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Package 'Metadata' has no changes to the classes it contains.
Package 'Metadata' has no changes to the diagrams it contains.
Package 'InfGrid' has no changes to the classes it contains.
Changed Diagrams:
Metadata:
|
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|---|
|
ModifiedDate |
2024-09-09 17:26:53 |
2024-12-05 22:22:56 |
|
Name |
InfIEC61970Dependencies |
InfGridDependencies |
|
Notes |
This diagram shows all 61970 packages and their logical dependencies. Note that the sub-packages under Dynamics package are not shown. |
This diagram shows all packages and their logical dependencies. Note that the sub-packages under Dynamics package are not shown. |
Diagram:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Changed Classes:
Attributes:
|
Baseline Model |
Destination Model |
||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
date |
Attribute 'date' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Form is YYYY-MM-DD for example for January 5, 2009 it is 2009-01-05. |
date |
Attribute 'date' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Form is YYYY-MM-DD for example for January 5, 2009 it is 2009-01-05. |
||||||||||||||
|
version |
Attribute 'version' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Form is XXvYY where XX is the major CIM release version and the YY is the minor version. For example 18v03. |
version |
Attribute 'version' Metadata:
|
0..1 |
Form is XXvYY where XX is the major CIM release version and the YY is the minor version. For example 18v03. |
||||||||||||||